497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
All resources

A level Chemistry: Further Synthetic Routes
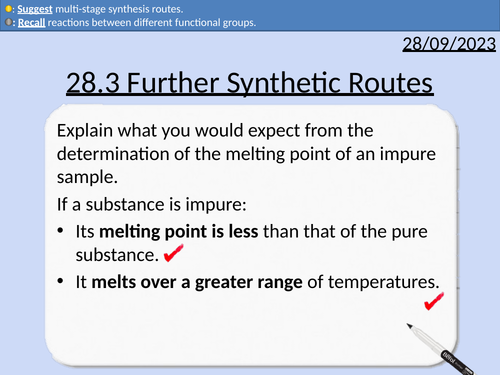
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

A level Chemistry: Condensation Polymers
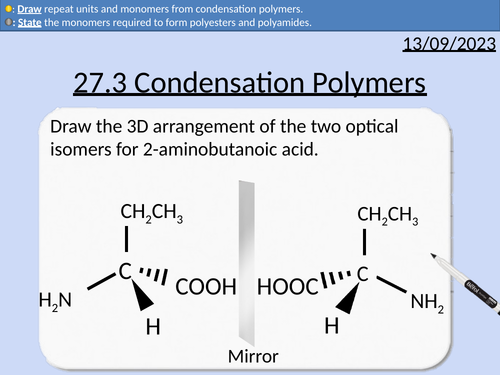
OCR A level Chemistry: 27.3 Condensation Polymers
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Recap of addition polymerisation
Identifying monomers and repeat units from condensation polymers
Polyesters and ester links
Polyamides and amide links
Polyesters and polyamides formed from one monomer
Polyesters and polyamide formed from two monomers
Alkali hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Acid hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters

A level Chemistry: Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
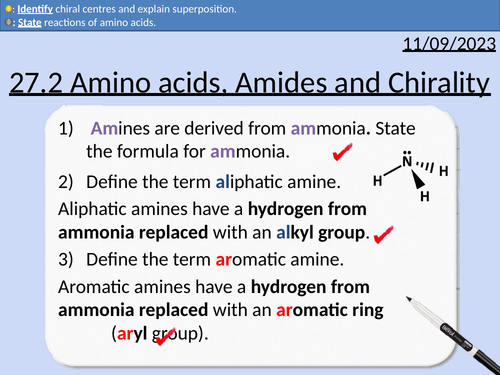
OCR A level Chemistry: 27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers

A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
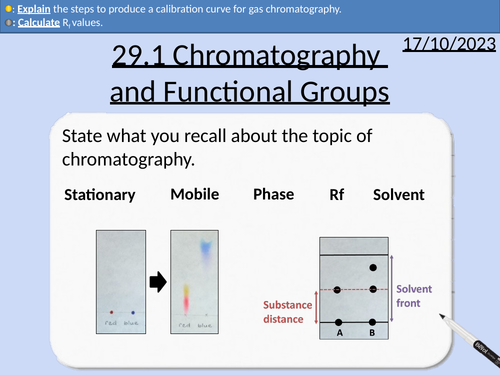
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
28.1 Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
28.2 Further Practical Techniques
28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

A level Chemistry: Proton NMR Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.4 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Carbonyl and Carboxylic Acids
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
26.1 Carbonyl Compounds
26.2 Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
26.3 Carboxylic Acids
26.4 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
The carbonyl group
Differentiating between aldehydes and ketones
Naming aldehydes and ketones
Oxidation of aldehydes
Electronegativity and polar bonds
Electrophiles, nucleophiles, and nucleophilic addition reactions
Reducing carbonyl compounds with sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (NaH4)
Primary and secondary alcohols from carbonyl compounds
Reacting carbonyl compounds with hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (NaBH4)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (HCN)
Testing for Carbonyl Groups
Brady’s reagent - 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine - 2,4-DNP
Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones
Tollen’s reagent - silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia
The Carboxyl Group and polarity of bonds.
Naming carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids as weak acids
Reactions of carboxylic acids with:
Metals
Metal oxides
Alkali
Carbonates
Changing solubility of carboxylic acids in water due to carbon chain length.
Naming acyl chlorides
Naming acid anhydrides
Naming esters
Esterification
Acid hydrolysis of esters
Alkali hydrolysis of esters
Producing acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids
Producing carboxylic acids from acyl chlorides
Producing esters from acyl chlorides and phenols
Primary, secondary, and tertiary molecules
Producing primary amides from acyl chlorides
Producing secondary amides with acyl chlorides
Producing esters and carboxylic acids wirh acid anhydride

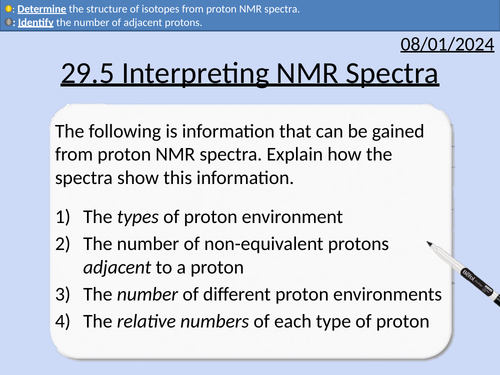
A level Chemistry: Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)

A level Chemistry: Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift ẟ / ppm

OCR A Level Physics: Kepler’s Laws
OCR A level Physics: 18.4 Kepler’s Laws
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The terms: eccentricity, aphelion, perihelion, astronomical unit
Kepler’s First Law
Kepler’s Second Law
Kepler’s Third Law
Graphs of T^2 against r^3 to determine the gradient (constant of proportionality, k).
Equating (4π)^2/𝐺𝑀 to the gradient (constant of proportionality, k)

GCSE Physics: Sound, Boundaries and Ultrasound
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.3 Sound Properties and Uses. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Ray diagrams
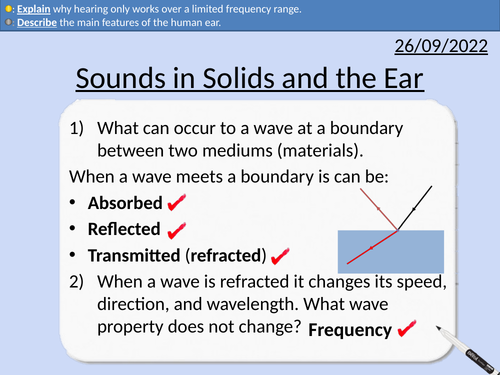
Absorption, reflection and transmission
Sonar
Ultrasound
Rearranging equation
Refraction
Relationship between wave speed and wavelength
Data analysis

GCSE Physics: Sounds in Solids and the Ear
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.4 Sound in Solids and the Ear. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Structure of the ear.
Frequency range of human hearing.
Explanation of the limited frequency range of humans.
Explanation for hearing deteriorating with age.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2.3 Forces in action
All resources for P2.3 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and comined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
• Stretching springs
• Stretching materials and storing energy
• Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
• Turning Forces
• Simple Machines
• Hydraulics

GCSE Physics: Imaging with Electromagnetic Waves
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.3 Imaging with Electromagnetic waves. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation

GCSE Physics: EM waves - Uses and Dangers
This presentation cover the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.2 Uses and Dangers of EM radiation. PowerPoint includes student activities with full worked answers.
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Gravitational Fields
OCR A level Physics: Gravitational Fields is apart of the Module 5: Newtonian world and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
18.1 Gravitational Fields
18.2 Newton’s law of gravitation
18.3 Gravitational field strength for a point mass
18.4 Kepler’s laws
18.5 Satellites
18.6 Gravitational potential
18.7 Gravitational potential energy
The terms: eccentricity, aphelion, perihelion, astronomical unit
Kepler’s First Law
Kepler’s Second Law
Kepler’s Third Law
Graphs of T^2 against r^3 to determine the gradient (constant of proportionality, k).
Equating (4π)^2/𝐺𝑀 to the gradient (constant of proportionality, k)
Key features of geostationary and low polar orbit satellites
Conditions for stable orbits for satellites
Applying Kepler’s laws to the orbits of satellites
Radial and uniformed field
Definition of gravitational potential energy
Deriving escape velocity
Force-Distance graphs for gravitational fields
Center of mass and treating spherical objects as point masses
Gravitational fields
Definition of gravitational potential
Applying the gravitational potential equation
Graph of gravitational potential against distance (V against r)
Combining gravitational potentials from more than one mass

OCR A level Physics: Energy Levels in Atoms
OCR A level Physics: 19.4 Energy Levels in Atoms
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Atoms have different electron arrangements
Ground state energy
Bound electron states being negative
Converting between joules and electronvolts
Calculating the change of energy between energy states
Calculating a photon’s frequency and wavelength

OCR A level Physics: Life Cycles of Stars
OCR A level Physics: 19.2 Life Cycles of Stars
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Calculating mass in kg from solar mass
Life cycle of stars with a mass between 0.5 and 10 solar masses
Life cycle of stars with a mass above 10 solar masses
Pauli exclusion principle and electron degeneracy pressure
Red giants and white dwarfs
The Chandrasekhar limit
Red supergiants to black holes and neutron stars
Stellar nucleosynthesis

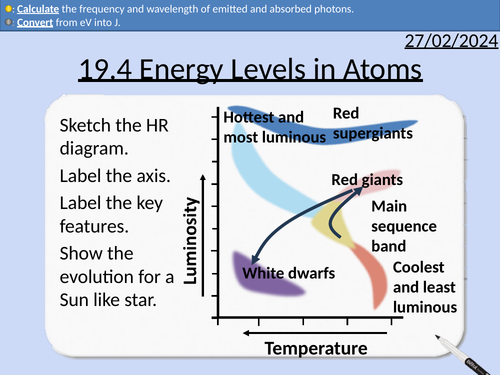
OCR A level Physics: Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
OCR A level Physics: 19.3 Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition of luminosity
Usual axis choice of a HR diagram.
Identifying the positions of the main sequence, white dwarfs, red giants, and red supergiants.
Description of how stellar evolution is shown in a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.

OCR A level Physics: Objects in the Universe
OCR A level Physics: 19.1 Objects in the Universe
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The size of astronomical objects: Universe, Galaxies, Solar systems, Stars, Planets, Planetary satellites, Comets, Artificial planetary satellites
Comparing planets and comets
The birth of stars
Stars in equilibrium during the main sequence