







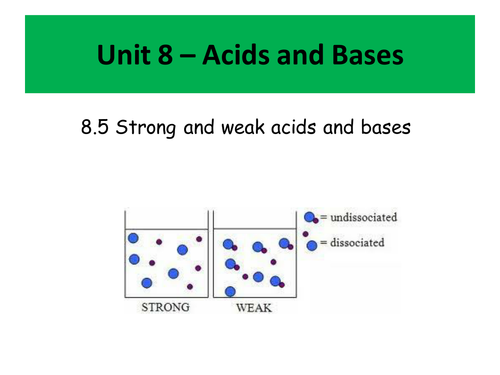
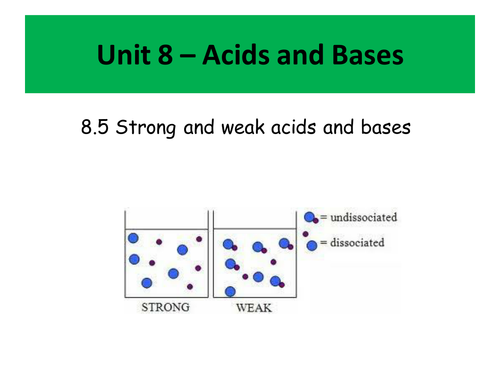
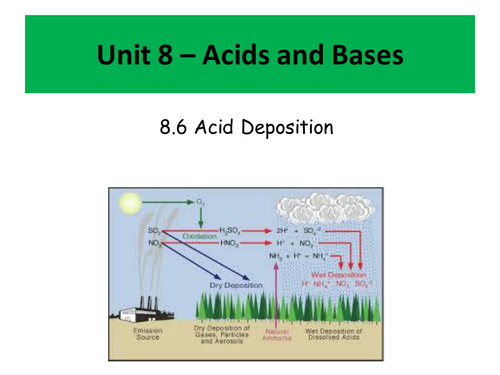
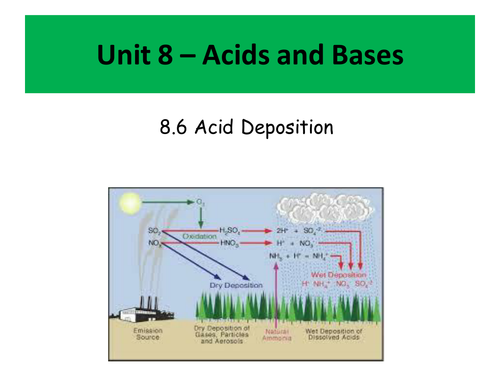
















This unit was delivered to cover unit 8 of the IB - Acids and Bases, however it would be suitable for most post-16 programs of study.
It begins by recapping the subjects that students should be familiar with from GCSE, before building into more advanced topics. Each PowerPoint comes with a ´student version´ which has gaps for the students to complete, and contains several exercises for students to do. I have also included past paper questions and answer schemes.
Topics covered are:
- What are acids and bases?
- Bronsted Lowry acids and bases (and conjugate acids and bases)
- Amphiprotic and amphoteric substances
- Lewis acids and bases
- Reactions of acids with metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates, bases and alkalis
- Making salts
- What is pH and how to calculate the pH of both acids and bases
- Using the dissociation constant of water to calculate pH
- Acid deposition - how it occurs and how it can be treated
- Calculations involving Ka, pKa, Kb, pKb, pH and pOH
- Using the relationships Kw = Ka x Kb and pKa + pKb = pKw
- Titration curves for titrations involving any combination of strong and weak acids and bases
- Indicators - how to select a suitable indicator for a titration
- How to calculate the pH of salt solutions
- Buffers - what are they, how are they made and how do they work (including calculations)
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
