406Uploads
122k+Views
41k+Downloads
Mathematics

Area Perimeter maths Net Cubes Compound Shapes Year 5
Work out the area an perimeter of cubes etc.
You can print out shapes and give to pupils.
Learning Objectives. Ma 1 Organising and explaining
Ma 3 Calculate perimeter/area of squares and rectangles.
· To explain methods and reasoning
· To solve mathematical problems, recognise and explain patterns and relationships.
· Calculate perimeters and areas of rectangles.
· Find the largest area that can be made with a rectangle that has a perimeter of 26 metres.
Success criteria.
· To be able to work out the area of a rectangle or square.
· To make different rectangles that all have the same perimeter.
· To recognise the largest area.
· To compare the relationship between the length of the sides and the area of the rectangle.
· To explain reasoning.
Model the way to answer the question referring to work of a few weeks ago on perimeters. How many different sized pig pens can be made using only 12 fencing panels?
Discuss how the children think they could solve this problem.
The Problem.
We want to make a school garden and grow vegetables. At night time the rabbits and deer will come and eat them. To stop them we need to put a fence around the area. However we can only afford to buy 26, one metre long panels.
Find the largest area we can fence off to make a rectangular vegetable patch?
Remember it can only have a perimeter of 26 metres.
Vocabulary.
add
subtract
multiply
dividedouble
half
equals
rectangle
square
area
perimeter
cm2
Resources:-
multi-link. L/A
rulers.
Squared paper.
Home work:- if applicable.
Assessment. Children exceeding the objectives.

Maths Puzzles Across Down Fill In The Gaps Simple Arithmetic 100 Grids
100 grids.
Pupils have to fill in the gaps.
The squares all have to add up.
These puzzles involve taking away and adding.

15 Powerpoints Year 5 Morning Work. Great Starters English Maths
15 Powerpoints that you can have on the board as your class enters.
Nice easy start to the day.
Easily adaptable. Nice bits of Math and English.

Spring Year 6 Maths Planning 13 weeks 36 page pdf
36 page pdf.
Maths for each of 13 weeks.
sample :
LO: To reflect shapes across a horizontal or vertical mirror line.
KEY QUESTION: DO I NEED TO USE A MIRROR TO REFLECT A 2D SHAPE?
Review the term reflection with the children. How would the children reflect a simple shape like a square across a mirror line? Show the children a more complex shape. How would the children go about reflecting this shape?
Explore the use of a mirror using a large version of a shape on the working wall. If you hadn’t got access to a mirror, how would you go reflect the shape?
Focus on process of identifying vertices within shapes, counting to the mirror line.
DS: Supports Triangles during teaching.
AG: Supports Squares during teaching.
LO: To draw and reflect a shape across a 45 degree mirror line.
Show the children a shape and have them model how to reflect across a vertical and horizontal mirror line. Show them a mirror line that is set at 45 degrees. Discuss possible strategies for carrying out the task of reflecting across the mirror line. Make sure the children stay on the grid lines and follow to the mirror line, then away from the mirror line to make a right angle.
MW: target high Focus Children within teaching. Check during lesson.
LO: To reflect a shape that crossing a 45˚ mirror line.
KEY QUESTION: HOW CAN I REFLECT A SHAPE THAT CROSSES THE MIRROR LINE?
Address misconceptions from previous lesson. Give the children an enlarged version of a triangle that crosses a diagonal mirror line. As a class, identify way in which the shape can be reflected across the mirror line. Take each point and reflect across a perpendicular set of gridlines. Model the use of start and end points. Whatever is in the upper part of the mirror line needs to be in the lower, vice versa.
DS: Supports triangles during lesson.
AG: Supports Circles during lesson.

Money Week Year 5 Year 6 Finances Banks Shopping
A nice little unit on financial planning.
Some calculations required for better financial knowledge.
Introduce ‘My Money’ week to children. Explain that we are going to spend all week discussing money, using mathematical operations, setting a budget and thinking about how we will deal with money in the future.
Activity One
Come back together and allow groups to share mind maps. Lead into a discussion on what money is; use online dictionary to look for definition. Come to the conclusion that it is a medium of exchange; we exchange money for goods or services.
Make a list on the IWB of things which people use money for. Separate the list by highlighting things which people need and things that they want.
TTYP – what is the ‘currency’ of the UK? Explain that it is called sterling and it is split into pounds and pence.
Use PPT to check that children recognise all notes and coins of sterling.
Activity One
Children work in groups to mind map ‘money’.
Each group to have three colours –create a key to show things they know, things they think they know and questions they have. If I gave you £1000 right now, what would spend it on?
What might you wish you had spent it on in the future?
Can the children name any currencies of other countries?
(Euro, US dollar, Aus dollar, Yuan China, Rupee India etc)

1000 Questions Advanced Addition Maths Mathematics KS2
1000 questions on advanced addition.
Pupils write the answers directly on the sheets. There are different numbers of digits that they can add up.
Answers all provided.

Christmas Planning Year 5 Three weeks worth English Maths
Three weeks of planning. Plus you can use other planning included for free from different years.
Example
To analyse and create a character and setting description for 23 Degrees 5 Minutes North.
I can express verbally what a character may be feeling, thinking or doing I can explain why I think a character may feel, think or do something I can describe a setting using figurative language
Starter 5 mins
Pen portrait of key characters in 23 Degrees 5 Minutes North: Children mind map/annotate information about the key characters that they know so far around an image of The Adventurer and Professor Erit. They add information about the internal feelings, thoughts and emotions within and the external information such as physical description, or known facts
Activity 1 5-10 mins
Use key questions and discussion in groups to think about answers to questions such as: When is this story set? Who am I? Where am I? Why am I here? Will I be able to find Professor Erit? How will I find him?
Emphasise the importance of chn giving evidence to support their opinion when they give a response to these questions.
Activity 10 mins
Return to image of the Adventurer and Professor Erit. Using a different coloured pencil, chn should add information about these characters
Main 20 mins
Give chn an image of the setting and ask them to mind-map descriptive words, phrases or sentences they could use to describe the narrative setting.
Model using the different kinds of sentence-types to record a setting description, using the vocabulary recorder in the mind-map. Chn use sentences to build suspense if they can.

1000 questions Equations Single Variable Mathematics KS2 Algebra
1000 questions with answers on Equations.
Single variables.
Pupils have to work out what y equals.

Back to School Year 3 Maths English Plans 19 English weeks 18 English weeks
Looking for some inspiration going back to school.
19 English weeks 18 English weeks
Plus some humanities planning on China etc
Sample
Children have white boards. I will describe a person and you must draw them From the twits Roald dahl(Mr Twits). Children share ideas from the first opening paragraph. What made this so visual. LANGUAGE
Look at a series of images. Witch, doctor, pirate.
Look at the features, are there similarities.
Elaborated pictures of people. Famous and non famous.
Discussion and focal point.
Play head band with the children. They have to describe the person they are holding and the partner has to guess who it is.
Expanding on words to describe
Steps to Success
Mild: To review characters
Spicy: To recognise features of a character
Hot: To describe your character
Extra Hot: How could you describe yourself? Tell me.
What sort of questions did you ask eachother?
Why? Who spoke about the hair colour. How could we describe this person to someone.

Back to School Year 4 Maths Planning Autumn Term
Weekly plans for the dreaded back to school Autumn term.
Cut and paste and adapt for your own personal use. I hated those Sundays ruined by planning.
example Today we are learning about decimals to two decimal places.
First ask what are decimals? Establish that decimals show us part of the number that is not a whole.
Display a number line with 0-1 with 9 unlabelled divisions.
In between 0 and 1 we have intervals that represent tenths (not tens). Decimals are like fractions the number line is divided into ten parts so each one is one tenth. Tenths are decimals to one place as there is only one digit after the decimal point. Give children magnified glass and ruler using the ruler ask children to look at the tenths in-between each cm.
When we write tenths as a decimals we write 0.1, 0.2… allow children to continue this asking them to stop when they get to the next whole number. What is the decimal point for? To separate the whole from its decimals.
In between the tenths there are hundredths (not hundreds) display 0.4 to 0.5 with unmarked intervals in between. Ask can anyone tell me what these intervals will be labelled? 0.41, 0.42…
Establish that 3.7 is bigger then 3.56. Ask why might I think 3.56 is bigger?
Why is 3.7 bigger?
When do we use decimals in real life? Place objects on a each table for the group to feel. Which one is heavier? Lighter? Get children to order them in order of weight. Give each table some scales, ask them to see if they were right and also to write the weights that they can read and make a note of them. Select some children to attempt to read the weights. Who has ever cooked or baked? What units of measurement would you use?
What units of measurements have we used here to way our objects?
How many grams are there in a kilogram? Give children some examples and ask them to convert the weights.
Model how to use scales weigh different objects ask class to read the scale.
Read scales and convert from grams to kilograms and vice-versa. L/A
TA support
To weigh objects and read on a scale.
EXT: Order objects in order of weight using estimation skills

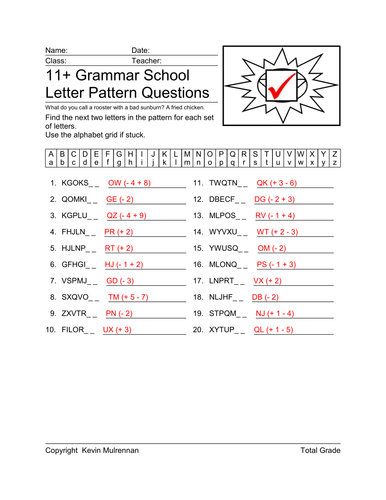
11+ Verbal Reasoning Questions Letter Patterns Vol 2
Another 100 worksheets on volume 2. I've included more questions per sheet and for some I have omitted the alphabet grid. I have designed 100 worksheets on letter patterns for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 100 worksheets provided on a cd. Letter patterns is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. Introduce some logic and problem solving skills to students with the Letter Patterns worksheet. Sets of letters related in some way are displayed. Students must find the next two letters in the pattern for each set of letters. You can see an answer sheet in my picture with the answers in red.

1000 questions Maths Advanced Addition Mathematics
1000 questions Maths Advanced Addition
Answer sheets provided.
Good for homework
Good to fill time
Good extension work

100 Worksheets Addition Maths Easy at Start Hard at the End
100 worksheets on addition.
I’ve used a nice big font.
They start off easy then get progressively harder.
Answer sheets provided for all worksheets.

Back to School Year 5 Autumn Term Mathematics 4 Groups
Some nice planning.
In 4 groups so lots of differentation.
Example :
L.O
To order positive and negative numbers and find differences between numbers
(not set) Dividing by 10,100 and 1000 quick fire questions Must: I can order sets of negative numbers Share with the children an image of a thermometer, what is it used for? What do we know about temperature? Children to mark on the thermometer temperatures they know ie body temp, boiling point etc.
Can temperature go below zero? What do we call those numbers?
Share with the children -15, -2, -20, -9 and -21. Where on the thermometer do these go? Discuss smallest to biggest ordering, which number is smaller/larger.
In pairs order a set of numbers (+ and -) L/A
Children to order sets of negative numbers. Moving on to reading temperature problems.
(activity 1-2 on pg6 NPM 6a)
Number lines/thermometer to support?

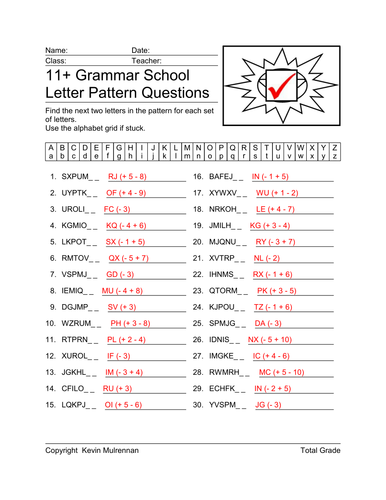
11+ Verbal Reasoning Questions Letter Patterns Vol 1
I have designed 100 worksheets on letter patterns for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 100 worksheets. Letter patterns is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. Introduce some logic and problem solving skills to students with the Letter Patterns worksheet. Sets of letters related in some way are displayed. Students must find the next two letters in the pattern for each set of letters. You can see an answer sheet in my picture with the answers in red.

Maths Patterns 100,000 Questions Numeracy
I have designed 100,000 questions on Maths patterns. You have to guess the patterns and fill in the answers. Makes a pleasant change from the same old same old textbooks that are around. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. You can pick and mix, leave questions out etc. it’s your choice! Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

100 Questions on Pythagoras Answers Provided Mathematics Geometry KS2
**100 questions on Pythagorus.
IF YOU LIKE THUS I HAVE A REALLY BIG FILE IN THE SHOP
15000 Pythagoras Questions Pythagorean Theorem Maths KS2 KS3
Answer sheets provided.
A good little exercise for your students. Using a calculator this should keep them busy and help you teach Pythagoras’ theorem.**

Division Worksheets for Primary School Children Maths Mathematics Homework
100 worksheets with answers sheets provided.
100 sheets of division questions.
Some have 10 questions, some 20, some 50.
A useful time filler or use them for a quick homework or start of day activity.

Rounding Numbers 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics
100worksheets on rounding numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
Answer sheets provided.
20 questions per sheet.
A good time filler or easy homework.

1000 Questions Addition Mathematics KS1 Adding Up
1000 questions with answers.
Pupils have to add up either 3 or 4 numbers under 10.