
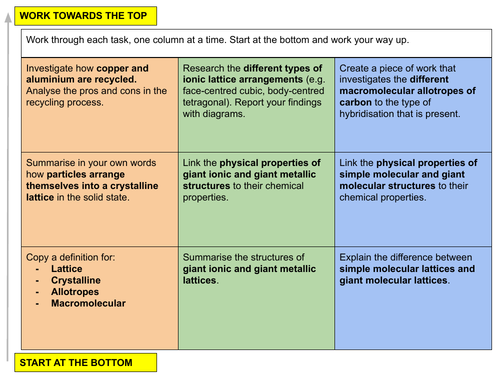

In this lesson we discuss the solid state and the different types of lattice structures that can exist. This is lesson fourteen in our physical chemistry series for Unit 4: States of Matter (from the Cambridge International AS Chemistry Curriculum (9701) 2019-2021 curriculum).
LESSON OBJECTIVE: Investigate lattice structures responsible for the solid state.
LEARNING OUTCOMES (from the Cambridge AS Chemistry Curriculum 2019-2021):
4.3 The solid state: lattice structures
a) describe, in simple terms, the lattice structure of a crystalline solid which is:
i) ionic, as in sodium chloride and magnesium oxide
ii) simple molecular, as in iodine and the fullerene allotropes of carbon (C60 and nanotubes only)
iii) giant molecular, as in silicon(IV) oxide and the graphite, diamond and graphene allotropes of carbon
iv) hydrogen-bonded, as in ice
v) metallic, as in copper
b) discuss the finite nature of materials as a resource and the importance of recycling processes
c) outline the importance of hydrogen bonding to the physical properties of substances, including ice and water (for example, boiling and melting points, viscosity and surface tension)
d) suggest from quoted physical data the type of structure and bonding present in a substance
Something went wrong, please try again later.
very helpful thank you !
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.