KS5 Acids and Bases, Redox and Organic Chemistry Schemes of Work
These 16 PowerPoints were planned as part of the IB scheme of work on Acids and Bases, Redox Chemistry and Organic Chemistry, and cover the necessary content for both the Standard and Higher Level topics. They would also be suitable for other post-16 courses.
Included are fully completed PowerPoints, student versions of the PowerPoints with sections to complete independently and some exam style questions.
Topics included are:
\- What are acids and bases?
\- Bronsted Lowry acids and bases (and conjugate acids and bases)
\- Amphiprotic and amphoteric substances
\- Lewis acids and bases
\- Reactions of acids with metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates, bases and alkalis
\- Making salts
\- What is pH and how to calculate the pH of both acids and bases
\- Using the dissociation constant of water to calculate pH
\- Acid deposition - how it occurs and how it can be treated
\- Calculations involving Ka, pKa, Kb, pKb, pH and pOH
\- Using the relationships Kw = Ka x Kb and pKa + pKb = pKw
\- Titration curves for titrations involving any combination of strong and weak acids and bases
\- Indicators - how to select a suitable indicator for a titration
\- How to calculate the pH of salt solutions
\- Buffers - what are they, how are they made and how do they work (including calculations)
Reduction and Oxidation
Oxidation states and how to determine them
Naming compounds using oxidation states
Oxidising and reducing agents
Half equations in molten substances
Half equations in acidic solutions
The activity series
Redox titrations
Winkler method to determine biochemical oxygen demand
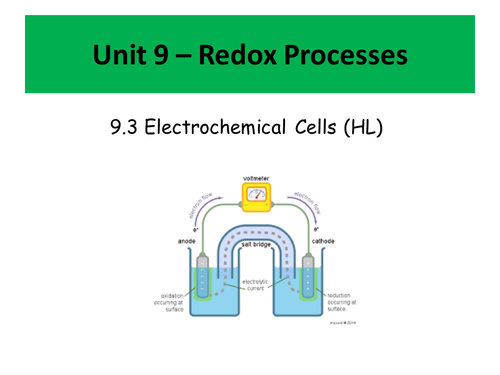
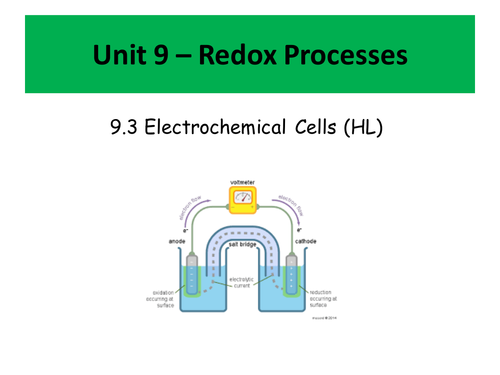
Voltaic Cells
Electrolytic Cells
Cell potentials
The standard hydrogen electrode
Ecell and spontaneity
Working out cell potentials
Polarity and direction of electron flow
The electrochemical series
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions
The effect of the nature of electrodes on the products
Electroplating
Electrolysis of water
Quantitative electrolysis
\- Different kinds of formula e.g. molecular, empirical
\- Alkanes
\- Alkenes
\- Compounds involving a benzene ring
\- Homologous Series
\- IUPAC nomenclature
\- Naming halogenoalkanes
\- Naming alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids
\- Esters
\- Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, halogenoalkanes and amines
\- Structural Isomerism
\- Functional Group Isomerism
\- Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
\- Combustion of alkanes
\- Reaction of alkanes with halogens
\- Reactions of alkenes
\- Addition polymerisation
\- Oxidation of alcohols
\- Nucleophilic Substitution mechanisms of primary, tertiary and secondary halogenoalkanes
\- Factors affecting the rate of nucleophilic substitution
\- Electrophilic Addition mechanisms
\- Markovnikov´s Rule
\- Electrophilic subtitution mechanisms
\- Reduction Reactions
\- Reaction pathways and synthetic routes
\- Cis-trans isomerism
\- Conformational isomerism
\- Optical isomerism
\- Optical Isomers and Plane-polarised light
\- Racemic mixtures
\- Diastereoisomers