406Uploads
123k+Views
41k+Downloads
English
Sale

11+ Grammar School Antonym Questions Literacy Worksheets
Antonyms are an important part of the 11+ grammar school exams. I have designed 100 worksheets on this area. I have chosen a group of over 600 words. There are 10 questions per sheets and pupils write a, b, c or d. The teacher will be able to have a lively discussion when going over the work with the pupils, discussing the meaning of all the words. Of course they can be used by not only grammar school pupils. They would suit anyone of the top end of primary, adults with learning difficulties or foreign students learning English.
Sale

Independent Reading Tasks learning Aids Lots of Ideas
Gathered together some great ideas for guided reading and Independent reading.
Flexible for all years.
Get them doing tasks whilst you help different groups.
example :
During guided reading your teacher and teaching assistant(s) will be listening to different groups read, and work with children to improve reading and comprehension skills. There will often be one or 2 groups that will work independently. This sheet has lots of activities for you to complete if you are working on your own for the lesson. You can do the activities in any order, but you will need to tick them off and fill in the dates when you worked on the activities so your teacher can check them. You will need to keep your sheets in your folder – make sure you number your work with the activity number too! For most of the activities you will need either your current reading book, one you have read recently, or one you know quite well.
Write a letter as a character in your book to either another character in your book, a new invented character or a real-life character.
Write a letter from yourself to a character in your book.
Write a letter to the author of your book – you could say what you like or dislike about the book, or give ideas for what else you would like included in the book.
Have a go at drawing a map of one of the places in the story. See how much you can include and how much detail you can add.
Pretend you are a travel agent and want people to visit the place in the story. Write a paragraph on what you would tell others.
Re-tell an event from the story from another characters point of view. For example, if Jenny is visiting a haunted castle with her wimpy brother Joe, can you change it from Jenny’s point of view to Joe’s?
Re-tell an event from the story as if you are a newspaper reporter and you are writing a newspaper article.
Imagine you could interview a character in your story – what would you ask them? What would their replies be? Write your interview with your character. Set it out so you use 2 different colours for your questions and your character’s answers.
Write the diary entry (or several) for a character in your story after something interesting has happened. Have a go at writing a second diary entry for a different character.
Have a go at continuing the story after the end of the book. What might happen next?
Sale

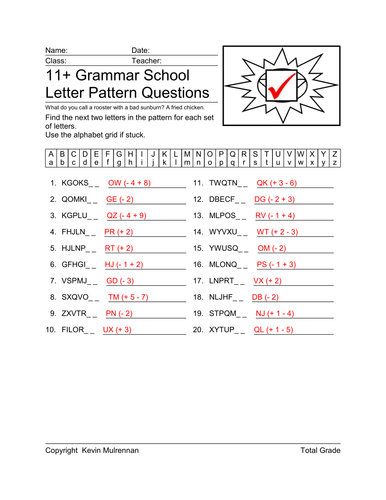
11 Plus Letter Patterns Volume One Logic Puzzles
100 sheets with answers.
The sort of thing that’s good for eleven plus prep.
Good for logical thinking.11+ Grammar School
Letter Pattern Questions
What do you call a rooster with a bad sunburn? A fried chicken.
Find the next two letters in the pattern for each set
of letters.
Use the alphabet grid if stuck.
KGOKS_ _ OW (- 4 + 8)
QOMKI_ _ GE (- 2)
KGPLU_ _ QZ (- 4 + 9)
FHJLN_ _ PR (+ 2)
HJLNP_ _ RT (+ 2)
GFHGI_ _ HJ (- 1 + 2)
VSPMJ_ _ GD (- 3)
SXQVO_ _ TM (+ 5 - 7)
ZXVTR_ _ PN (- 2)
FILOR_ _ UX (+ 3
Sale

Flashback Story Planning Year 6 Late Again For School Powerpoints Worksheets
Great planning.
sample :
Key Questions Teaching
Show the children the PowerPoint ® about different sentence types.
Ask the children to give some examples of sentence types that we use in own writing.
Remind the children of the BOYS and 2A sentences. Write suggestions down. Ask could we extend these sentences, giving more detail?
Model how we might come up with a simple sentence – ‘I walked into school’ – and add another simple sentence to give more detail.
Tell pupils this week we will be focusing on flashback stories. Ask children what does it mean to flashback?
Ask pupils if they can recall the main stages of a narrative. Put up mixed words on board.
Can pupils recall the order?
Opening
Build up
Dilemma
Events
Resolution
End
Tell pupils effective flashback stories often open in the middle of action. This week we will focus on how to write an effective flash back opening.
First we are going to explore a possible story plot. Today’s lesson we are going to look at a picture still and pupils are going to work in pairs to work out what is happening / happened.
What does it mean to flashback? How should a narrative be structured? Why is this a good structure?
Tell pupils there are two ways to start an effective flashback story opening. We can use a 3-ed sentence or an If… If… If… sentence.
This week we are going to explore 3-ed sentences.
The technique we are going to use is called the Cliff hanger 3-ed sentence.
First part of our lesson we are going to look at just the 3- ed sentence. Explain to the pupils, -ed sentences describe a characters emotion/feelings.
The sentence starts with 3 adjectives which end in –ed.
Eg. Frightened, confused, amused.
Show another still picture from ‘Holes’. (see slide 2 of PPT). Ask children to write as many adjectives ending in ‘ed’ as they can think of to describe the scene.
Together, use these adjective and come up with a 3-ed sentences to describe this scene.
E.g. Disgusted, puzzled, repulsed, he held the shoes away from his nose.
Children now to generate their own using the words.
Now show slide 3. Children to generate 3-ed sentences.
Which words best describe the image? Why?
Which sentence is the most effective? Why? Would changing the order of the adjectives make it sound better/worse? Why?
Sale

11+ Verbal Reasoning Questions Letter Patterns Vol 1
I have designed 100 worksheets on letter patterns for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 100 worksheets. Letter patterns is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. Introduce some logic and problem solving skills to students with the Letter Patterns worksheet. Sets of letters related in some way are displayed. Students must find the next two letters in the pattern for each set of letters. You can see an answer sheet in my picture with the answers in red.
Sale

Classic Narrative Poems Noyes Maggie and the Dinosaur Dave Ward The Works
Sample planning :
Genre: Poetry Unit 2 – Classic/Narrative poems.
Focus Texts: ‘The Highwayman’ by Alfred Noyes. ‘Maggie and the Dinosaur’ by Dave Ward.‘The Works’ (poetry anthology) by Paul Cookson. ‘The Puffin book of utterly brilliant poetry’ (Anthology) edited by Brian Patten.
Prepare to share a narrative poem from an anthology: Maggie & the Dinosaur, p463 in The Works by Paul Cookson.
Explain that an Anthology is a collection of poems specially chosen by a person: an anthologist.
Highlight that Narrative poems are poems which tell a story. Point out that not all narrative poems have the same structure although each poem will probably have its own! They often have many verses just like a song, with each verse telling the next part of the story.
Ask the children to respond to the narrative poem we shared. Which parts, lines & words did they enjoy the most? Did they like the way that the poem was read? Narrative poems are often long so they need to be read in a way that keeps the audience interested from start to finish. Just like a good story reader would make a story sound interesting.
Children to be split into mixed ability groups of four and given copies of two poems:
‘Dave Dirt’s Christmas presents’ and ‘GreedyGuts’ both by Kit Wright.
Ask the question: how can you be sure that you are looking at a narrative poem? They should decide which they would like to share with the class. How are they going to read it?
Altogether, in pairs, individually on rotation? Allow each group time & space to practice for presentation.
Groups to present their poems.
Other groups to offer constructive feedback.
Success Criteria:
I know that a narrative poem is one which tells a story.
I can contribute to a group activity, taking turns where necessary.
Sale

Kindlekrax Teaching Materials and Planning Back to School Year 5 Literacy
Planning and worksheets.
Read chapter 3 and 4. Discuss the characters of Ruskin and Elvis. Do you like these characters? Explain. What do they look like? How do they move? Do they have friends/ family? What clothes do they wear? Discuss. Draw up a list of ideas.
Task: To compare the characters of Ruskin and Elvis supporting your description with evidence from the text. Children to describe each character and complete an illustration.
Children to check over their work and improve it. Discuss the comparisons they have made. Which character is the most interesting? Which do you like? Why?
Highlight the WALT. Read p.27 ‘The playground was made of asphalt that sparkled in the sunlight like crushed diamonds on black velvet.’
Describe your school using images like this.
The hall was…
My classroom was…
My teacher is…
Task: Write a character description of Ruskin using the three shot camera frame.
Model how to write the character description using the frame (use Elvis). Long shot, mid shot, close up and reveal.
Sale

Back to School Literacy Year 6 Stories by significant authors J K Rowling
Lots of great planning for an exciting unit.
Nice powerpoints.
Sample :
Share the learning outcome for the unit with the children; share the concept of the working wall. What is narrative? Fact or fiction? Ascertain that this unit is about fiction/narrative/stories. We have three weeks to achieve our learning outcome.
Ask children what they know about JK Rowling. Who is she? What is her job? (use correct terminology- she is an ‘author) Where is she from? (Born in Gloucestershire) Can children name any of her books? (Harry Potter series plus several supplements)
Etc.
Activity One
Come back together, show children a picture of JK Rowling – does this help?
Children to move to next group’s poster and add any more info that they can now think of. Is there anything they agree/disagree with?
Lead into a class discussion on this famous children’s author:
Has anybody read any of her books?
What are her stories about? What genre do you think her stories are written in? (Clarify what we mean by ‘genre’ if needed). What is the purpose of narrative writing? (Display ‘to entertain and enthrall’ on the working wall).
Read first tale from ‘Tales of the Beadle Bard’ – The Wizard and the Hopping Pot. Discuss what is distinctive about this story (what does it remind you of?)
Sale

Harry Potter Puzzles Crosswords Word Searches J K Rowling
Puzzles for Harry Potter.
Great for Friday afternoons when the kids go mad.
Sample clues.
ACROSS
A person who is born to magic parents but has
no magic ability.
Hooded dark arts creatures who at one time
followed Voltemort.
The wizarding world’s main newspaper.
The day a person dies and becomes a ghost.
A very powerful dark wizard who killed James
and Lily Potter.
Fifth year exam for students of the Hogworts
Academy.
An expensive broom that Sirius buys for
Harry.
The train that takes Hogworts students to and
from the school.
Nearly Exhausting Wizarding Test.
Buttery drink which can be bought by
students in Hogsmeade.
Sale

English year 5 and 6 The Mysteries of Harris Burdick Planning and Powerpoints Literacy year 5
A great collection for teaching this interesting topic.
You get powerpoints and planning.
Sample :
Punctuate sentences accurately, including using speech marks and apostrophes.
Use commas to mark clauses.
Group and classify words according to their type and meaning.
Read a variety of texts, commenting on the author’s choice of vocabulary.
Construct sentences which are punctuated correctly; including the use of commas, speech marks and apostrophes.
Use a range of connectives to join sentences.
Experiment with complex sentences.
Whole Class Shared Learning
Discuss pronouns (homework)
Define each type of word: Noun, adjective, verb and adverb. Build up a sentence as we go.
Show the children a picture on the whiteboard of a horse galloping and of a lightning bolt. Children to write down 3 (LA) or 5(MA and HA) important nouns from the picture. Share. On the left of the noun, children to write an adjective to modify or describe the noun. Share. After the noun, children to write a verb and then an adverb to qualify the verb.
e.g. The black horse galloped elegantly along the beach.
Praise the children on yesterday’s literacy work – they showed knowledge of the function of nouns, adjectives, verbs and adverbs (HA showed knowledge of the difference between common, proper and pro nouns).
Children to name a range of punctuation – I record on the board (I do not add to it at this point).
Ask volunteers to illustrate uses of the punctuation named. Look on the punctuation pyramid – have we named any L5 punctuation? This is what we should be aiming at all the time.
Children to have a variety of sentences to up level punctuation on their whiteboards.
Come back to ‘The Mysteries of Harris Burdick’. Read through all of the captions and talk about ‘reading’ the illustration. Allow children time to talk about the ‘mystery’ – what do they think happened to Harris Burdick?
Choose a picture from ‘The Mysteries…’ and list all of the questions which it provokes. What do children think of the pictures? Do the captions answer any of the questions?
Talk about the settings in the pictures – often they are recognisable, familiar settings where things are not as they seem. Explain that we would call this ‘Stories in a familiar setting’.
Model the task.
Use PPT to study speech punctuation.
Use the pictures from ‘The Mysteries…’ to write some possible dialogue.
Model possible conversations, including synonyms for said and adverbs plus adverbial clauses. With correct punctuation.
Look at some of the pictures from ‘The Mysteries …’
Think / discuss some of the characters in the pictures. Use adjectives to describe them – give them names. From the pictures come up with verbs to describe what they are doing then add adverbs and adverbial clauses.
Sale

Year 4 Planning Autumn Term Literacy Numeracy KS2
Important! If you’d like to buy the whole year’s planning (Autumn, Spring and Summer) you’d be better off buying my bundle.
Planning for the Autumn term for year 4.
You get 160 mb of material so good value imo.
I taught mainly in Catholic schools so has a Catholic bent. But as we live in a multicultural society, this should be no problem.
You get planning for:
creative curriculum
Literacy
Numeracy
P.E. (some)
Science (some)
R.E. (Advent, Abraham, Judaism etc)
Loads of great lessons to ease your Sunday afternoons. Just cut and paste into your school template.
Sale

Charlie and the Chocolate Factory Planning Roald Dahl Literacy
Three weeks great planning. Don’t expect lessons on Charlie. It’s report writing in English using Charlie with powerpoints etc
Great powerpoints
Zip file has more. I’ve put some example stuff on to give you a flavour.
Introduce the new unit and read the writing outcome with the children.
Complete a skills audit verbally. TTYP – what skills do you already have that will help you to achieve the outcome? What skills do you think you will need to revise? Are there any completely new skills you will need?
Introduce the focus text. We know a lot about Roald Dahl from our biography unit. Has anyone ever read ‘Charlie…’?
Seen the films?
Explain that we need to know the story line and the characters, so we are going to spend today’s lesson using the 2005 film as a visual text. The rest of the week will be spent comparing the visual text to the written text and completing various activities and pieces of writing.
Become familiar with the story by using a visual text.
Use both visual and written texts to analyse character and setting descriptions. Finish any of the DVD which we didn’t finish yesterday.
Use the written text to read the character descriptions of Charlie, his parents, grandparents and the four other winners of golden tickets.
Activity One
Come back together, discuss and put information on working wall.
Repeat with setting descriptions.
Look at a still of Charlie’s house from the film and read the setting description for it.
Look at the still from the ‘meadow’ in the chocolate factory and read the description on pages 87-90.
Activity Two
Revise features of journalistic writing.
Compose a newspaper article using the correct form and language.
Working in pairs, children to sketch a story mountain onto a whiteboard. Children to then summarise ‘Charlie…’ using one or two sentences for each section of the mountain.
Come back together and discuss.
Read chapter five of the text. What main event is happening? The announcement of the golden ticket competition.
Watch 14:28 – 15:44 – how does the film embellish the details given in the book?
Explain today’s task, you are a senior news reporter for the ‘International Herald’ a newspaper which is published in many different countries, many different languages all over the world. Your editor has asked you to write a newspaper article about this event. Your report will be published the day after Willy Wonka’s signs went up. You will be reporting on the competition, the prizes and the mania sweeping the world.
TTYP – what are main features of a journalistic piece of writing?
Come back together and list for the working wall:
Headline, paragraphs, subheadings, quotations, orientation, 5 ws, past tense, direct, formal, balanced etc.
Brainstorm some headlines for our article.
List the 5 Ws on the working wall.
Give each child a checklist and an inverted pyramid.
Sale

Year 6 Cross Curricular Literacy History World War 2 English
To plan and write a recount text, using appropriate form, features and language.
To understand the value of the ‘home front’ during WWII.
To discuss and write about the life of children during WWII.
Understand the role of the ‘home front’ and the impact of rationing. Explain that this week’s literacy lessons are linked closely to our current history topic. We are moving on to a geography topic after half term.
Recap what we have learned recently in history lessons.
What were the main causes for WWII? Dates? Political leaders? Axis? Allies? How was the war fought? What was the Blitz? What sort of places did the Germans target? Why?
Last lesson I asked you to discuss the posters issued by the British Government. What did you find out?
Show the quote: “I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat. You ask, What is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory.” TTYP – who do you think said this?
Come back together and establish that it was part of a speech by Winston Churchill when he became PM in May 1940. At this time, victory seemed a long way off.
Show map of the world. Explain that, at the time of this speech, the German forces had already conquered Norway and Denmark. Now, they were sweeping through Belgium and the Netherlands. By 20 May, they reached the English Channel. More than 500 000 British and French troops were trapped on the French coast at Dunkirk. Hundreds of boats, big and small, repeatedly sailed from Britain and brought nearly 340 000 safely back to England. The German advance went on. On 17th June France surrendered. Most of North-West Europe was now in Hitler’s hands. The German leader began to plan the invasion of Britain, only 34 KM away.
Britain now stood alone with scarcely anyone to help. The USA had not yet entered the war. The countries of the British Empire such as Australia and Canada were too far away. Churchill encouraged the people of Britain with defiant speeches. “We shall go on to the end,” he said, “we shall never surrender.”
What was providing a natural barrier for the British against the Germans? The sea. However, it also caused problems. Britain’s farmers could not grow enough food to feed the population. Large amounts had to be brought in from home by ships. Merchant or goods ships were slow and lightly armed and so were easy targets for German U-boats and bomber aircraft. Between March and May 1941 over 320 merchant ships bound for Britain were sunk. Food such as flour, meat and sugar were in short supply.
Sale

Roald Dahl Charlie and the Chocolate Factory Write An Advert Persuasive
Some nice little lessons on the Road Dahl classic plus some great powerpoints.
sample :
Support for spelling
Count the syllables. CT will remind children what a syllable is and provide a list of words on the board. Children will count how many syllables there are and record on their whiteboards. CT will provide children with three types of chocolate (number 1, 2 and 3) and a blind fold. In pairs one child will be blindfolded and the other will pass the chocolate for the children to try.
Children will watch a clip of Willy Wonka from the film ‘Charlie and the Chocolate factory” CT will review the features of a formal letter:
Address in top write hand corner
Date (on left)
Greet using the persons formal title
Introduce yourself
State the reason you are writing
Lots of connectives
Persuasive techniques
Close the letter with ‘Yours Sincerely’
Formal language
Children will write a business letter to Mr Wonka persuading him to make their chocolate bar.
Sentence types
Children will work in pairs; one as an instructor and one as the listener.
instruct listener to walk to cone on playground.
Imperative verbs – CT will explain that children will have just used lots of imperative verbs which are ‘bossy verbs’.
CT will display sentences on the board and children will need to change them into an imperative sentence.
CT will display a set of instructions and children will suggest features including:
• A goal
• List of equipment
• Time connectives
• Present tense
• Imperative verbs
• Numbered steps
• Short, clear and direct sentences
• Picture of finished article
Children will then create a set of instructions for making the rocky road bites,
Sale

Charlie Small Gorilla City Literacy Planning Year 5
Some great planning for Charlie Small Gorilla City.
You get microsoft word documents.
Plus Notebook files if you can play those.
Sample :
LO:
I can investigate a character and list key questions.
Prior to lesson, create a display area in the class – or another area of the school – consisting of a copy of Charlie Small’s journal (see GORILLA CITY cover), photographs of settings and animals from the text, a map (copied from the book) and his rucksack. Also include a fact file on any 2 of the creatures mentioned in the text ~ e.g. the hyena or gorilla. The contents of his rucksack may be listed on cards; or some of the items actually on display.
TA or other adult in school to enquire about these items and chn asked to ‘investigate.’
Teacher/TA to read note from Charlie – see inside book cover.
In small groups, chn list questions they would like to ask the author – Charlie Small – and discuss what they would like to learn further about his expedition(s).
Class share ideas.
LO:
I can identify author style and purpose.
I can choose effective vocabulary to describe a character.
Explore the cover design and shared reading of the Publisher’s note, plus the note from Charlie.
Discuss the impact of the illustrations, writing style, the crinkled and stained journal entry by Charlie and use of words in capitals for emphasis.
With response partner, chn talk, then make notes on what they have learnt about Charlie from his opening note. * Have an outline of a silhouette on the wall to represent
Charlie.
Teacher or TA read pages 2-6.
In pairs, chn list some key words to describe Charlie’s personality, behaviour, likes and dislikes, based on what they have learnt so far. Ask them to select their most powerful adjective and write it on a Post-It note. Add these to the role on wall.
Extension: discuss the use and purpose of each item in the rucksack.
Sale

Literacy Year 5 or 6 Stories from Other Countries 3 Weeks Planning Ahmed's Secret Heide
Great planning for year 5.
Plenty to keep you going for three solid weeks.
Powerpoints, planning, worksheets etc etc
The zip has the lot. I have put up some on the ordinary download so you can look.
Sample planning :
Genre: Narrative Unit 3 – ‘Stories from other cultures’
Focus Texts: ‘Abela’ by Berlie Doherty (class reader), ‘The day of Ahmed’s secret’ by Florence Parry Heide, ‘Stories from around the world’ Usborne books.
Objectives
Primary Framework Phase 1
• Create roles showing how behaviour can be interpreted from different viewpoints
• Know and apply common spelling rules
• Infer writers’ perspectives from what is written and from what is implied
• Compare different types of narrative and information texts and identify how they are structured
• Experiment with different narrative form and styles to write their own stories
Adapt sentence construction to different text-types, purposes and readers
Punctuate sentences accurately, including using speech marks and apostrophes.
Learning/Writing outcome for unit: Write a story from a different character’s point of view. Reflect on writing critically and edit it against success criteria.
LO: Whole Class Shared Learning
Guided and Independent Activities: Plenary:
M Understand and use the word ‘culture’.
Begin to recognise the features of a story from another culture. Show the words ‘narrative’ and ‘fiction’. Children to TTYP and talk about what they mean. Come back together and elicit that they are words for ‘story’. We are going to be studying a narrative unit for two weeks. Briefly recap the five structural features of a story. What types of stories have we studied so far? (Myths, legends and stories by a significant author).
Show the word ‘culture’. Children to TTYP and discuss.
Come back together and explain that a culture refers to “the attitudes and behaviour that are characteristic of a particular social group.” Emphasise that we are not necessarily talking about different religions or even other countries – there are a lot of different cultures even within one country.
Lead to class discussion.
Provide children with copies of ‘The Day of Ahmed’s Secret’ – explain that this story is from Africa. Ahmed lives in a city called Cairo – the capital of Egypt. Show on a map. Have we heard anything about Cairo in the news recently?
Read half of the story and then challenge children to discuss on their tables:
The features of the story.
Their predictions about Ahmed’s secret.
Come back together, read the rest of the story and discuss.
How is Ahmed’s life different from your lives? In his culture it is perfectly normal for children to be working very hard and taking over the family business from his Father. What does his pride at being able to write his own name suggest about his level of education? About his place in society?
Create a working wall list of features to include:
Capital letters used at the start of each sentence and full stops at the end.
Sale

Year 5 Literacy Planning Roald Dahl Material Poetry Iron Man Big Write
About a months work of year 5 Literacy planning.
Some nice Roald Dahl stuff in there.
sample :
Recap on the children’s knowledge of poetry i.e. alliteration, similes, metaphors and onomatopoeia as the Iron Man is rich in poetic features. Introduce the book to the children. Highlight the cover of the book. What do you think the book will be about? Discuss with partners, share ideas with the class. Read the blurb. Why do you think the book is described as a modern fairy tale?
Introduce that the author of the book is also a poet. Share that there are many poetic features in the text that are used to describe the characters and setting e.g. similes, metaphors and onomatopoeia. The children will have to take notes of these features. Read chapter 1 to the children. Ask the children to jot descriptions of Iron Man on their whiteboards while listening to the story. Use a PowerPoint to highlight the description of Iron Man on page 1-2.The children will create a mind maps on Iron Man. They will create a description his movements, his features and his personality.
Focus: Characters
WALT : To create a description of a character from a text.
WILF:
Use of adjectives, verbs and poetic features (i.e. similes, alliteration and onomatopoeia).
Use neat handwriting. Share sentences with the class and discuss the descriptions they have created. What type of character is he? What similes are used in the text?
Sale

Year 4 Planning Spring Term Numeracy Literacy KS2
Important! If you’d like to buy the whole year’s planning (Autumn, Spring and Summer) you’d be better off buying my bundle.
Planning for the Spring term for year 4.
You get 160 mb of material so good value imo.
I taught mainly in Catholic schools so has a Catholic bent. But as we live in a multicultural society, this should be no problem.
You get planning for:
creative curriculum
Literacy
Numeracy
P.E. (some)
Science (some)
R.E. (Christmas, Lent etc)
Loads of great lessons to ease your Sunday afternoons. Just cut and paste into your school template.
Sale

Back To School Planning Year 4 Year 5 First Week Rules Activities Powerpoints
back to school activity pack.
Ideal for year 4 and 5. Can be adapted for different years of course.
I mainly taught in these years groups, and this planning helped so much in that tricky first week,
There;s a bit of everything. Planning of course, rules, display, activities
Just packed with vital little time savers.
Some really goo VCOP stuff too.
Plenty of resources. Give it a go!
Sale

Wolves in The Wall Planning Plus Literacy Arguments Neil Gaiman
Great 4 weeks planning for this Literacy topic.
Really nice powerpoints.
Plus free bonus. Plenty of argument planning using Olympics.
Example planning :
Identify and discuss the various features of a fiction text, including characters, settings, themes and dilemmas, the author’s intentions, the structure and organisation of the text and the way language is used to create effects on the reader.
Speaking
Use the techniques of dialogic talk to explore ideas, topics or issues.
Creating and shaping texts
Set their own challenges to extend achievement & experience in writing.
Understanding and interpreting texts
Understand how writers use different structures to create coherence and impact.
Text structure and organisation
Use varied structures to shape and organise text coherently
Sentence structure and punctuation
Express subtle distinctions of meaning, including hypothesis, speculation and supposition, by constructing sentences in varied ways
Use punctuation to clarify meaning in complex sentences
To produce several pieces of writing based around the focus text.
To learn and identify the features of a formal/impersonal text and comment on occasions where this may be necessary.
To produce a formal letter, speech and broadcast using appropriate form, features and content.
Remind children of last week’s immersion into the focus text. TTYP – what did you think of the text? If you could talk to the author, what would you say to him? Ask him?
Display a ‘Likes/Dislikes/Patterns/Questions’ board on the whiteboard. Explain that we are going to focus on the ‘patterns’ section today.
Re-read the last few pages of the book and add ‘false endings’ to the patterns section.
Have some photocopied pages from the book in the centre of the tables (each table to have different pages).
Give groups ten minutes to note any patterns they see on whiteboards.
Come back together and note on the board to include:
False endings.
Simile
Lucy asking her Mother, Father and brother for advice, always in that order.
Adjectives for the noises she hears.
Alliteration and onomatopoeia.
Phrase “You know what they say…”
Appearance of pig puppet.
What effect do these patterns have on the reader? They give the text fluency, a rhythm almost like a poem. They make the text easier to read and digest. The repetition also mimics the repetition of Lucy’s pleas to her family to listen to her about the noises. They make the reader frustrated on Lucy’s behalf.
Have one child write a definition of ‘atmosphere’ on a sentence strip for the working wall. A general feeling or mood.
There are a few different atmospheres in this book. Discuss. List tension, frustration, relief etc on the board.