497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
Physics

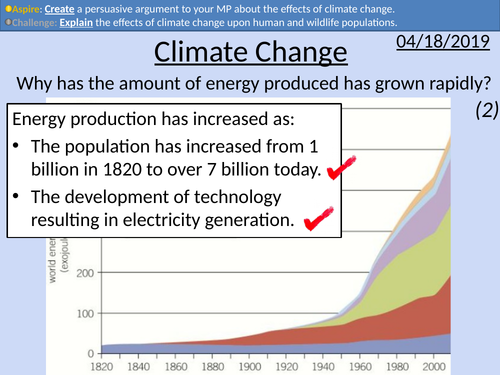
GCSE Physics: Climate Change
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Types of greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapour.
• Greenhouse effect with activity
• Class discussion on news report of effects of climate change
• Extended writing task with student friendly mark scheme and scaffolding
• Data analysis task
• Explanation of data collection of CO2 levels

GCSE Physics: Constructing Circuits
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Constructing Series Circuit
• Constructing Parallel Circuits
• Analysing results for Potential Difference
• Analysing results for Current
• Clear resource list, diagrams and photos to aid teaching.

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.

OCR Applied Science: 6.3 Electrical Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Current as flow of charge in a conductor.
Use the equation: I = ΔQ ÷ Δt
Ohm’s law illustrates the relationship of V ∝ I
Use the equation: potential difference (V) = current (A) × resistance
Use the equations for adding resistors in series and parallel
Compare electromotive force and potential difference
Use the equation: charge © = current (A) × time (s)
Use and recognise the equation for mean drift velocity
Use the equation: energy transferred (work done) (J) = charge © × potential difference (V)
Use the equation: energy transferred (J, kWh) = power (W, kW) × time (s, h)
Use the equation: power (W) = energy (J) ÷ time (s)

GCSE Physics: Floating and Sinking
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.5 Floating and Sinking
Content Covered:
Balanced Forces
Rearranging equations
Mass and weight
Gravitational field strength
Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Difference in pressure causing up thrust
Combining two equations
Worked solutions
Exam Style Questions
Problems with answers
Demonstration

GCSE Physics: Wave Velocity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.2 Wave Velocity.
Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Simple experiment for the speed of sound
Speed of sound experiment with microphones and oscilloscope.
Ripple tank demonstration and explanation
The speed equation
Measuring distance and time
Echoes
Definition of mechanical waves
Water waves as a transverse waves
Converting from cm, mm, and km into m.
Definition and equation for frequency.
Wave speed equation
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Circular Motion
OCR A level Physics: Thermal Physics apart of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.2 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 26 Nuclear Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
26.2 Binding Energy
26.3 Nuclear Fission
26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Materials
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Materials.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Hooke’s Law to Young Modulus.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Work, Energy and Power
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from conservation of energy to derivations for kinetic energy.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current
OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Fundamental charge and relative charge
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Ideal Gas
OCR A level Physics: Ideal Gas is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Quantum Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Quantum Physics.
All presentations are full lesson PowerPoints with worked examples and homeworks with complete worked answers.
The Photon Model
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Producing photoelectrons
Kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Linking frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency and energy.
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.
Wave Particle Duality
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.2 Powering Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.3 Wave Interactions
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction
Convex and Concaves lenses
Eyes and corrective lenses
Refraction and wavelength
Focal points for lenses
Determining the type of images produced through a lens
Names of colours for the visible spectrum
Coloured filters
Coloured objects acting as a coloured filters
White light and refracting prism
Refraction and wavelength
Specular reflection
Diffuse scattering
Scattering - Why the sky is blue and milk is white.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.1 Physics on the move
All resources for P8.1 Physics on the move GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion
OCR A level Physics: Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Particle Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 24 Particle Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
24.1 Alpha-particle scattering experiment
24.2 The Nucleus
24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
24.4 Quarks
24.5 Beta decay
Developments of scientific models
Thompson’s plum-pudding model
Rutherford’s nuclear (planetary) model
Rutherford’s experiment, observations, and conclusions
Using Coulomb’s law to find the minimum distance between particles
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.
The Standard Model of particle physics
Quarks, anti-quarks and their charges
Baryons and mesons
Properties of neutrinos
Nuclear notation
Nuclear decay equations
Beta-plus and beta-minus decays
Quark transformation
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Laws of Motion
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Materials.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Newton’s laws to conservation of momentum in two dimensions.