406Uploads
122k+Views
41k+Downloads
All resources

100 Questions on Pythagoras Answers Provided Mathematics Geometry KS2
**100 questions on Pythagorus.
IF YOU LIKE THUS I HAVE A REALLY BIG FILE IN THE SHOP
15000 Pythagoras Questions Pythagorean Theorem Maths KS2 KS3
Answer sheets provided.
A good little exercise for your students. Using a calculator this should keep them busy and help you teach Pythagoras’ theorem.**

Division Worksheets for Primary School Children Maths Mathematics Homework
100 worksheets with answers sheets provided.
100 sheets of division questions.
Some have 10 questions, some 20, some 50.
A useful time filler or use them for a quick homework or start of day activity.

Rounding Numbers 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics
100worksheets on rounding numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
Answer sheets provided.
20 questions per sheet.
A good time filler or easy homework.

1000 Questions Addition Mathematics KS1 Adding Up
1000 questions with answers.
Pupils have to add up either 3 or 4 numbers under 10.

Teaching Resources Worksheets Rounding Numbers to the Nearest Ten
100 worksheets with answers provided.
20 questions per sheet.
Pupils have to round numbers to the nearest 10.
I have included a few that you have to round to the nearest 100.
A good time filling exercise or a nice easy homework to reinforce what has been taught in the classroom.

Teaching Resources worksheets Area Perimeter Mathematics
I have designed 100 worksheets on calculating area and perimeter for primary school children. There is a wide variety of difficulty. Some sheets just require area, some perimeter, some a mixture of the two. In some rectangles are used, others have triangles. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

Teaching Resources worksheets Shapes Maths Triangles Octagons
I have designed 100 worksheets on shapes for primary school children. They have to write the name of the shape on the sheet. An answer sheet is in the picture. A great reinforcement exercise or you can give a sheet to a bright pupil to keep them occupied. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

Number Order 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics KS1
100 worksheets with answers on Number Order.
Pupils have to put the numbers in the correct order.
There are at least 10 sets of numbers per sheet.
A nice little time filler.

1000 Questions Advanced Division with Remainders KS2 Mathematics Calculator Use
Please check out my bundles which provide great value.
1000 questions on division.
Great for calculator use.
Answers provided.
Pupils divide a three digit number by a 2 digit one.
There are remainders in these questions.

Year 4 Planning Autumn Term Literacy Numeracy KS2
Important! If you’d like to buy the whole year’s planning (Autumn, Spring and Summer) you’d be better off buying my bundle.
Planning for the Autumn term for year 4.
You get 160 mb of material so good value imo.
I taught mainly in Catholic schools so has a Catholic bent. But as we live in a multicultural society, this should be no problem.
You get planning for:
creative curriculum
Literacy
Numeracy
P.E. (some)
Science (some)
R.E. (Advent, Abraham, Judaism etc)
Loads of great lessons to ease your Sunday afternoons. Just cut and paste into your school template.

Year 6 Cross Curricular Literacy History World War 2 English
To plan and write a recount text, using appropriate form, features and language.
To understand the value of the ‘home front’ during WWII.
To discuss and write about the life of children during WWII.
Understand the role of the ‘home front’ and the impact of rationing. Explain that this week’s literacy lessons are linked closely to our current history topic. We are moving on to a geography topic after half term.
Recap what we have learned recently in history lessons.
What were the main causes for WWII? Dates? Political leaders? Axis? Allies? How was the war fought? What was the Blitz? What sort of places did the Germans target? Why?
Last lesson I asked you to discuss the posters issued by the British Government. What did you find out?
Show the quote: “I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat. You ask, What is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory.” TTYP – who do you think said this?
Come back together and establish that it was part of a speech by Winston Churchill when he became PM in May 1940. At this time, victory seemed a long way off.
Show map of the world. Explain that, at the time of this speech, the German forces had already conquered Norway and Denmark. Now, they were sweeping through Belgium and the Netherlands. By 20 May, they reached the English Channel. More than 500 000 British and French troops were trapped on the French coast at Dunkirk. Hundreds of boats, big and small, repeatedly sailed from Britain and brought nearly 340 000 safely back to England. The German advance went on. On 17th June France surrendered. Most of North-West Europe was now in Hitler’s hands. The German leader began to plan the invasion of Britain, only 34 KM away.
Britain now stood alone with scarcely anyone to help. The USA had not yet entered the war. The countries of the British Empire such as Australia and Canada were too far away. Churchill encouraged the people of Britain with defiant speeches. “We shall go on to the end,” he said, “we shall never surrender.”
What was providing a natural barrier for the British against the Germans? The sea. However, it also caused problems. Britain’s farmers could not grow enough food to feed the population. Large amounts had to be brought in from home by ships. Merchant or goods ships were slow and lightly armed and so were easy targets for German U-boats and bomber aircraft. Between March and May 1941 over 320 merchant ships bound for Britain were sunk. Food such as flour, meat and sugar were in short supply.

Teaching Resources 100 worksheets Time Passages KS2 Maths Mathematics
I have designed 100 worksheets on time passages for primary school children. They have to draw the time hands on the clocks on the sheets. What time will it be? - There are two clocks . The first clock shows a time, the second clock is blank. A question like "What time will it be in 2 hr and 20 min?" appears below the clocks. The student draws the answer on the second clock. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

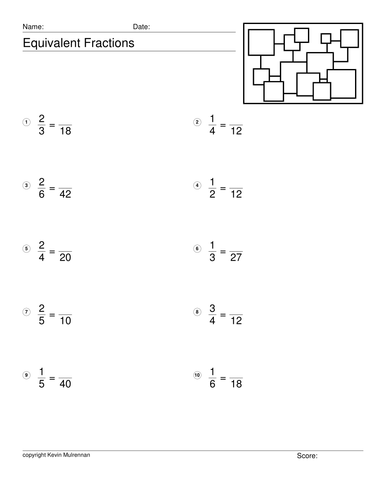
Equivalent Fractions 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths
100 worksheets with answers.
20 per sheet.
Pupils have to write the equivalent fractions.

Year 5 to Year 6 Transition Materials Primary School Ideas Last Day
Ideas for that tricky day.
Word doucument with loads of ideas.
Lovely powerpoint to guide you into year 6.
Plus some other bits and bobs such as French lessons etc
sample:
Transition day – Year 6
9am – 9.30am: Whole school assembly.
9.30am – 10.45am: Circle time. Worries, concerns, hopes and dreams.
Gather children’s thoughts on moving to year 6. Discuss how they are feeling. Discuss with children it is natural to be feeling apprehensive. Send children to table groups to complete table of things in year 6 they are looking forward to and things they are worried about. Discuss as a class and complete class table to refer back to after 1st week.
Go through our expectations of them for year 6 and the rewards and sanctions they will receive. Discuss. Also mention Sats and Confirmation.
Discuss their personal targets for year and ask them to think of one thing they really want to improve on and aim for in year 6. Reinforce idea of a fresh start.
Discuss how we are all going to turn over a new leaf and send ch. to places to do so and write personal target for year on a leaf template. Place anonymously in time capsule. Discuss what one is and how they work. Discuss we will not open until end of year 6.
Talk about Year 6. TTYP what are your main thoughts? Come back together and discuss SATs, Confirmation, Easter fair and residential.
Star activity.
11am – 11.30am: Class rules
11.30am – 12pm: Expectations, rewards & sanctions.
Spare time = ‘Billionaire Boy’.

Charlie and the Chocolate Factory Planning Roald Dahl Literacy
Three weeks great planning. Don’t expect lessons on Charlie. It’s report writing in English using Charlie with powerpoints etc
Great powerpoints
Zip file has more. I’ve put some example stuff on to give you a flavour.
Introduce the new unit and read the writing outcome with the children.
Complete a skills audit verbally. TTYP – what skills do you already have that will help you to achieve the outcome? What skills do you think you will need to revise? Are there any completely new skills you will need?
Introduce the focus text. We know a lot about Roald Dahl from our biography unit. Has anyone ever read ‘Charlie…’?
Seen the films?
Explain that we need to know the story line and the characters, so we are going to spend today’s lesson using the 2005 film as a visual text. The rest of the week will be spent comparing the visual text to the written text and completing various activities and pieces of writing.
Become familiar with the story by using a visual text.
Use both visual and written texts to analyse character and setting descriptions. Finish any of the DVD which we didn’t finish yesterday.
Use the written text to read the character descriptions of Charlie, his parents, grandparents and the four other winners of golden tickets.
Activity One
Come back together, discuss and put information on working wall.
Repeat with setting descriptions.
Look at a still of Charlie’s house from the film and read the setting description for it.
Look at the still from the ‘meadow’ in the chocolate factory and read the description on pages 87-90.
Activity Two
Revise features of journalistic writing.
Compose a newspaper article using the correct form and language.
Working in pairs, children to sketch a story mountain onto a whiteboard. Children to then summarise ‘Charlie…’ using one or two sentences for each section of the mountain.
Come back together and discuss.
Read chapter five of the text. What main event is happening? The announcement of the golden ticket competition.
Watch 14:28 – 15:44 – how does the film embellish the details given in the book?
Explain today’s task, you are a senior news reporter for the ‘International Herald’ a newspaper which is published in many different countries, many different languages all over the world. Your editor has asked you to write a newspaper article about this event. Your report will be published the day after Willy Wonka’s signs went up. You will be reporting on the competition, the prizes and the mania sweeping the world.
TTYP – what are main features of a journalistic piece of writing?
Come back together and list for the working wall:
Headline, paragraphs, subheadings, quotations, orientation, 5 ws, past tense, direct, formal, balanced etc.
Brainstorm some headlines for our article.
List the 5 Ws on the working wall.
Give each child a checklist and an inverted pyramid.

Roald Dahl Charlie and the Chocolate Factory Write An Advert Persuasive
Some nice little lessons on the Road Dahl classic plus some great powerpoints.
sample :
Support for spelling
Count the syllables. CT will remind children what a syllable is and provide a list of words on the board. Children will count how many syllables there are and record on their whiteboards. CT will provide children with three types of chocolate (number 1, 2 and 3) and a blind fold. In pairs one child will be blindfolded and the other will pass the chocolate for the children to try.
Children will watch a clip of Willy Wonka from the film ‘Charlie and the Chocolate factory” CT will review the features of a formal letter:
Address in top write hand corner
Date (on left)
Greet using the persons formal title
Introduce yourself
State the reason you are writing
Lots of connectives
Persuasive techniques
Close the letter with ‘Yours Sincerely’
Formal language
Children will write a business letter to Mr Wonka persuading him to make their chocolate bar.
Sentence types
Children will work in pairs; one as an instructor and one as the listener.
instruct listener to walk to cone on playground.
Imperative verbs – CT will explain that children will have just used lots of imperative verbs which are ‘bossy verbs’.
CT will display sentences on the board and children will need to change them into an imperative sentence.
CT will display a set of instructions and children will suggest features including:
• A goal
• List of equipment
• Time connectives
• Present tense
• Imperative verbs
• Numbered steps
• Short, clear and direct sentences
• Picture of finished article
Children will then create a set of instructions for making the rocky road bites,

Charlie Small Gorilla City Literacy Planning Year 5
Some great planning for Charlie Small Gorilla City.
You get microsoft word documents.
Plus Notebook files if you can play those.
Sample :
LO:
I can investigate a character and list key questions.
Prior to lesson, create a display area in the class – or another area of the school – consisting of a copy of Charlie Small’s journal (see GORILLA CITY cover), photographs of settings and animals from the text, a map (copied from the book) and his rucksack. Also include a fact file on any 2 of the creatures mentioned in the text ~ e.g. the hyena or gorilla. The contents of his rucksack may be listed on cards; or some of the items actually on display.
TA or other adult in school to enquire about these items and chn asked to ‘investigate.’
Teacher/TA to read note from Charlie – see inside book cover.
In small groups, chn list questions they would like to ask the author – Charlie Small – and discuss what they would like to learn further about his expedition(s).
Class share ideas.
LO:
I can identify author style and purpose.
I can choose effective vocabulary to describe a character.
Explore the cover design and shared reading of the Publisher’s note, plus the note from Charlie.
Discuss the impact of the illustrations, writing style, the crinkled and stained journal entry by Charlie and use of words in capitals for emphasis.
With response partner, chn talk, then make notes on what they have learnt about Charlie from his opening note. * Have an outline of a silhouette on the wall to represent
Charlie.
Teacher or TA read pages 2-6.
In pairs, chn list some key words to describe Charlie’s personality, behaviour, likes and dislikes, based on what they have learnt so far. Ask them to select their most powerful adjective and write it on a Post-It note. Add these to the role on wall.
Extension: discuss the use and purpose of each item in the rucksack.

Numeracy Maths Year 4 Planning Angles Protractors Perimeter Area
Some nice planning and worksheets for year 4.
Nearly 3 mb of stuff.
sample plannimng :
Draw rectangles and measure and calculate their perimeters; find the area of rectilinear shapes drawn on a square grid by counting square Perimeter, names of 2d shapes
Addition
Total
Mentally adding 4 numbers (single and two digit) WALT – draw find the perimeter and area of a rectangle
WILF – accurate measurements
Knowledge of what perimeter is
Knowing what area is and how to calculate
Good mental methods
Children will know how to find the perimeter of a rectangle. Pupils will also need to be reminded of units of measure that we may need to use – mm/cm.
Target maths P82 In real life situations, when would you need to know the perimeter of something? What unit of measurement might we need for the suggested things?

1000 Questions Advanced Division No Reminders KS2 Mathematics Calculator Use
Please check out my bundles which provide great value.
1000 questions on division. There are no remainders
Great for calculator use.
Answers provided.
Pupils divide a three digit number by a 2 digit one.

1000 Questions Multiplication Mathematics KS2 Calculator Use
Please check out my bundles which provide great value.
1000 questions on multiplication.
Great for calculator use.
Answers provided.
Pupils multiply a 2 digit number by a 2 digit one.