
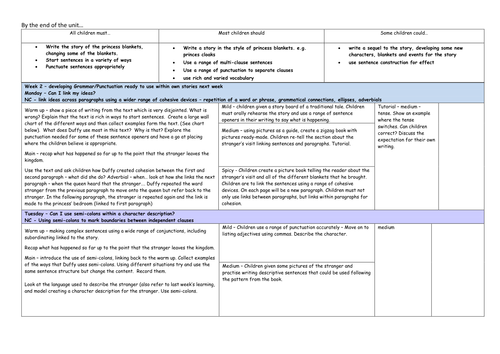
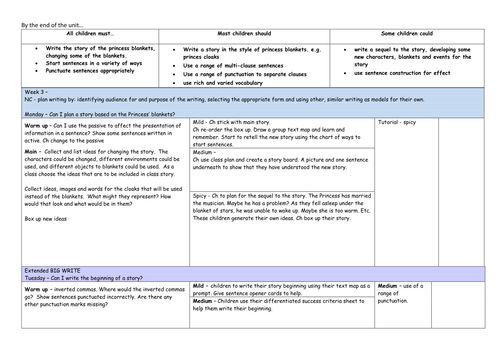
3 week narrative planning based on the new curriculum, differentiated 3 ways. Mild, Medium and Spicy. Smart board resources provided
Objectives covered
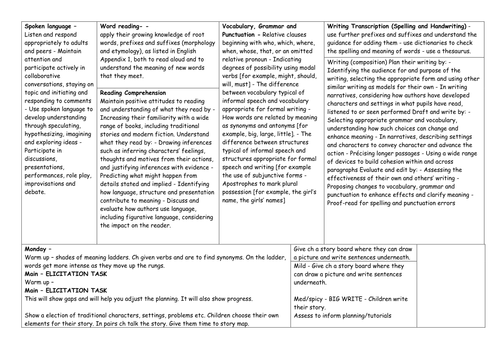
Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation -
Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that, or an omitted relative pronoun - Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must] -
The difference between vocabulary typical of informal speech and vocabulary appropriate for formal writing -
How words are related by meaning as synonyms and antonyms [for example, big, large, little]. -
The difference between structures typical of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing [for example the use of subjunctive forms -
Apostrophes to mark plural possession [for example, the girl’s name, the girls’ names]
Writing (composition)
Plan their writing by: - Identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing, selecting the appropriate form and using other similar writing as models for their own - In writing narratives, considering how authors have developed characters and settings in what pupils have read, listened to or seen performed Draft and write by: - Selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning - In narratives, describing settings and characters to convey character and advance the action - Précising longer passages - Using a wide range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs Evaluate and edit by: - Assessing the effectiveness of their own and others’ writing - Proposing changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance effects and clarify meaning - Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors
Objectives covered
Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation -
Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that, or an omitted relative pronoun - Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must] -
The difference between vocabulary typical of informal speech and vocabulary appropriate for formal writing -
How words are related by meaning as synonyms and antonyms [for example, big, large, little]. -
The difference between structures typical of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing [for example the use of subjunctive forms -
Apostrophes to mark plural possession [for example, the girl’s name, the girls’ names]
Writing (composition)
Plan their writing by: - Identifying the audience for and purpose of the writing, selecting the appropriate form and using other similar writing as models for their own - In writing narratives, considering how authors have developed characters and settings in what pupils have read, listened to or seen performed Draft and write by: - Selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary, understanding how such choices can change and enhance meaning - In narratives, describing settings and characters to convey character and advance the action - Précising longer passages - Using a wide range of devices to build cohesion within and across paragraphs Evaluate and edit by: - Assessing the effectiveness of their own and others’ writing - Proposing changes to vocabulary, grammar and punctuation to enhance effects and clarify meaning - Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors
Something went wrong, please try again later.
The planning is clear but I experienced great difficulties with the notebook format, notebook Pro wouldn't open it and the free version online wouldn't let me 'tweek' the glitches.
The planning is clear and helpful. The notebook files have a fairly good amount of information however the layout is not always clear and thus needed quite a lot of tweeking.
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
£6.00
