499Uploads
171k+Views
73k+Downloads
Physics

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear decay equations
OCR A level Physics: 25.2 Nuclear decay equations
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Typical speeds of radiation produced form nuclear decays
Conservation rules for nuclear decays
Nuclear notation
Alpha decays
Beta-minus and beat-plus decays
Gamma decays
Decay chains

OCR A level Physics: Half-life and Activity
OCR A level Physics: 25.3 Half-life and Activity
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The reason why radioactive decays are considered random and spontaneous
Rolling dice being a good analogue for radioactive decays
Definition of half-life
Determining half-life from a graph.
Calculating half-life from a table of data.
Activity of a sample in Bq
The decay constant derivation

OCR A level Physics: Binding Energy
OCR A level Physics: 26.2 Binding Energy
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability

OCR A level Physics: Radioactive Dating
OCR A level Physics: 25.6 Radioactive Dating
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
State what isotopes of carbon are used in carbon dating.
Explain how carbon dating works.
Calculate the age of objects with carbon dating.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Radioactivity
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 25 Radioactivity is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
25.1 Radioactivity
25.2 Nuclear decay equations
25.3 Half-life and Activity
25.4 Radioactive Decay Calculations
25.5 Modelling Radioactive Decay
25.6 Radioactive Dating
Types of ionising radiation (alpha, beta-plus/beta-minus, gamma)
Penetration power and ionising power
Detecting radiation with a Geiger (GM tube) counter
Background radiation and correct count rates
Electric and magnetic fields affect ionising radiation
Cloud chambers
Typical speeds of radiation produced form nuclear decays
Conservation rules for nuclear decays
Nuclear notation
Alpha decays
Beta-minus and beat-plus decays
Gamma decays
Decay chains
The reason why radioactive decays are considered random and spontaneous
Rolling dice being a good analogue for radioactive decays
Definition of half-life
Determining half-life from a graph.
Calculating half-life from a table of data.
Activity of a sample in Bq
The decay constant derivation
Decay constant and half-life
Using exponentials to calculate activity and number of nuclei present
Solving Differential Equations (beyond A-level Physics course)
Iterative Method
Selecting appropriate time intervals
Comparing answers from the iterative method and exact solution.
State what isotopes of carbon are used in carbon dating.
Explain how carbon dating works.
Calculate the age of objects with carbon dating.

OCR A level Physics: Einstein's Mass-Energy Equation
OCR A level Physics: 26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence

OCR A level Physics: Radioactive Decay Calculations
OCR A level Physics: 25.4 Radioactive Decay Calculations
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Decay constant and half-life
Using exponentials to calculate activity and number of nuclei present
Solving Differential Equations (beyond A-level Physics course)

OCR A level Physics: Modelling Radioactive Decay
OCR A level Physics: 25.5 Modelling Radioactive Decay
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Iterative Method
Selecting appropriate time intervals
Comparing answers from the iterative method and exact solution.

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Fusion
OCR A level Physics: 26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Nuclear equations
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 26 Nuclear Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
26.2 Binding Energy
26.3 Nuclear Fission
26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Fission
OCR A level Physics: 26.3 Nuclear Fission
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2 Forces Full scheme
All resources for P2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Distance, time, and speed
Vectors and scalars
Acceleration
Distance-time graphs
Velocity-time graphs
Equations of motion and Kinetic Energy
Forces and interactions
Free-body Diagrams
Newton’s first law
Newton’s second law
Everyday forces and their effects
Momentum
Work and Power
Stretching springs
Stretching materials and storing energy
Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
Turning Forces
Simple Machines
Hydraulics

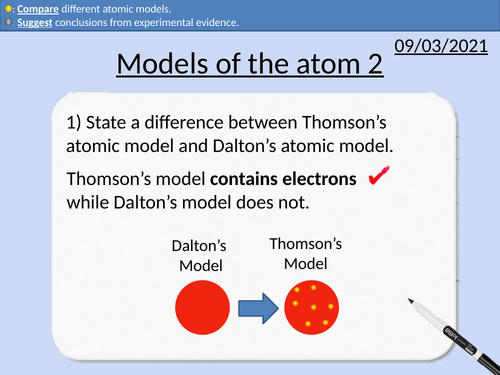
GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 2
This presentation includes:
Why scientific models change over time
Electric charge
Rutherford’s atomic model
Rutherford’s experiment
Bohr’s atomic model