Study guide for Motion, Forces, and Energy including conservation of energy and heat. Includes full answer key! Study guide is 6 pages, answer key is 9.
Standards Covered:
1. Motion and Forces
Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects.
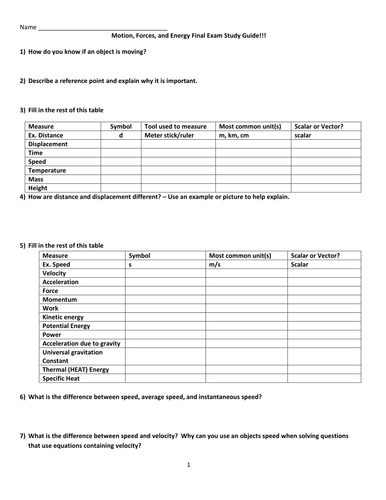
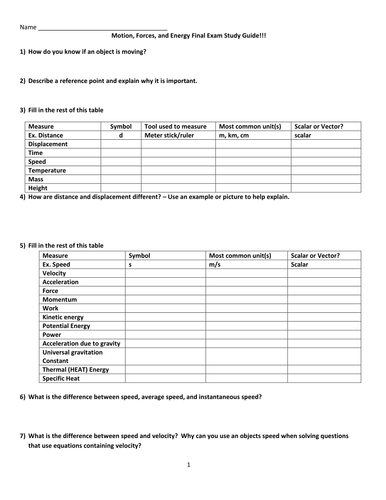
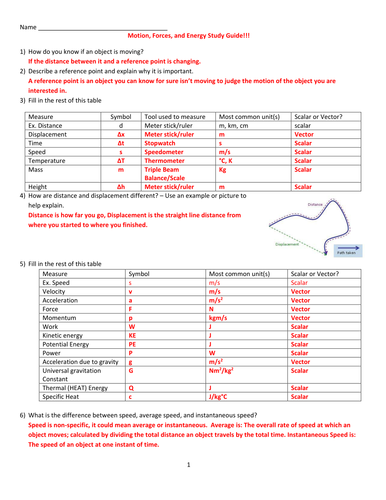
1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work).
1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve problems involving displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and constant acceleration.
1.3 Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position vs. time, distance vs. time, speed vs. time, velocity vs. time, and acceleration vs. time where acceleration is constant.
1.4 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion.
1.5 Use a free-body force diagram to show forces acting on a system consisting of a pair of interacting objects. For a diagram with only co-linear forces, determine the net force acting on a system and between the objects.
1.6 Distinguish qualitatively between static and kinetic friction, and describe their effects on the motion of objects.
1.7 Describe Newton’s law of universal gravitation in terms of the attraction between two objects, their masses, and the distance between them.
1.8 Describe conceptually the forces involved in circular motion.
2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum
Central Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects.
2.1 Interpret and provide examples that illustrate the law of conservation of energy.
2.2 Interpret and provide examples of how energy can be converted from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy and vice versa.
2.3 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively how work can be expressed as a change in mechanical energy.
2.4 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively the concept of power as work done per unit time.
2.5 Provide and interpret examples showing that linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity, and is always conserved (law of conservation of momentum). Calculate the momentum of an object.
3. Heat and Heat Transfer
Central Concept: Heat is energy that is transferred by the processes of convection, conduction, and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures.
3.1 Explain how heat energy is transferred by convection, conduction, and radiation.
3.2 Explain how heat energy will move from a higher temperature to a lower temperature until equilibrium is reached.
3.3 Describe the relationship between average molecular kinetic energy and temperature. Recognize that energy is
Standards Covered:
1. Motion and Forces
Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects.
1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work).
1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve problems involving displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and constant acceleration.
1.3 Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position vs. time, distance vs. time, speed vs. time, velocity vs. time, and acceleration vs. time where acceleration is constant.
1.4 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion.
1.5 Use a free-body force diagram to show forces acting on a system consisting of a pair of interacting objects. For a diagram with only co-linear forces, determine the net force acting on a system and between the objects.
1.6 Distinguish qualitatively between static and kinetic friction, and describe their effects on the motion of objects.
1.7 Describe Newton’s law of universal gravitation in terms of the attraction between two objects, their masses, and the distance between them.
1.8 Describe conceptually the forces involved in circular motion.
2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum
Central Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects.
2.1 Interpret and provide examples that illustrate the law of conservation of energy.
2.2 Interpret and provide examples of how energy can be converted from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy and vice versa.
2.3 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively how work can be expressed as a change in mechanical energy.
2.4 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively the concept of power as work done per unit time.
2.5 Provide and interpret examples showing that linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity, and is always conserved (law of conservation of momentum). Calculate the momentum of an object.
3. Heat and Heat Transfer
Central Concept: Heat is energy that is transferred by the processes of convection, conduction, and radiation between objects or regions that are at different temperatures.
3.1 Explain how heat energy is transferred by convection, conduction, and radiation.
3.2 Explain how heat energy will move from a higher temperature to a lower temperature until equilibrium is reached.
3.3 Describe the relationship between average molecular kinetic energy and temperature. Recognize that energy is
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
$4.00