31Uploads
26k+Views
46k+Downloads
All resources

Introduction to Sub Programs for GCSE Computer Science Part1
This is an excellent resource to support knowledge required in OCR computer science J277 specification. How to use sub programs (functions and procedures) to produce structured code. This resource can be delivered from a non specialist and answers to solutions are available on request. Students must be encouraged to take their time and think through problems before showing solutions. Students must also reflect on their code development by answering/ discussing log questions.

Introduction to Web Design - HTML & CSS
This Ofsted friendly resource is perfect for supporting KS3 students with web development. Teachers can plan with ease and intent, non specialist can implement and impact can be measured affectively.

Introduction to Databases Year 8
This Ofsted friendly resource with scheme of learning is perfect with all the points required for intent, implementation and impact.

Computing Keywords Countdown starter
Use this countdown computing keyword quiz to introduce KS3 students to vital keyterms. Can be used as a starter or a whole lesson. A great resource to use as a cover lesson. Students are given some time to come up with computing keyterms from a range of letters. Points are awarded for words and words containing more letters score more points. Students are asked match the definition to the keywords. -
BIT
RAM
ROM
BYTE
BINARY
SYNTAX
BROWSER
SOFTWARE

Computer Science J276/02 Computational thinking, algorithms and programming Lesson
To support GCSE Computer Science students in accessing exam questions for (Paper2-J276/02) Big Mark questions
Practise solving problems using computational thinking (Abstraction, Decomposition & Algorithms)
Develop Python Coding skills (Demonstrate use of variables, functions, data types and casting)
Know how to test a program efficiently.

Year 9 Computer Science Assessment
This year 9 computer science assessment could either be used at the start of the year to assess suitability or at the end to assess learning. Another option is to do both and measure student progress and impact of teaching. Students aspiring to student computer science at GCSE must aim to score between 30 and 75. Answers/ Mark scheme provided.

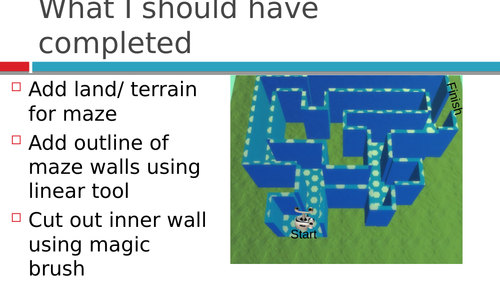
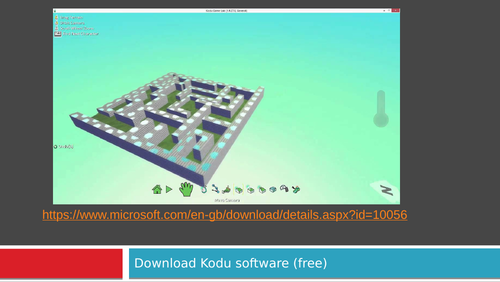
Kodu-Rhythm Lesson 4 (An introduction to coding using kodu)
Kodu is a friendly graphical programming language where students can build their own world and program objects within. This series of lesson uses kodu to introduce computer science terminology such as algorithm and variables to develop computational thinking skills.

What is an ALGORITHM
An introduction to algorithms using a flowchart with sequence, selection and iteration. The worksheet provided enables students to slow down their thinking to focus on each instruction in the algorithm until the last instruction is executed and the program ends.

Kodu-Rhythm Lesson 3(An Introduction to coding using Kodu)
Kodu is a friendly graphical programming language where students can build their own world and program objects within. This series of lesson uses kodu to introduce computer science terminology such as algorithm and variables to develop computational thinking skills.

Kodu-Rythm Lesson 2(An Introduction to coding using Kodu)
Kodu is a friendly graphical programming language where students can build their own world and program objects within. This series of lesson uses kodu to introduce computer science terminology such as algorithm and variables to develop computational thinking skills.

Kodu-Rythm Lesson 1(An Introduction to coding using Kodu)
Kodu is a friendly graphical programming language where students can build their own world and program objects within. This series of lesson uses kodu to introduce computer science terminology such as algorithm and variables to develop computational thinking skills.

Introduction to algorithms
A gentle and friendly introduction to algorithms with a simple worksheet to enable students to develop computational thinking. Understanding how algorithms work and how they are used by computers is fundamental to achieving success in GCSE computer science. This lesson introduces KS2 and KS3 students to algorithms. This lesson could be used alongside the algorithms in scratch series.

GCSE Computer Science Exam Revision: Topic 1
This comprehensive revision for GSCE computer science covers all the knowledge a student requires to achieve a top grade in the exam for computer architecture topic. Knowledge is structured into simple to understand slides, with concepts scaffolded into clear diagrammatic illustrations for students to self study. Non specialist teachers can use this PP to teach students vital knowledge they need to know for the exam. Also included are practice exam questions to familiarize themselves to the style of GCSE exam questions and also give them confidence in applying knowledge learned.

Scratch Exercises for computational thinking
Build students ability to make independent progress and think computationally with a range of programming skills using scratch. Students will learn vital keywords required as fundamental building block for computer science GCSE. Each exercise is independent of each other. Challenges range from simple to difficult and students are encouraged to consider and compare alternative solutions. Solutions for each challenge is provided, easy to follow and understand even for a non specialist teacher. This series of exercises is targeted at KS3 students, although KS4 students will also benefit from it as a revision tool for GCSE computer science. It is strongly advised that these exercises are used after students are taught fundamental skills from algorithms in scratch series.

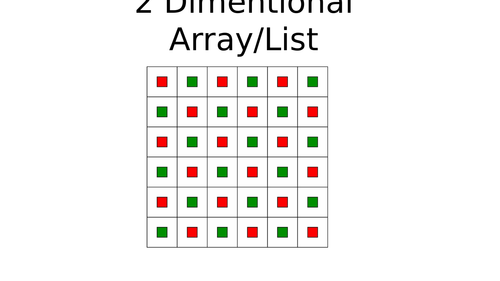
GCSE Computer Science 2 Dimensional Array: Illustration with (python) worked example exam question
This PP introduces 2 dimensional lists/ array, how items are stored and retrieved in memory, with practical exercises and worked examples using python. In addition, there is a practice exam question with python solution for students to try, which will support knowledge and build understanding.

Introduction to HTML & Web Design Lesson 1
Aimed at KS2 and KS3 students, this introduction to web design, using HTML is a structured practical approach to gaining fundamental knowledge required for ICT and computing courses at KS4. No expensive software required, effective and simple exercises. Clear objectives which identifies student level and assesses the student workbook provided.

Teaching Python Coding: An Exercise for GCSE Computer Science coursework preparation-Answers
This Power Point supports students preparing for GCSE computer science, using python code for notorious game rock paper scissors. Students are expected to examine the code by identifying variables, explaining the coding keywords, structure and approach. In addition, students are given the opportunity to test the code and come up with suggestions for improving the design. Solutions to all questions provided.

Python Coding Exercise for GCSE Computer Science coursework preparation
This Power Point supports students preparing for GCSE computer science, using python code for notorious game rock paper scissors. Students are expected to examine the code by identifying variables, explaining the coding keywords, structure and approach. In addition, students are given the opportunity to test the code and come up with suggestions for improving the design.

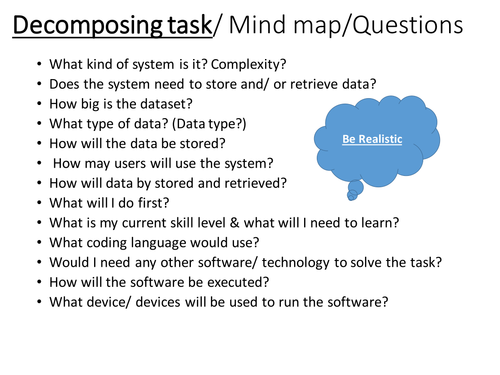
GCSE Computer Science example Project Walkthrough - Structure - Approach(NEA)
Undertaking a non examined assessment is an overwhelming task for both students and teachers. Providing the right type of support in terms of structure, approach and feedback, whilst adhearing to examining board rules and regulations is key. This PowerPoint provides a techer/ student discussion and walkthrough of a problem, to a possible solution. It also provides a structure for students to present their solution in an easy to mark format. Analysis, design, development and evaluation is covered. There is plenty emphasis on computational thinking and decomposing the problem to a managable size.

Computational thinking starters and plenaries
This set of computational thinking starters and plenaries will support the teaching of all aspects of computer science. Ranging from simple to difficult, a great way to develop students ability to think and prepare for new computer science curriculum.