





Reactivity 1. What drives chemical reactions?
Reactivity 1.1—Measuring enthalpy changes
Reactivity 1.1.1—Chemical reactions involve a transfer of energy between the system and the surroundings, while total energy is conserved.
Reactivity 1.1.2—Reactions are described as endothermic or exothermic, depending on the direction of energy transfer between the system and the surroundings.
Reactivity 1.1.3—The relative stability of reactants and products determines whether reactions are endothermic or exothermic.
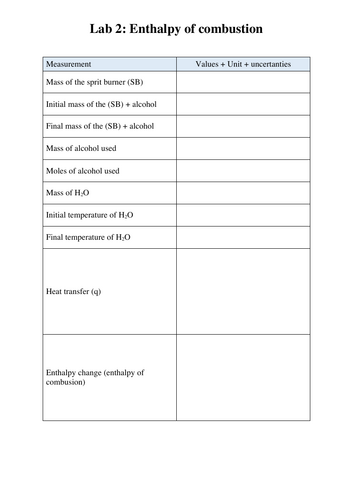
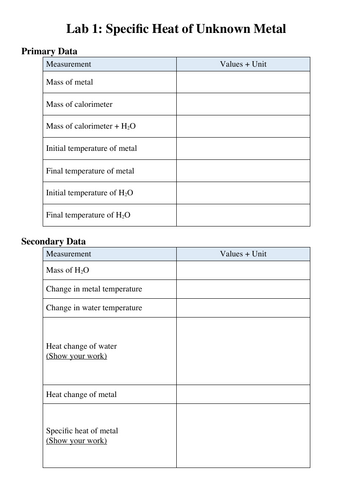
Reactivity 1.1.4—The standard enthalpy change for a chemical reaction, ΔH⦵, refers to the heat transferred at constant pressure under standard conditions and states. It can be determined from the change in temperature of a pure substance.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
