499Uploads
172k+Views
73k+Downloads
All resources

OCR A level Physics: Spectra
OCR A level Physics: 19.5 Spectra
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum and wavelengths
Definition of spectroscopy
Electrons and energy levels
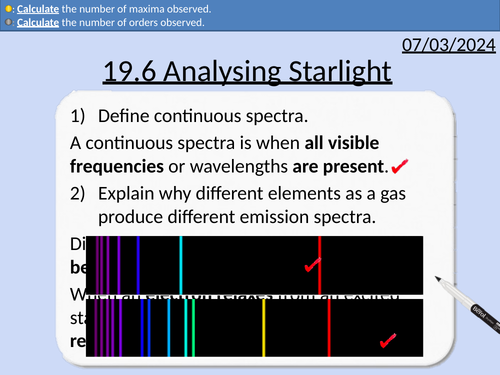
Continuous spectra
Emission spectra from gases
Absorption spectra from gases

OCR A level Physics: Analysing Starlight
OCR A level Physics: 19.6 Analysing Starlight
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electromagnetic interference
Double slit experiment
Path and phase difference
Diffraction grating
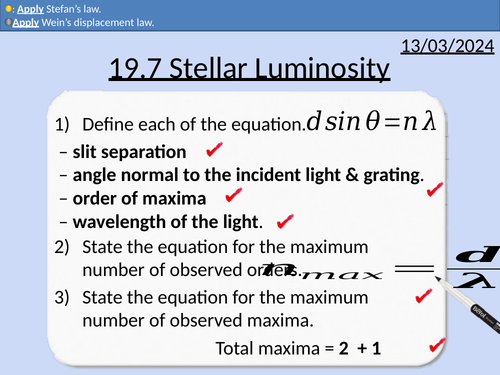
The grating equation
Lines per millimeter to grating spacing
Maximum order, n
Maximum number of maxima

OCR A level Physics: Stellar Luminosity
OCR A level Physics: 19.7 Stellar Luminosity
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency/wavelength, and temperature
Black body radiation
Wein’s displacements law
Stefan’s law (Stefan-Boltzmann law)
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Stars
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 19 Stars is apart of the Module 5: Newtonian world and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
19.1 Objects in the Universe
19.2 Life Cycles of Stars
19.3 Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
19.4 Energy Levels in Atoms
19.5 Spectra
19.6 Analysing Starlight
19.7 Stellar Luminosity
The size of astronomical objects: Universe, Galaxies, Solar systems, Stars, Planets, Planetary satellites, Comets, Artificial planetary satellites
Comparing planets and comets
The birth of stars
Stars in equilibrium during the main sequence
Calculating mass in kg from solar mass
Life cycle of stars with a mass between 0.5 and 10 solar masses
Life cycle of stars with a mass above 10 solar masses
Pauli exclusion principle and electron degeneracy pressure
Red giants and white dwarfs
The Chandrasekhar limit
Red supergiants to black holes and neutron stars
Stellar nucleosynthesis
Definition of luminosity
Usual axis choice of a HR diagram.
Identifying the positions of the main sequence, white dwarfs, red giants, and red supergiants.
Description of how stellar evolution is shown in a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
Atoms have different electron arrangements
Ground state energy
Bound electron states being negative
Converting between joules and electronvolts
Calculating the change of energy between energy states
Calculating a photon’s frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum and wavelengths
Definition of spectroscopy
Electrons and energy levels
Continuous spectra
Emission spectra from gases
Absorption spectra from gases
Electromagnetic interference
Double slit experiment
Path and phase difference
Diffraction grating
The grating equation
Lines per millimeter to grating spacing
Maximum order, n
Maximum number of maxima
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency/wavelength, and temperature
Black body radiation
Wein’s displacements law
Stefan’s law (Stefan-Boltzmann law)

OCR A level Physics: Hubble’s Law
OCR A level Physics: 20.3 Hubble’s Law
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The Cosmological Principle
Hubble’s Observations
Hubble’s Law
Hubble’s constant and the gradient of a graph
Converting between km s-1 Mpc-1 into s-1
The expanding Universe model.

OCR A level Physics: The Doppler Effect
OCR A level Physics: 20.2 The Doppler Effect
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The definition of the Doppler effect
Changes in pitch of sound waves due to relative motion
Absorption spectra and electron energy levels
Red-shift and blue-shift absorption spectra
The Doppler equation
The condition for velocity for the Doppler equation

OCR A level Physics: Astronomical Distances
OCR A level Physics: 20.1 Astronomical Distances
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Astronomical distances: light-years, parsec, astronomical unit
Astronomical angles - degree, arcminute, arcsecond
Parallax Angle

OCR A level Physics: The Big Bang Theory
OCR A level Physics: 20.4 The Big-bang
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Georges Lemaître’s Theory
Evidence for the Big Bang Model
Hubble’s Law (expanding Universe)
Microwave Background Radiation
Source of the Microwave Background Radiation
Hubble’s constant and the age of the Universe

OCR A level Physics: Evolution of the Universe
OCR A level Physics: 20.5 Evolution of the Universe
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The evolution of the Universe from the Big-bang to 13.7 billion years later
The composition of the Universe
Experimental evidence for dark matter
Experimental evidence for dark energy

GCSE OCR Physics 9-1 Paper 1 Revision Booklets
OCR GCSE Physics Paper 1 for higher tier (triple and combined) are covered with individual revision booklets.
Each booklet has:
Link to specification number
Denotes if it is higher or combined material
Equations to recall and apply for that section
Equations to apply for that section
Key Points
Exam questions
Mark Schemes for each question
Triple Booklets:
P1.1 The Particle Model
P1.2 Changes of State
P1.3 Pressure
P2.1 Motion
P2.2 Newton’s Laws
P2.3 Forces in action - Simple Machines
P2.3 Forces in action - Springs and Gravitational Energy
P3.1/2 Electricity
P4.1 Magnetism
P4.2 Uses of Magnetism
Combined Booklets:
P1.1 The Particle Model
P1.2 Changes of State
P2.1 Motion
P2.2 Newton’s Laws
P2.3 Forces in action - Springs and Gravitational Energy
P3.1/2 Electricity
P3.3 Magnetism and Fields

GCSE OCR Physics 9-1 Paper 2 Revision Booklets
OCR GCSE Physics Paper 2 for higher tier (triple and combined) are covered with individual revision booklets.
Each booklet has:
Link to specification number
Denotes if it is higher or combined material
Equations to recall and apply for that section
Equations to apply for that section
Key Points
Exam questions
Mark Schemes for each question
Triple Booklets:
P5.1 Wave Beahviour and Wave Velocity
P5.2 Electromagnetic Waves
P5.3 Wave Interactions
P6.1 Radioactive Emissions
P6.2 Uses and Hazards - Fusion and Fission
P7 Energy
P8.1 Physics on the move
P8.2 Powering Earth
P8.3 Beyond Earth
Combined Booklets:
P4.1 Wave Beahviour and Wave Velocity
P4.2 Electromagnetic Waves
P4.3 Radioactice Emissions
P6 Energy
P6.2 Physics on the move
P6.3 Powering Eaerth
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Cosmology (Big Bang)
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 20 Cosmology (Big Bang) is apart of the Module 5: Newtonian world and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
20.1 Astronomical Distances
20.2 The Doppler Effect
20.3 Hubble’s Law
20.4 The Big-bang Theory
20.5 Evolution of the Universe
Astronomical distances: light-years, parsec, astronomical unit
Astronomical angles - degree, arcminute, arcsecond
Parallax Angle
The definition of the Doppler effect
Changes in pitch of sound waves due to relative motion
Absorption spectra and electron energy levels
Red-shift and blue-shift absorption spectra
The Doppler equation
The condition for velocity for the Doppler equation
The Cosmological Principle
Hubble’s Observations
Hubble’s Law
Hubble’s constant and the gradient of a graph
Converting between km s-1 Mpc-1 into s-1
The expanding Universe model.
Georges Lemaître’s Theory
Evidence for the Big Bang Model
Hubble’s Law (expanding Universe)
Microwave Background Radiation
Source of the Microwave Background Radiation
Hubble’s constant and the age of the Universe
The evolution of the Universe from the Big-bang to 13.7 billion years later
The composition of the Universe
Experimental evidence for dark matter
Experimental evidence for dark energy

OCR A level Physics: Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.1 Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
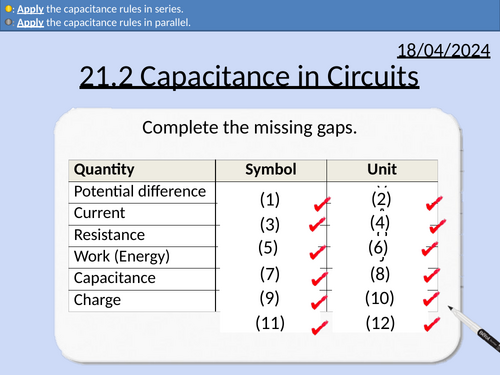
Electrical quantities, symbols, and units
SI prefixes and standard form
Definition of a capacitor
Structure of a capacitor
Calculating capacitance, charge, and potential difference.

OCR A level Physics: Energy Stored by Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.3 Energy Stored by Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
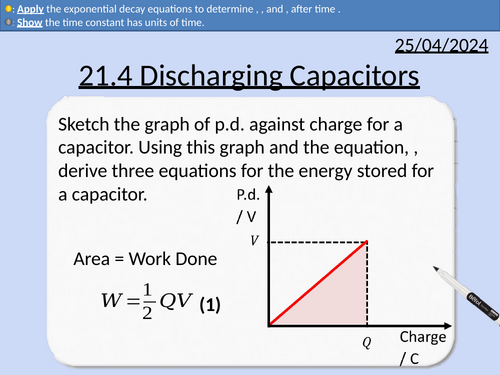
Work done of a capacitor depends upon the initial potential difference and capacitance.
Work done is provided by the source of potential difference.
Deriving three equations for work done of a capacitor.

OCR A level Physics: Discharging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.4 Discharging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Exponential increase and exponential decay
Explaining how capacitors discharge through a resistor in parallel
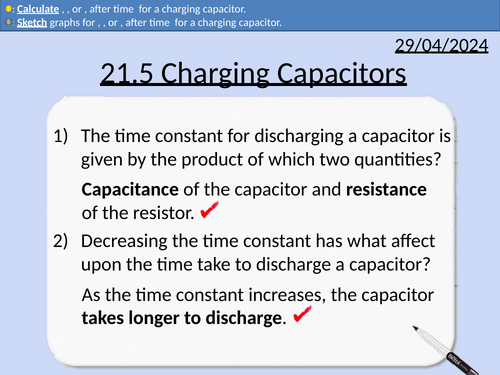
Definition of time constant for a capacitor
Showing that time constant has units of seconds
Iterative method for finding how capacitors discharge
Using exponentials and logs.
Solving a differential equation (needed for A-level Maths).

OCR A level Physics: Charging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.5 Charging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Explaining how capacitors charge with a resistor in series
Explaining how 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Sketching graphs for 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, after time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.

OCR A level Physics: Capacitors in Circuits
OCR A level Physics: 21.2 Capacitors in Circuits
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Uses of capacitors in circuits.
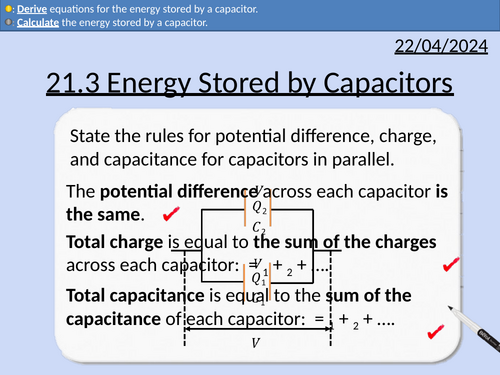
Rules for capacitors in parallel (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Rules for capacitors in series (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Applying the rules in series and parallel.
Creating a circuit to calculate the charge stored on the capacitor.

OCR A level Physics: Uses of capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.5 Charging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Calculating power output from a circuit containing a capacitor
A rectifier circuit - changing an alternating input to a smooth output
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Capacitance
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 21 Capacitance is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
21.1 Capacitors
21.2 Capacitors in circuits
21.3 Energy stored by capacitors
21.4 Discharging capacitors
21.5 Charging capacitors
21.6 Uses of capacitors
Electrical quantities, symbols, and units
SI prefixes and standard form
Definition of a capacitor
Structure of a capacitor
Calculating capacitance, charge, and potential difference.
Uses of capacitors in circuits.
Rules for capacitors in parallel (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Rules for capacitors in series (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Applying the rules in series and parallel.
Creating a circuit to calculate the charge stored on the capacitor.
Work done of a capacitor depends upon the initial potential difference and capacitance.
Work done is provided by the source of potential difference.
Deriving three equations for work done of a capacitor.
Exponential increase and exponential decay
Explaining how capacitors discharge through a resistor in parallel
Definition of time constant for a capacitor
Showing that time constant has units of seconds
Iterative method for finding how capacitors discharge
Using exponentials and logs.
Solving a differential equation (needed for A-level Maths).
Explaining how capacitors charge with a resistor in series
Explaining how 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Sketching graphs for 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, after time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating power output from a circuit containing a capacitor
A rectifier circuit - changing an alternating input to a smooth output

OCR A level Physics: Electric Fields
OCR A level Physics: 22.1 Electric Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electric field line pattern from point charges, uniformly charged objects, and capacitors.
Rules for electric field lines
Interacting field lines for attraction and repulsion
Detecting electric fields with a charged gold leaf
Definition of electric field strength
Explaining that electric field strength is a vector with magnitude and direction
Apply the equation for electric field strength