


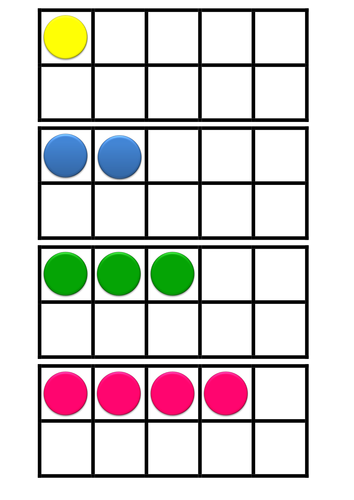
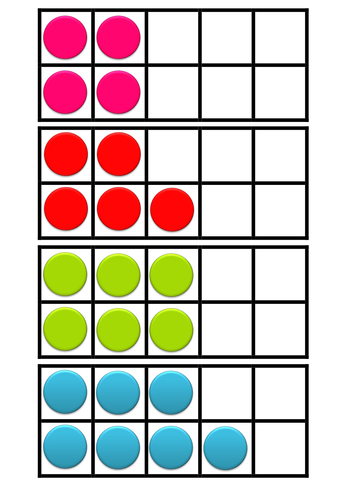









Ready-to-go ideas for developing pupils’ ability to add and subtract mentally and to reason about number. These activities link strongly with the CPA (concrete, pictorial, abstract) approach to teaching maths.
I created these activities for a research project I was conducting in school as part of my Maths Specialist Teacher qualification. They are all aimed at improving children’s mental addition and subtraction by developing a broad range of strategies and encouraging them to reason about number. We had found that children were entering KS2 with only a handful of (often cumbersome) mental strategies, e.g. partitioning into tens and units, using number bonds to ten only or counting on/back in ones, and weren’t always applying them appropriately. We used the activities with Y3 and Y4 children, but it can be used from Y2 upwards as it links very strongly with the Y2 curriculum.
The resource includes differentiated activities with written descriptions and accompanying interactive whiteboard slides and paper resources where applicable. Slides were originally in SMARTboard format and this is perhaps the best software to use if you have it as the slides can be interacted with this way; however, I have also copied the slides over to a PowerPoint presentation for those without SMARTboard software. Also included is a wall display, which shows visual representations of different strategies for mental addition and subtraction. The activities can be adapted for all year groups and abilities and you will find a lot more mileage in this resource once you get started and the impact on the classes studied in terms of both their confidence and ability in mental maths was phenomenal.
National Curriculum Links
- Pupils should partition numbers in different ways (for example, 23 = 20 + 3 and 23 = 10 + 13) to support subtraction.
- Recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use related facts up to 100
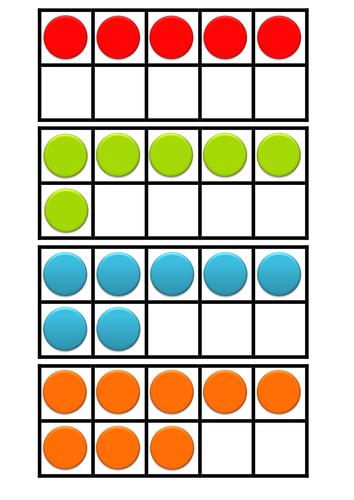
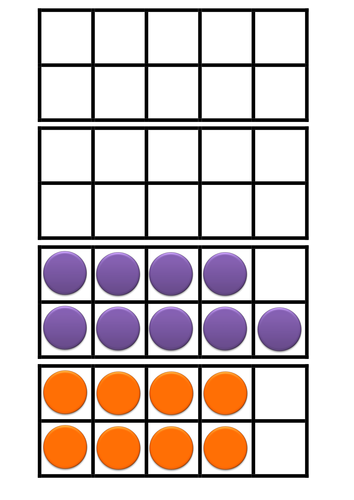
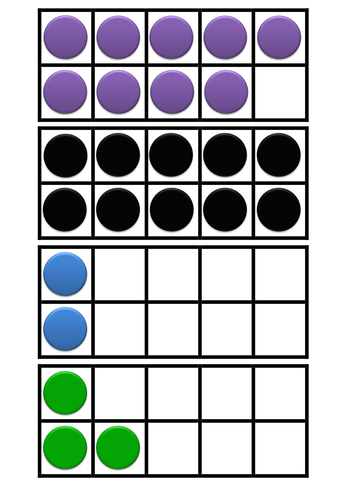
- Add and subtract numbers using concrete objects, pictorial representations, and mentally, including: a two-digit number and ones; a two-digit number and tens; two two-digit numbers; adding three one-digit numbers.
- Show that addition of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and subtraction of one number from another cannot
- Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems.
- Pupils practise addition and subtraction to 20 to become increasingly fluent in deriving facts such as using 3 + 7 = 10; 10 – 7 = 3 and 7 = 10 – 3 to calculate 30 + 70 = 100; 100 – 70 = 30 and 70 = 100 – 30. They check their calculations, including by adding to check subtraction and adding numbers in a different order to check addition (for example, 5 + 2 + 1 = 1 + 5 + 2 = 1 + 2 + 5). This establishes commutativity and associativity of addition.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.