

LESSON OBJECTIVE: Investigate substitution and elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes and describe some of their uses and pollution.
In this lesson we investigate the homologous series of halogenoalkanes but introducing key reactions they undergo (substitution and elimination), describe their uses, how they act as pollutants and the detrimental effect they have had on the ozone layer. This is lesson eight in our organic chemistry series of Unit 16: Halogen derivatives (from the Cambridge International AS Chemistry Curriculum (9701) 2019-2021 curriculum).
Learning Outcomes:
(taken from the Cambridge International AS and A Level Chemistry (9701) 2019-2021 curriculum)
16.1 Halogenoalkanes
a) recall the chemistry of halogenoalkanes as exemplified by:
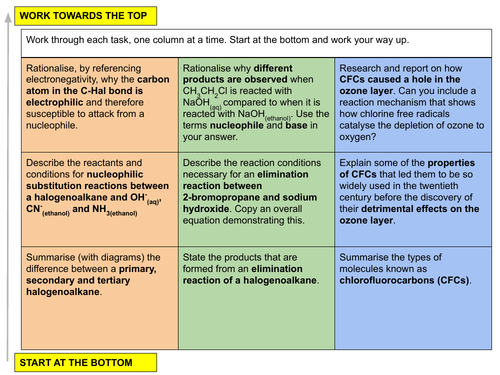
(i) the following nucleophilic substitution reactions of bromoethane: hydrolysis, formation of nitriles, formation of primary amines by reaction with ammonia
(ii) the elimination of hydrogen bromide from 2-bromopropane
16.2 Relative strength of the C-Hal bond
b) explain the uses of fluoroalkanes and fluorohalogenoalkanes in terms of their relative chemical inertness
c) recognise the concern about the effect of chlorofluoroalkanes on the ozone layer
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have downloaded this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.