34Uploads
42k+Views
26k+Downloads
Physics

Phases of the Moon
A PPT (02 +) with animated sequences that demonstrates how the shape of the Moon appears to change throughout the lunar month. During animations a bar appears under the navigation buttons that wipes across until the animation has finished; it can be paused. For the buttons to work, the macro security level has to be set to medium. This is very easy and only needs to be done once; it will not compromise your computer. Select then then select. This is for ver. 2002; it might be different for later versions. COMMENTS WILL BE MUCH APPRECIATED

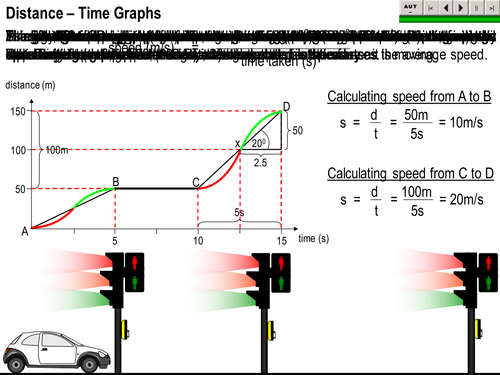
Distance Time graphs
A Distance - Time graph lesson with animated sequences that demonstrates the difference between average and instantaneous speeds. During animations a bar appears under the navigation buttons that wipes across until the animation has finished; it can be paused. For the buttons to work, the macro security level has to be set to medium. This is very easy and only needs to be done once; it will not compromise your computer. Select <Tools> then <Macro> then <Security> select<Medium>. This is for ver. 2002; it might be different for later versions. COMMENTS WILL BE MUCH APPRECIATED

Internal Combustion Engine
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the energy transfers that take place in an internal combustion engine.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do Internal Combustion Engines Work?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to identify the major components in an internal combustion engine
to identify the energy transfers that take place in an internal combustion engine
Synthesis
to construct a Sankey diagram
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Dispersion of White Light
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how white light is split-up into its component colours.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used with younger pupils and at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How Can Light Be Split Up Into Its Component Colours?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to identify the colours of the spectrum
to identify the colour of the spectrum that is refracted the most and the colour that is refracted the least
Comprehension
to explain how the amount of refraction produces the colour spectrum
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Rutherford-Bohr Atomic Model
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the structure of the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How Does Atomic Number Dictate Position In The Periodic Table?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to state the properties of sub-atomic particles
to define atomic number and mass number
Comprehension
to state the difference between group number and period number
Analysis
to calculate the number of neutrons from the mass number and atomic number
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Gravitational Potential Energy
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences using a roller coaster to show the transfer of gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy, and visa versa.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used for more able younger pupils or at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How Do Roller Coasters Work?
Learning Outcomes
Analysis
to calculate gravitational potential energy (GPE).
to infer the gain in kinetic energy (KE) from the amount of GPE transferred.
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Apollo 11 and the Moon Landing
A montage with music and narration that explores the political and technological developments during the cold war. A big file (15MB) , so please wait.
I tried to load it on the 40th anniversary of the Moon landing but the file was too big. Maybe the TES are able to accommodate bigger files now.
cold war
space exploration
moon landings
ussr
usa

Radioactive Decay
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the radioactive decay series of uranium 238.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
Why does uranium turn into lead in 4.5 billion years?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to recognise the effect that radioactive decay has on the atomic number and the mass number of a radioisotope
Analysis
to calculate the change in atomic number and mass number due to alpha and beta emissions
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

SONAR
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how SONAR uses ultrasound to detect objects underwater.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How can objects be detected underwater?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe how echoes can be used to detect objects underwater
to name some applications of SONAR
Comprehension
to explain why ultrasound is used for SONAR
Analysis
to calculate distances based on echo delay times
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Refraction
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how light is refracted as it changes speed at a boundary
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How is it possible to tell the difference between diamond and glass?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe how the change in speed of light at a boundary affects its direction
to recognise that light slows down by different amounts in different transparent materials
Analysis
to calculate the change in direction of light at different boundaries
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Electric Bells
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the workings of an electric bell.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 11 to 14 year old pupils. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do electric bells work?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to identify the components of an electric bell
Comprehension
to explain the sequence of events involved in the workings of an electric bell
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on a racing car.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
Can an object move if the forces acting on it are balanced?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to to identify the forces acting on a moving object
to describe the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on moving and stationary objects
Analysis
To calculate the size and direction of a resultant force
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Current in a Series Circuit
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how current behaves in a series circuit.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 11 to 14 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How does electricity work in a series circuit?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to identify the parts of a filament lamp
to describe the energy transfers that take place in a filament lamp
to state the number of charge carriers (electrons) at any point in a series circuit
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Acceleration of Freefall
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the derivation of the acceleration of a falling object due to gravity.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
By how much does a falling object accelerate?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe a method for determining the acceleration of a falling object
Analysis
to calculate the speed of a falling object
to calculate the acceleration of a falling object
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Sound Waves and Hearing
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the nature of sound waves and how the ear converts these into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 11 to 14 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level for the purposes of revision. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson .
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do we hear sounds?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe a sound wave in terms of particles and energy transfer
Comprehension
to explain the processes within the ear that lead to our perception of sound
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Strain Energy
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences using a crossbow to show how strain energy is calculated
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at over 16 year old pupils but could also be used for younger pupils. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do crossbows work?
Learning Outcomes
Comprehension
To state the relationship between:
energy, force and extension
force, the spring constant and extension
energy, the spring constant and extension
Analysis
to calculate the strain energy stored in a stretched object
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

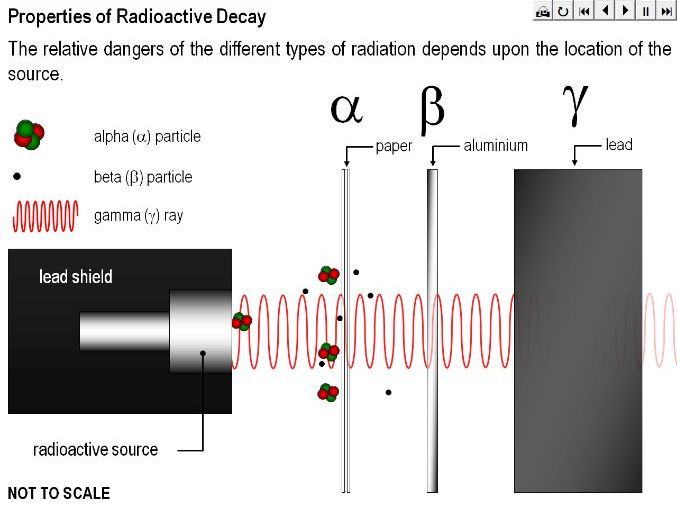
Properties of Radioactive Decay
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the properties of radioactive decay.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson but could be spread over two lessons if needs be.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
What are the Properties of Radioactive Decay?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe the three different types of radioactive decay
to state the penetrating properties of the different types of radioactive decay
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Controlling Current
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how a variable resistor controls current.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 11 to 14 year old pupils but can also be used at a higher level as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do Dimmer Switches Work?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to state how a variable resistor can control the total resistance of a circuit
to state how the total resistance of a circuit affects the current flowing through the components
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Polar Orbiting Satellites
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing how a polar orbiting satellite produces an image of the Earth.
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used for younger pupils as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
How do Spy Satellites Work?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to describe the motion of polar orbiting satellites relative to the rotation of the Earth and the Sun
to list the uses of polar orbiting satellites
Comprehension
to explain how polar orbiting satellites produce a two dimensional image of the three dimensional Earth
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.

Change of State
The main presentation is a PowerPoint with animated sequences showing the processes involved in changing from a solid to a liquid to a gas
Support Material
Readme (instructions for whole lesson)
Learning Outcomes (PowerPoint)
Starter Activity (PowerPoint and Worksheet)
Main Activity (PowerPoint with worksheets and answer sheets)
Lesson Notes (hand-out)
Plenary Activity (PowerPoint and worksheet)
It is intended for all science teachers but particularly those who are not physics specialists. It is, primarily, aimed at 14 to 16 year old pupils but can also be used for younger pupils as a precursor to a more in-depth study of this topic. Normally, the activities would fill a 45 to 60 minute lesson.
If you buy this resource, please print the Readme document as it contains the instructions and details of the files included.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are based on Bloom’s taxonomy of hierarchical classification: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The lesson title and learning outcomes are:
What processes are involved when substances change state?
Learning Outcomes
Knowledge
to define the processes whereby substances change state
to recognise the connection between particle motion and state
Differentiation
The activities have varying degrees of differentiation; please refer to the Readme document.