
TOPIC 5 SEPARATE SCIENCE PAPER 1 - NEW for SEPTEMBER 2017
Learning objectives: LESSON 1
Objectives:
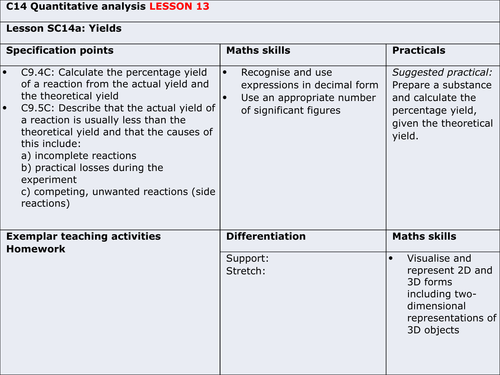
To understand the difference between the actual yield and the theoretical yield
To be able to calculate the percentage yield of a reaction from the actual yield and the theoretical yield
To recall how to calculate masses using moles
All extension questions available on each slide
Answers all underneath each slide
Support also available where necessary
AfL sections and mini quizzes
Reducing the need for photocopying
No exam questions due to copy write
Main topics include:
- calculating percentage yields from theoretical and actual yields
- calculating percentage yields from reacting masses using moles to calculate the theoretical or actual yield
- why is the actual yield usually less than the theoretical (practical losses, incomplete reactions and competing/unwanted side reactions)
Enjoy !!!!
PLEASE LEAVE FEEDBACK and REVIEWS
All relating to specification (any pictures used have all been taken from the internet and I am not trying to claim rights to any pictures or information used)
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 27%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc14 Quantitative analysis: TITRATION, ATOM ECONOMY, MOLAR VOLUME, CONCENTRATION CORE PRACTICAL TITRATION, PERCENTAGE YIELD Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc15 Dynamic Equilibria + the Haber process: Haber process, Le Chatelier, Fertilisers, Fuel Cell, industry processes SEPARATE TRIPLE SCIENCE ONLY
10 lessons in total <br /> Including a CORE PRACTICAL - Titration (only SS)<br /> <br /> Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc14 Quantitative analysis:<br /> 1. MOLAR VOLUME of gases and Avogadro's law of gases <br /> Objectives:<br /> STARTER: To know how to interconvert between cm3 and dm3 and to work out the concentration equation<br /> To know how to define molar volume of gases at room temperature and pressure <br /> To be able to use the molar volume in calculations involving the masses of solids and volumes of gases <br /> To understand how to use Avogadro’s law to calculate volumes of gases involved in gaseous reactions. <br /> 2. CONCENTRATION with mol and grams per dm3 and interchanging between the two <br /> Objectives:<br /> STARTER: To know how to interconvert between cm3 and dm3 and to work out the concentration equation<br /> To be able to calculate concentrations in g dm-3 (H)<br /> To be able to calculate concentrations in mol dm-3 (H)<br /> To understand how to interconvert between mol dm-3 and g dm-3 (H)<br /> 3. PERCENTAGE YIELDS + moles SEPARATE or TRIPLE <br /> Objectives:<br /> To understand the difference between the actual yield and the theoretical yield <br /> To be able to calculate the percentage yield of a reaction from the actual yield and the theoretical yield <br /> To recall how to calculate masses using moles<br /> 4 + 5. TITRATION CORE PRACTICAL and Titration calculations<br /> Objectives:<br /> To understand how to carry out an acid and alkali titration <br /> To be able to carry out calculations using the results of titrations to calculate an unknown concentration of solution or unknown volume of solution (H)<br /> To consolidate learning with questions (H)<br /> 6. ATOM ECONOMY<br /> Objectives:<br /> To recall the atom economy of a reaction <br /> To make Magnesium sulphate in 3 different ways then work out which is the best (most economical!)<br /> To explain why a particular reaction pathway is chosen to produce a particular product, given data (HIGHER OBJECTIVE)<br /> <br /> Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc15 Dynamic Equilibria + the Haber process<br /> <br /> 7. TOPIC 5 Sc16a TOPIC 5 Chemical cells and Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells <br /> Objectives:<br /> To know that a chemical cell produces a voltage until one of the reactants is used up <br /> To be able to recall how a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell functions <br /> To evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of fuel cells for given uses <br /> <br /> 8. Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc15 Dynamic Equilibria: Industrial processes including large scale of the Haber process - Edexcel 9-1 Sc15b PART 1<br /> Objectives:<br /> To understand Le Chatelier’s Principle (H)<br /> To predict how the position of the equilibrium is affected by changes in conditions(H)<br /> To understand how the time taken to reach equilibrium is affected by changes in the conditions (H)<br /> <br /> 9. Edexcel 9-1 Sc15b PART 2<br /> Objectives:<br /> To recall the conditions for the Haber process <br /> To explain how the conditions are chosen for industrial chemical reactions (H)<br /> To explain the reaction pathways chosen from industrial processes (H)<br /> <br /> 10.<br /> Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc15 Dynamic Equilibria: Haber process + Fertilisers<br /> Learning objectives:<br /> STARTER <br /> Mini test covering all the basics from combined (reversible reactions, Haber conditions, dynamic equilibrium, definitions)<br /> Objectives:<br /> To recall 3 essential elements for plant growth<br /> To be understand how to name several fertilisers made from different acid and alkali compounds <br /> To describe and compare the laboratory preparation and the industrial production of ammonium sulfate <br /> <br /> RRP £30 saving 27%
Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc14 Quantitative analysis: TITRATION, ATOM ECONOMY, MOLAR VOLUME, CONCENTRATION CORE PRACTICAL TITRATION, PERCENTAGE YIELD SEPARATE TRIPLE SCIENCE ONLY
Edexcel 9-1 TOPIC 5 Sc14 Quantitative analysis: 1\. MOLAR VOLUME of gases and Avogadro's law of gases Objectives: STARTER: To know how to interconvert between cm3 and dm3 and to work out the concentration equation To know how to define molar volume of gases at room temperature and pressure To be able to use the molar volume in calculations involving the masses of solids and volumes of gases To understand how to use Avogadro’s law to calculate volumes of gases involved in gaseous reactions. 2\. CONCENTRATION with mol and grams per dm3 and interchanging between the two Objectives: STARTER: To know how to interconvert between cm3 and dm3 and to work out the concentration equation To be able to calculate concentrations in g dm-3 (H) To be able to calculate concentrations in mol dm-3 (H) To understand how to interconvert between mol dm-3 and g dm-3 (H) 3\. PERCENTAGE YIELDS + moles SEPARATE or TRIPLE Objectives: To understand the difference between the actual yield and the theoretical yield To be able to calculate the percentage yield of a reaction from the actual yield and the theoretical yield To recall how to calculate masses using moles 4\. TITRATION CORE PRACTICAL and Titration calculations Objectives: To understand how to carry out an acid and alkali titration To be able to carry out calculations using the results of titrations to calculate an unknown concentration of solution or unknown volume of solution (H) To consolidate learning with questions (H) 5\. ATOM ECONOMY Objectives: To recall the atom economy of a reaction To make Magnesium sulphate in 3 different ways then work out which is the best (most economical!) To explain why a particular reaction pathway is chosen to produce a particular product, given data (HIGHER OBJECTIVE)
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
