NEW AQA GCSE Cells 8 Calculating Magnification
2018 AQA GCSE Combined Science Specification<br />
Topic - Cells<br />
<br />
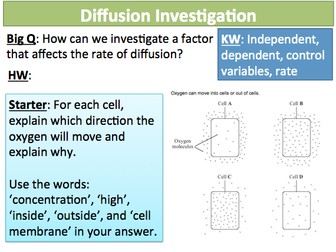
Notes - main activity is the kerboodle worksheet practicing calculating magnification. Can't upload for copyright reasons - but my suggestion would be to use a mixture of examples where pupils find one of the three variables in a mixed calculation worksheet, so pupils practice identifying when to rearrange.<br />
<br />
Part of specification covered:<br />
<br />
Students should be able to demonstrate an understanding of the scale and size of cells and be able to make order of magnitude calculations, including the use of standard form.<br />
<br />
Students should be able to use estimations and explain when they should be used to judge the relative size or area of sub-cellular structures.<br />
<br />
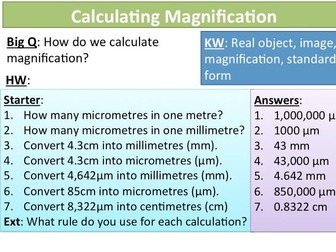
Students should be able to carry out calculations involving magnification, real size and image size using the formula:<br />
Magnification = size of image / size of real object<br />
Students should be able to express answers in standard form if appropriate.<br />
<br />
MS 1b, 2a, 2h<br />
WS 4.4<br />
Use prefixes centi, milli, micro and nano.<br />
<br />
MS 1d, 3a<br />
AT 7<br />
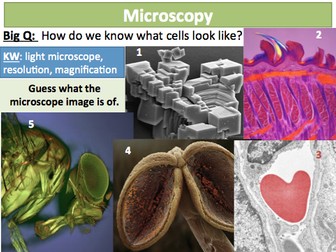
Images of cells in videos, bio-viewers, photographs and micrographs can be used as comparison for students’ own drawings.<br />
<br />
AT 1 and 7<br />
<br />
<br />
MS 1a, 1b, 2h, 3b<br />
WS 4.4<br />
Use prefixes centi, milli, micro and nano.