499Uploads
172k+Views
73k+Downloads
Physics

GCSE Physics: Radiation and Temperature
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.4 Radiation and Temperature
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.2 Powering Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.

GCSE Physics: Energy Sources
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.1 Energy Sources
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides,
Waves,
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal

GCSE Physics: Radiation and the body
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.2.1 Radiation and the body
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Background radiation definition
Sources of background radiation
Contamination and irradiation
Medical examples of irradiation - X-rays, sterilisation, gamma knife
Medical examples of contamination - Tracers
Half-life and penetration power for radioactive tracers.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.1 Physics on the move
All resources for P8.1 Physics on the move GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
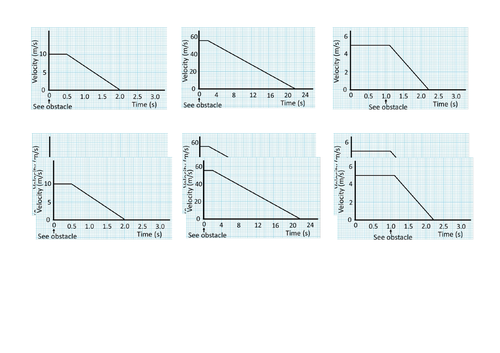
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.

GCSE Physics: Forces in Collisions
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.4 Forces in Collisions. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.

GCSE Physics: Braking and Stopping Distances
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.3 Braking and Stopping Distances. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s

GCSE Physics: Reaction Time and Thinking Distance
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.2 Reaction Time and Thinking Distance. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s

GCSE Physics: Everyday Motion
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.1 Everyday Motion. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P7.2 Power and Efficiency
All resources for P7.2 P7.2 Power and Efficiency GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
All powerpoints include student activities and worked examples.
Electrical Work Done
Paying for Electricity
Electrical Energy Transfers
Electrical Heating
Thermal Conductivity
Efficiency and Sankey Diagrams

GCSE Physics: Efficiency
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.5 Efficiency.
All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Efficiency Ratings
Improving efficiency with insulation and lubrication
Maximum efficiency
Efficiency equation
Sankey diagrams

GCSE Physics: Electrical Heating
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.3 Electrical Heating Transfers. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Walls and Insulation
Thermal energy dissipation
Reducing thermal energy dissipation with lubrication and insulation
Heating substances and state changes
Work done = Power x Time
Change in thermal energy = Mass x Specific Heat Capacity x Change in temperature
Thermal energy for state change = Mass x Specific latent heat

GCSE Physics: Electrical Energy Transfers
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.2 Electrical Energy Transfers. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Energy stores
Energy transfers
Current heats wires
Wasted energy in motors and heating elements
Specific heat capacity and electrical energy
Thermal energy = Mass x Specific Heat Capacity x Change in Temperature
Energy = Charge x Potential Difference

GCSE Physics: Electrical Power and Work Done
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.1 Electrical Power and Work Done. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Definition of power
Converting between W and kW
Converting between seconds, minutes, and hours
Calculating work done in kWh and J
Converting between kWh and J

GCSE Physics: Energy transfers and Conservation of energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.1b Energy stores transfers and Conservation of energy.
This PowerPoint covers while including student activities and worked answers:
The law of conservation of energy.
The energy transfer pathways:
Mechanically – with forces
Electrically – with current
Heating by particles
Heating by radiation
Describing stores and transfers for:
Object projected upwards or up a slope,
A moving object hitting an obstacle,
An object being accelerated by a constant force,
A vehicle slowing down,
Bringing water to a boil in an electric kettle
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5 Waves
Resources for P5 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Definition of a wave
Mechanical waves
Electromagnetic waves
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
Amplitude
Wavelength
Frequency
Time period
Calculating frequency and equation
Relationship between frequency and wavelength when speed is constant.
Calculating time period from frequency with equations
The speed equation
Measuring distance and time
Simple experiment for the speed of sound
Improving experiments
Echoes
Speed of sound experiment with microphones and oscilloscope.
Ray diagrams
Absorption, reflection and transmission
Sonar
Ultrasound
Rearranging equation
Refraction
Relationship between wave speed and wavelength
Structure of the ear.
Frequency range of human hearing.
Explanation of the limited frequency range of humans.
Explanation for hearing deteriorating with age.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction
Convex and Concaves lenses
Eyes and corrective lenses
Refraction and wavelength
Focal points for lenses
Determining the type of images produced through a lens
Names of colours for the visible spectrum
Coloured filters
Coloured objects acting as a coloured filters
White light and refracting prism
Refraction and wavelength
Specular reflection
Diffuse scattering
Scattering - Why the sky is blue and milk is white.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.3 Wave Interactions
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction
Convex and Concaves lenses
Eyes and corrective lenses
Refraction and wavelength
Focal points for lenses
Determining the type of images produced through a lens
Names of colours for the visible spectrum
Coloured filters
Coloured objects acting as a coloured filters
White light and refracting prism
Refraction and wavelength
Specular reflection
Diffuse scattering
Scattering - Why the sky is blue and milk is white.

GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Refraction
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.2a Electromagnetic Reflection.
Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction

GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Reflection
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.1a Electromagnetic Reflection. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.2 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation