177Uploads
22k+Views
5k+Downloads
All resources

AQA A - level Sociology -Media - what are sociological views on popular culture
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand what are sociological views of popular culture (e.g. define popular culture, other terms used to refer to it, explain sociological views on popular culture and to analyse and evaluate those views.
Covers the following key terms:
Popular culture
High culture
Low culture
Mass culture
Critical Theory
Social repression (extension)
Social conformity (extension)
Tabloidisation
Infotainment
Key terms you SHOULD know that might come up:
Social control, False consciousness, Profit, Ideology, Dominant ideology/Hegemony, Class inequality, Pluralism, Neo-Marxism, Media products, Media technology, Agenda-setting, Gate-keeping, Lords of a Global village
Covers the following key sociologists: Marcuse, The Frankfurt School, Strinati, Livingston, Curran et al (2009)
**REQUIRES textbook - 'SOCIOLOGY For AQA Volume 2 by Browne, Blundell & Law **
Answers to all main activities included
Includes a 10 marker with three model paragraph plans
RESOURCES AT THE END OF PPT
Bundle

SOCIOLOGY Research Methods - INTRO, PET ISSUES, SAMPLING METHODS
Detailed and differentiated set of student-led lessons made for AQA A/AS-LEVEL SOCIOLOGY but can be differentiated for GCSE (see below-L2) and any SPEC (as it goes through the main methods, terms, issues for social research in general:
Intro to Methods
Explores primary vs secondary methods, quantitative vs qualitative methods, validity and reliability as a way to introduce students to the main main research methods.
Explores practical (time, cost, research opportunity, requirements of funding body & subject matter), ethical (informed consent, confidentiality, harm to participants, vulnerable groups & covert research) and theoretical issues (validity, reliability, representativeness, methodological perspectives, interpretivism & positivism).
*** Catered towards A-LEVEL AQA sociology but if main activity can be replaced, the rest can be used for GCSE and ANY SPEC.**
*** Main activity uses pages 92-94 of the AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend**
explores sampling methods, sampling frame, representative (sample), generalising (findings) and the relationship between these and positivism vss interpretivism and theoretical issues
LESSON COMES WITH ANSWERS

AQA A-level Sociology - Media: The globalisation of popular culture
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand what impact might globalisation have on popular culture and what role might the media have in this (e.g. how to describe globalisation and identify the impact it has had on popular/mass culture,
To explain the impacts of a global popular/ mass culture and the role of the media in creating it using real-life examples and to analyse and evaluate the impacts of a global popular/ mass culture and the role of the media in creating it).
Covers the key following terms: Globalisation, Cultural homogenisation , Global culture, Cultural imperialism , media imperialism, Transnational, The Culture-Ideology of Consumerism, Cocacolonisation
Covers key terms you should know that might come up:
Popular/ mass culture, High culture, Low culture, Culture, Cultural products, Norms, Values, Subculture, Cultural capital
Covers key sociologists: Strinati/Giddings/ Postmodernists, Kellner/Sklair/ Flew, Sklair/ Ritzer, Sklair
Based on the information in textbook - 'SOCIOLOGY For AQA Volume 2 by Browne, Blundell & Law **
INCLUDES ALL ANSWERS FOR MAIN ACTIVITIES
INCLUDES A KEY TERM AND DEFINITIONS SHEET
Includes an exam question with scaffolding
RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END PPT

How to answer 12 markers
Includes model 12 marker answer that is annotated.
Includes a detailed success criteria for writing 12 markers
Includes a writing frame that will help students write out their own writing frame.
Lesson tries to teach students from the content they have learnt.

AQA A-level Sociology Education Topic 5 Role of education - Marxist view
Detailed student led lesson on the Marxist views of the role of education adapted to stretch and challenge the most able whilst scaffolding to allow pupils who need support the opportunity to access higher level thinking.
Covers the following Marxist key functions of education: reproducing class ienquality, legitimising class inequality, correspondence principle,
Covers the following functionalist sociologists: Althusser, Bowles and Gintis and Willis
Covers the following key term:
State apparatuses
Ideological state apparatuses
Repressive state apparatuses
Ideology
Correspondence principle
Hierarchy
Alienation
Fragmentation
Extrinsic reward
Competition
Promotes a spiral curriculum by making links to key terms that students might have previously been taught within the education unit and for Marxism as a theory that link to this lesson.
Makes links to methods in context 20 marker - provides scaffolding and possible questions that link to Willis’ study.
Promotes, facilitates and scaffolds Oracy.
Provides guidance for answering 4 markers.
Uses and refers to ’ AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend ’ textbook
DETAILED ANSWERS INCLUDED FOR THE MAIN ACTIVITIES ON THE FUNCTIONS OF EDUCATION ONLY
NOTES -RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF THE PPT.

AQA GCSE Sociology – Introduction to 3 and 4 markers
**** A lesson to explicitly teach Y10 students how to answer 3 and 4 markers for the first time (in preparation for their first ever Sociology assessment).
**Provides a detailed and scaffolded success criteria for each type of 3 marker and for 4 markers.
****Includes model answers for the different types of 3 markers and 4 markers
****NOTE- This preparation lesson does NOT teach students how to answer a 4-marker using an Item or teach how to answer research methods 4 marker.
****RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF THE PPT.

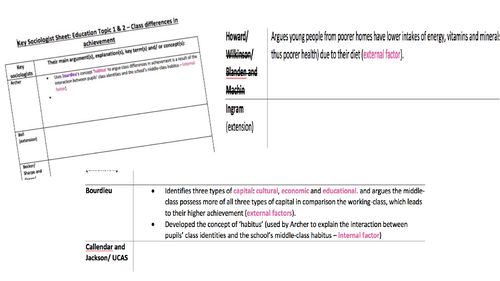
AQA A-level Sociology Education Topic 1- 2 key sociologists sheets
Detailed and scaffolded (e.g. SOME sentence starters/ prompts, model examples of what sociologists say (and what students are expected to write and how), etc.) key sociologists sheets that requires students to write done what key sociologists from education:
Topic 1 - Class differences in achievement (external factors)
Topic 2 - Class differences in achievement (internal factors)
Sociologists in alphabetical order
Good form of revision and revision resource for the students.
**BASED ON CONTENT in textbook - AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend ’ textbook

AQA A-level Sociology Education Topic 5 Role of education - Functionalist view
Detailed student led lesson on functionalist views of the role of education adapted to stretch and challenge the most able whilst scaffolding to allow pupils who need support the opportunity to access higher level thinking.
Covers the following functionalist key functions of education: installing social solidarity, bridging the gap between the family and wider society through secondary socialisation, teaching specialist skills needed for work and role allocation.
Covers the following functionalist sociologists: Durkheim, Parsons and Davis and Moore.
Covers the following key term:
Function or role (e.g. of an institution)
Social solidarity
Formal curriculum
Hidden curriculum
Ascribed status
Achieved status
Universalistic standards
Particularistic standards
Meritocracy
Socialisation
Role allocation
Promotes a spiral curriculum by making links to key terms that students might have previously been taught that link to this lesson.
Promotes, facilitates and scaffolds Oracy.
Develops the skills needed to answer 10 markers with items - allows students to apply knowledge to an item 10 marker with guidance and includes a detailed success criteria to help them answer this.
Uses and refers to ’ AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend ’ textbook
DETAILED ANSWERS INCLUDED FOR MAIN ACTIVITIES
NOTES -RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF THE PPT.

AQA GCSE Sociology - Y10 Mock assessment and feedback lesson
Includes an assessment and feedback lesson.
Student will need a textbook for information for the feedback lesson - This makes refers to pages in Owens & Woodfield textbook with page numbers
Includes writing frame that can be used to help students with improving their exam structure and answers.
Assessment is on family and education and excludes research methods questions (paper 1).
Guides students with how to know which topic to draw information from per exam question.
Feedback lesson would take a double lesson

1. AQA A-level Sociology - Media: Pluralist, Critical theorists & Postmodernists views
**Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand Pluralist, Critical theorists & Postmodernist views of society. Students should be able to explain how pluralist, critical and postmodernist view the globalisation of popular culture. To analyse and evaluate how pluralist, critical and postmodernist view the globalisation of popular culture.
Covers the following key terms: [Cultural] Hybridisation, Taboidisation, Media conglomerates, Infotainment, Hyper-realitY, simulacra
**Key sociologists covered:
Compaine, Thussu, Baudrillard, Garrod, Tomlinson, Strinati
**Key you SHOULD ALREADY KNOW that you might include in your table:
Tabloidisation- Cultural imperialism – Media imperialism Infotainment – Transnation corporation -Media conglomerates - Secondary socialisation Postmodernism – Concentration of ownership Media imperialism Cultural imperialism – Media products – Media institutions – Media technology **
** Activities require pages from the AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend**
Resources can be found at the end of the PPT
Teaching to all activities includes
ANSWERS TO ALL ACTIVITIES INCLUDED
Bundle

AQA GCSE Sociology Educational policy before 1988, after 1988 (marketisation) and that tackle inequality
L1 -AQA GCSE Sociology Education - Policies tackling inequality:
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand to what extent might education reforms have tackled educational inequality (e.g the main education policies and reforms that have had an impact on the education system, using examples - how education policies or reforms have tackled inequality in education).
Covers educational policies that tackle class, gender and ethnic differences in educational achievement and gender differences in subject choice.
Covers the following policies: Marketisation policies and social inclusion
Key terms students SHOULD know that link:
Educational policies/ reforms, Marketisation, Open enrolment, Academies, Formula funding, League tables, Ofsted reports, Tripartite system, Class differences in educational achievement, Gender differences in educational achievement, Ethnic differences in educational achievement, Gender differences in subject choice, External vs internal factors, Cultural vs Material factors, Material deprivation, Cultural deprivation, Speech codes, Gender roles, socialisation, Gendered subject images, Gendered career opportunities
ANSWERS TO MOST ACTIVITIES INCLUDED
RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF PPT
L2 - AQA GCSE Sociology Education - Education policies from 1988 (marketisation):
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand what impact might marketisation have had on British education system ( define marketisation, the impact of the 1988 Education Reform act on the British education system and the policies it brought about).
Includes ‘teaching to all’ pedagogical technique
Cover the following key terms:
Marketisation
Marketisation of education
Market forces (extension)
Privatisation (of education)
Covers the following reforms:
1988 Education Reform Act
Covers the following policies:
League tables
Ofsted reports
Academies
Free schools
Specialist schools
Open enrolment
Business sponsorship
ANSWERS TO ALL MAIN ACTIVITIES INCLUDED .
Key terms students should know that link: Education reform/ policy Labelling, Streaming, Setting, Banding, Academies, Free-schools, Differences in achievement (class, gender, ethnicity), Internal vs External factors, Local Education Authority (LEA), Social processes
RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF PPT
L3 - AQA GCSE Sociology Education - Education policy before 1988:
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand Education reforms before 1988 (e.g. The main educational policies before 1988, the impact of educational policies before 1988, how to apply sociological perspectives to educational policies and evaluate them).
Cover the following key terms:
Education policy
Education reform
The tripartite system
Secondary modern
Comprehensive system
Secondary moderns
State-run schools
Eleven- plus exam
Compulsory [state] education
Selective schools
ANSWERS TO ALL MAIN ACTIVITIES INCLUDED
Key terms students should know:
Grammar vs comprehensive schools , Academies/ free schools,
State-run education/ schools, Working-class subculture, Culture Norms, values, setting Mixed-ability classes, Banding Local Education Authority (LEA), Independent/ private schools
RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF PPT

AQA A-level Sociology -Developing AO3 skills - Explicit criticisms and explained analysis
Detailed student led lesson on what is meant by explicit (vs juxtaposed) criticisms and explained analysis and how to demonstrate these high level AO3 skills needed for A*-A answers for AQA exams. The lesson is adapted to stretch and challenge the most able whilst scaffolding to allow pupils who need support the opportunity to access higher level thinking.
INCLUDES:
SIX MODEL PARAGRAPHS- from theory and methods (postmodernism and Marxism), methods in context, crime (punishment), media and family. THOSE WHO DO NOT TEACH FAMILY OR MEDIA will have 4 model paragraphs in total)
ANSWERS FOR ACTIVITIES
AfL
A 7 page information sheet on explicit criticisms and explained analysis from the skills booklets (can be bought separately - includes other guidance and skills for preparing for exams) that explain the two different skills, success criteria with sentence starters of how to demonstrate each and provides brief examples (of explicit criticisms, juxtaposed criticisms, explained analysis, analysis that is limited to an isolated statement). Also includes analysis guidance and sentence starters for research methods paragraphs and guidance of how students might go even further by explaining their criticisms.
**NOTE **- Activity on slide 8 is challenging. If students struggle too much with it, show answers on slide 9 and move onto the progress check activity that will make clearer how explicit criticisms are written.
**NOTE ** -The focus of evaluations are criticisms for this lesson
RESOURCES CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF THE PPT (AND INFO SHEET FROM SKILLS BOOKLET IS ATTACHED AS A WORD DOC)
Bundle

KEY TERMS SHEET - AQA A-level Sociology Education: Topics 1-5
Alphabetical key term sheet for AQA A-level Sociology Education Topics 1-5. Contains the main key terms used in Topic 1-6 of the education unit for AQA A-level Sociology:
-Topic 1 - Class differences in achievement (external factors)
-Topic 2 - Class differences in achievement (internal factors)
-Topic 3 - Ethnic differences in achievement
-Topic 4 - Gender differences in achievement
-Topic 5 - Role of education
-Topic 6 - Education policy
*** Includes scaffolding, e.g. some sentence starters (to model to students how to incorporate key sociologists into their definitions) and prompts to help students remember how key term links to the topic. **
*** Includes a section with key terms that students should know from previous learning (for topic 3 sheet ethnic differences - this would be terms that link to key terms covered in class differences in achievement, e.g. labelling, pupil identities, material deprivation, speech codes etc) that link to this topic. **
Good form of revision for students and can be used as a revision resource to develop AO1 once filled out.
**BASED ON CONTENT textbook - AQA A Level Sociology Book One Including AS Level: Book one 3rd Revised edition by Rob Webb, Hal Westergaard, Keith Trobe, Annie Townend ’ textbook
Bundle

A-LEVEL SOCIOLOGY INTRO LESSONS - nature vs nurture, functionalism, marxism, feminism, QUIZ & ANSWERS
Detailed and differentiated (up and down) student-led lessons that help students to develop their knowledge and understanding from previous lesson(s). L2 uses page 8 from AQA Book 1 by townsend but CAN BE USED FOR ANY SPEC using resources within lesson (see below). Comes with key term sheet for the lesson.
1. Introduction to Sociology - provides an overview of Sociology course (spec to AQA A-level but can easily be edited to suit ANY SPEC and GCSE) and the sociological imagination.
2. How do sociologists explain behaviour? -Nature vs Nurture lesson -explores the nature vs debate, norms, values, socialisation (primary/secondary) and social control as an introduction to Sociology. Uses page 8 of the AQA A-level Book 1 by Townsend to introduces students to the nature vs nurture debate but this can be replaced and the rest of the lesson can still be used.
3. Introduction to functionalism -explores value consensus, social order, biological/ organic analogy, structuralism, consensus theories to introduce students to the key functionalist views and ideas.
4. Introduction to Marxism -explores capitalism, ownership, interests, structuralism, conflict theories, exploitation as a way to introduce students to the main Marxist views and ideas.
5. Introduction to feminism - explores sex, gender, gender roles, patriarchy, socialisation, gender inequality as a way to introduce students to the main feminist views of society and ideas.
6. Quiz lesson - small revision activity
25 min quiz (on nature vs nurture, key functionalist, Marxist, feminist’s ideas and terminology) —LESSONS CAN BE FOUND ON MAIN PAGE. Includes:
answers/ mark-scheme
scaffolding for students to peer assess (but quiz can also be marked by teacher)
Made for AQA but can be used for ANY SPEC
Can be differentiated down for GCSE, but I recommend purchasing the GCSE Intro lessons bundle which have alread been edited to meet the needs of KS4 students.

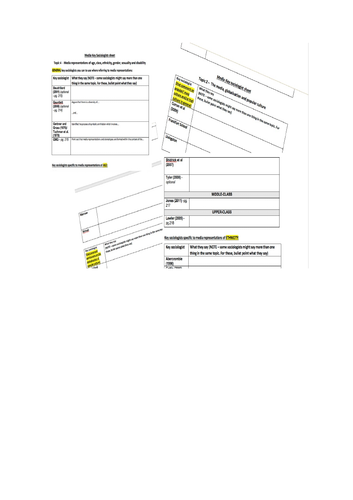
KEY SOCIOLOGISTS SHEETS AQA A-level Sociology Media: Topics 1-4
Detailed and scaffolded (e.g. SOME sentence starters/ prompts, separating sociologists who comment on different aspects of each topic, SOME page numbers for sociologists that might be more difficult to find, etc.) key sociologists sheets that requires students to write done what key sociologists from topics 1-4 say.
Contains the main key sociologists in Topics 1-4 of the media unit for AQA A-level Sociology:
Topic 1 - Ownership and control of the media output
Topic 2 - The media, globalisation and popular culture
Topic 3 -the processes of selection and presentation of the content of the news
Topic 4 -media representations of age, social class, ethnicity, gender, sexuality and disability.
**REQUIRES textbook - 'SOCIOLOGY For AQA Volume 2 by Browne, Blundell & Law **

KEY TERM SHEETS AQA A-level Sociology Media: Topic 1-4
Detailed and scaffolded key term sheet that requires students to fill out the definitions themselves. (e.g. SOME sentence starters/ prompts, separating key terms in term of social groups for topic 4, identifiy the key terms that relate to media stereotypes for topic 4, etc.)
Contains the main key terms used in Topic 1-4 of the media unit for AQA A-level Sociology:
Topic 1 - Ownership and control of the media output
Topic 2 - The media, globalisation and popular culture
Topic 3 -the processes of selection and presentation of the content of the news
Topic 4 -media representations of age, social class, ethnicity, gender, sexuality and disability.
The bottom of the sheet has a section dedicated to the key terms learnt in previous units and topics that might link to this topic. Good form of revision for the students and allows for a spiral curriculum.
**REQUIRES textbook - 'SOCIOLOGY For AQA Volume 2 by Browne, Blundell & Law **
Bundle

AQA GCSE Sociology - Research Methods: Intro lessons
L1 - How do sociologisrs collect their data?
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand how sociologist collect data for sociological research (e.g. difference between primary and secondary methods, quantitative and qualitative data.
Covers the following key terms: research methods, sociological research, data, research process, Primary methods vs Secondary Methods, qualitative vs quantitative data, closed vs open questions, validity and reliability.
L2 - How do sociologists begin their research?
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand how sociologists begin their research (e.g. what is meant by research design, hypothesis, research questions, aims , pilot study, the first two stages of research process and assessing its usefulness.
Covers the following key terms: Research design, Hypothesis, Research questions, Research aims and Pilot study
Makes links to key terms that students should have already covered the following key terms: Respondent, Response rate, Participants, Sociological research, Research process and Data
Answers to all activities included
L3 - How might sociologists collect their sample?
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand how might sociologist select their sample for sociological research (e.g. the sampling method, consequences sampling methods may have on social research, the different types of sampling methods and how they are used.
Covers the following key terms: Target population, Sample, Sampling frame, Probability (or random sampling) vs Non-probability sampling, Simple random sampling, Systematic random sampling, Stratified random sampling, Snowball sampling, Quota sampling, Representative sample vs unrepresentative sample, Generalise; Generalisability; To make generalisations, Opportunity sampling extension), Cluster sampling (extension) and Positivists vs interpretvivists (extension)
Answers to most activities are included
L4 - What PET issues might sociologists need to consider when conducting research?
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand what are PET issues that sociologists consider when designing and conducting research (e.g. define and identify possible practical, ethical and theoretical (PET) advantages and disadvantages of social research and explaining PET’s differences
Covers the following key terms: Practical issue, Ethical issues, Theoretical issues,Anonymity, Confidentiality , Informed consent, Covert research (extension), Pseudonym (extension), Mixed method (extension) Findings (of research) (extension).
Key bodies, laws and theories we will cover: British Sociological Association, Data Protection Act 1998, Positivism, Interpretivism
Answers to most main activities are included
RESOURCES FOR ALL LESSONS CAN BE FOUND AT THE END OF THE PPT IF NOT INCLUDED AS A SEPARATE DOCUMENT.
Bundle

WRITING FRAMES (for improving essay writing) - AQA A-level Sociology: Families – Topics 2-6 20 marker
Detailed writing frame that scaffolds (from introduction to conclusion) a full answer for a 20 marker on:
Topic 2 - Childhood - evaluate explanations of childhod
Topic 3 - Theories of the family - whether the family is beneficial
Topic 4 - Demography - position of the old
Topic 5 - Changing family patterns -divorce
Topic 6 - Family diversity - whether individual choice in personal relationships has made family life less important
*** Based on AQA specification**
*** Supports students with planning the 20 marker (using the item) - using planning success criteria.
**
*** Outlines the success criteria and provides sentence starters for the full essay (intro, main body and conclusion). Success criteria used for paragraphs in main body of essay is PEELE/A**
*** Outlines the key terms, sociologists, theories that can be used when answering the question.**
*** Supports students who need support and guidance with writing essays whilst providing students who are already good at writing essays opportunities to further improve their essay skills. **

AQA A-level Sociology: Media - The Social Construction of the News
Detailed lesson with lots of scaffolding based on adaptive teaching that help students understand ‘Media - The Social Construction of the News’
Covers the following key terms: The social construction of the news, Agenda-setting, Gate-keeping, Norm-setting, Globalisation, Citizen journalism, News values, Hierarchy of credibility, Primary definers, Churnalism
Covers the following sociologists: Davies
GMG, Curran and Seaton, Bagdikan, Cohen/ Mccomb, Gramsci, Philo, Galtung and Ruge, Becker, Hall
Lesson teaches the whole of topic 3 of media.
ANSWERS TO THE MAIN ACTIVITIES INCLUDED
The starter activities requires you to give students examples of news stories but can be replaced with your own starter.
Includes a teaching to all activity
Includes a discussion activity with scaffolding and prompts.
Includes a 10 marker with guidance to help students with selecting points from the item as well as possible points from the item and detailed scaffolding to help students answer the question.
Bundle

GCSE AQA Sociology INTRO LESSONS & QUIZ
Detailed and differentiated (up and down) student-led lessons that help students to develop their knowledge and understanding from previous lesson(s). Includes 6 lessons (the last being a quiz lesson) and a key term sheet that covers the key terms in these lessons:
**L1 – Intro to GCSE AQA Sociology: **
an overview of the course, exam and curriculum
An activity on how to create and maintain a safe space for discussions
suggested revision websites and youtube channels that students can use to develop their knowledge and understanding of key ideas and concepts.
activities to introduce students to Sociology and sociological thinking/ inquiry.
Expectations
L2 – How might sociologists explain behavior?
Explores, norms, values, socialisation (primary/secondary) and social control, agencies and agents of socialisation and social control as an introduction to Sociology.
Also looks at the importance of primary socialisation and the consequences of it inadequately performed.
3 marker with a success criteria and student friendly mark-scheme
L3 – Intro to functionalism
Explores value consensus, social order, biological/ organic analogy, structuralism, consensus theories and social cohesion as way of introducing students to the key main functionalist views and ideas.
3 marker with a success criteria and student friendly mark-scheme
L4 – Intro to Marxism
explores capitalism, profit, social class, ownership, interests, structuralism, conflict theories, exploitation, false consciousness and social relations of production as a way to introduce students to the main Marxist views and ideas.
**L5 – Intro to feminism **
explores sex, gender, gender roles, patriarchy, gender inequality as a way to introduce students to the main feminist views of society and ideas.
3 marker with a success criteria and student friendly mark-scheme
**L6 – Quiz lesson **
small revision activity –that looks at the similarities and differences between functionalism, Marxism and feminism
25 min quiz (on basic sociological concepts, key functionalist, Marxist, feminist’s ideas and terminology)
answers/ mark-scheme for quiz
scaffolding for students to peer assess (but quiz can also be marked by teacher)
SAME as A-level intro quiz but excludes questions on the nature – nurture debate.
Made to meet the needs of the AQA SPEC but can be edited to meet the needs of any spec, e.g. key terms in L2-5 meet the AQA spec
Answers included for main activities and quiz
**L2,3 & 5 include 3 marker, success criteria to answer this and student-friendly mark-scheme for self and/ or peer-assessment. **