






















































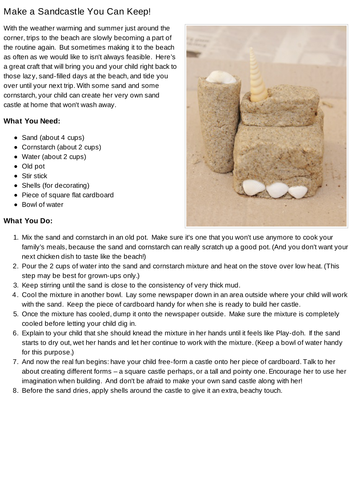
























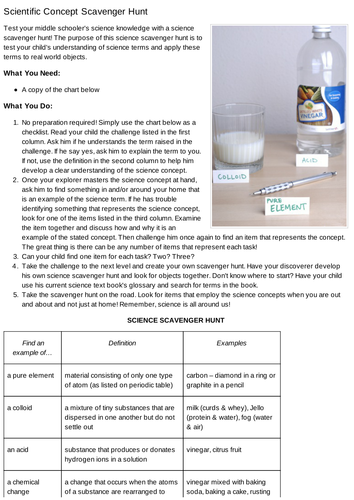




















Active Learning means students engage with the material, participate in the class, and collaborate with each other. Don’t expect your students simply to listen and memorize; instead, have them help demonstrate a process, analyze an argument, or apply a concept to a real-world situation.
Students learn through their participation in the attainment of knowledge by gathering information and processing it by solving problems and articulating what they have discovered. Each activity below provides students with opportunities to deepen their learning by applying concepts and articulating new knowledge and many of these activities also provide the instructor feedback about the students’ learning.
Whether you’re facing a lecture hall filled with 300 students or a seminar table with 15 students, one of your primary goals for the class should be to actively engage students with the material. Students learn more when they participate in the process of learning, whether it’s through discussion, practice, review, or application (Grunert, 1997). This is in stark contrast to traditional styles of teaching, where students are expected to sit for hours, listening and, theoretically, absorbing information presented by the instructor.
Incorporate active learning strategies into every component of your course design. For example, encouraging short partner discussions during lectures (i.e., think-pair-share), adding problem- or case-based research projects to the curriculum, and incorporating time for small-group critical analysis exercises during seminars are all great ways to actively engage students in learning.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.