

LESSON OBJECTIVE: Understand the mechanism of electrophilic addition reactions for alkenes and predict the products of these reactions (applying Markovnikov’s rule when appropriate).
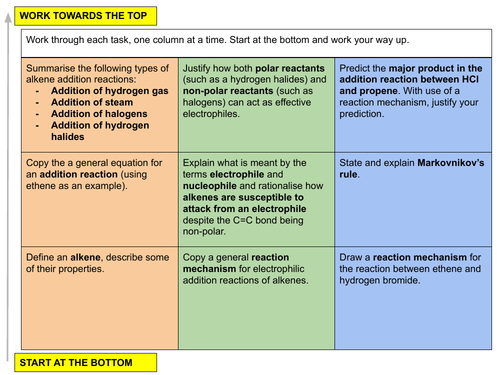
In this lesson we introduce the homologous series of the alkenes by investigating alkene addition reactions, the mechanism by which this electrophilic addition occurs and the effect the carbocation stability and Markovnikov’s rule will have on predicting the product of these types of reactions. This is lesson six in our organic chemistry series of Unit 15: Hydrocarbons (from the Cambridge International AS Chemistry Curriculum (9701) 2019-2021 curriculum).
Learning Outcomes:
(taken from the Cambridge International AS and A Level Chemistry (9701) 2019-2021 curriculum)
15.2 Alkenes
a) describe the chemistry of alkenes as exemplified, where relevant, by the following reactions of ethene and propene (including the Markovnikov addition of asymmetric electrophiles using propene as an example):
(i) addition of hydrogen, steam, hydrogen halides and halogens
b) describe the mechanism of electrophilic addition in alkenes, including using bromine/ethene and hydrogen bromide/propene as examples
c) describe and explain the inductive effects of alkyl groups on the stability of cations formed during electrophilic addition
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have downloaded this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.