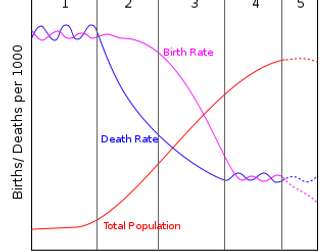
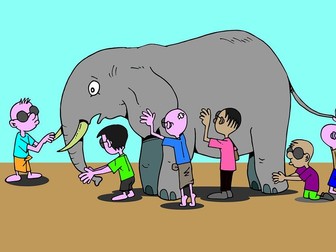
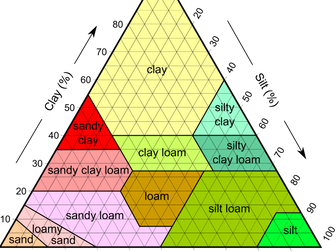
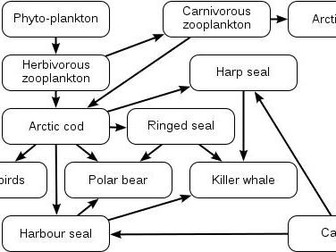
IB DP Theory of Knowledge - Introduction to Indigenous Knowledge Systems AOK
<p>This activity introduces students to the Area of Knowledge (AOK) of Indigenous Knowledge Systems (IKS). Specifically, it helps students use aspects of the IKS specific knowledge framework (applying KCs, and WOKs to an IKS real life situation) to introduce students to the strengths and weaknesses of Indigenous Knowledge Systems.<br />
Understanding and using the strengths and limitations of this AOK is essential for students to effectively analyse and evaluate their knowledge questions (KQ) when preparing their TOK Essays and Presentations.<br />
Lesson length: 45 minutes to 1 hour<br />
Background information and link to video provided.<br />
A worksheet to help students apply the knowledge framework (pages 1 and 2) and answer key for the teacher are provided. The document is available as a PDF for printing and a Word document for editing and student digital responses.</p>