

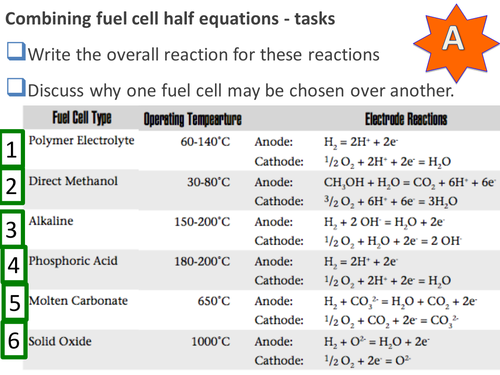


This is a lesson for A level chemistry on fuel cells. It begins with getting students to consider whether hydrogen would be a good source of energy to power cars for the future. Required learning from previous lessons is electrode potentials and half cells. The hydrogen balloon demo could be shown at the start to get students to appreciate that a lot of energy is released in a short amount of time from a small amount of fuel. Hydrogen produces the most amount of energy per gram for any chemical fuel. Students then draw a diagram to show how the standard electrode potential of an oxygen half cell could be determined - i.e. use a H+ reference electrode in one beaker and connect using a salt bridge to another beaker with O2- ions and O2 gas being bubbled through and using platinum as the electrode. Students then learn that O2 gas is reduced in the presence of H2O (i.e. bubbled through water) to OH- ions not O2- ions. This forms the basis of the hydrogen fuel cell where oxygen is bubbled in to one beaker with a platinum (or carbon) electrode, hydrogen is bubbled into another beaker with a platinum (or carbon) electrode and a salt bridge is attached between the beakers. Students could carry out this practical in pairs by using balloons filled with hydrogen and oxygen and allowing the gases to escape under water in the 250ml beakers. Filter paper soaked in sodium hydroxide could act as the salt bridge. Students then compare different types of fuel cell and write overall equations. There is a 5 mark exam question that can be used as an end of lesson plenary or homework. Please rate this resource and leave feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
£5.00
