66Uploads
14k+Views
20k+Downloads
History

iGCSE Medicine Edexcel c1848-1948History (paper 2 - B2)
iGCSE medicine Edexcel series of lessons. This is a series of lessons that covers Edexcel’s iGCSE history B2 Changes in medicine, c1848–c1948.
Link to free content revision [https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12942792 ][https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12942792)
Link to (paid) exam lesson with answers to most regularly assessments: https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12941140
If there is exam question that is related to the lesson, it has been included at the end of the ppt, with the mark scheme. Updated with 2023 exam questions
The lessons are squeezed into 21 lessons:
1.1 Barriers to Progress
1.2 & 2.4 Nightingale and Scutari - 2r, Nov 2020, b
1.3 Dangers in surgery - 2b, June 2020, b
1.4 Problems and improvements in public health - 2b, June 2022, Cii
2.1 & 3.1 Pasteur and Koch - 2br June 2022, ©
2.2 Lister and impact of antiseptics - 2019, 2022
2.3 improvements in public health - 2021, 2022
2.5 Elizabeth Garrett and progress of women - 2021, 2022
3.2 Improvement in surgery - 2r, June 2019, Qb
3.3 Impact of Public Health Act, 1875
3.4 Science and medicine - 2.Nov 2020 Ci
3.5 Marie Curie
4.1 The Liberal Government’s public health measures
4.2 WW1 and medical treatment - 2r, June 2019, a
4.3 WW1 and surgery - 2019, 2020, 2021 & 2022
4.4 WW1 and women
5.1 Fleming, Florey, and Chain (penicillin) - 2019, 2021, 2022
5.2 WW2 and surgery - 2. Nov 2020, a
5.3 WW2 and women
5.4 WW2 and other medical developments - Nov & June 2021
5.5 NHS and its Impact
• Most of the lessons use the Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History Changes in Medicine, c. 1848 – 1948 book (ISBN 9780435185404).
• Each lesson begins with knowledge recall that is self-assessed.
• Relevant past exam questions are included, with mark schemes. Some questions have a choice of multiple different exam questions. For example, 4.3 WW1 eas examined in 2019, 2020, 2021 & 2022. All of these Qs have been included at the end of the ppt.
• There is also a Personalised Learning Checklist (PLC) that breaks the specification down into its constituent parts and tracks what exam questions have been asked for each topic. This reveals what topics seem to be asked multiple times and allows students to practise those questions.
• There is an A3 homework sheet to give out. The pupils will need access to YouTube. They watch a video about the topic and then write down a few bullet points. The idea is that they do this before they arrive to lesson, but it could be used as homework too.
#igcse #historyofmedicine

iGCSE superpower relations, 1943-72 Edexcel (paper 1 - 6) Cold War
Edexcel iGCSE A World Divided: superpower relations, 1943-72 (paper 1 - 6) Cold War.
This is a series of 20 lessons that covers iGCSE Edexcel history, paper 1, option 6 A World Divided: superpower relations, 1943-72.
Previous exam questions have been included in the relevant lesson, with the mark scheme.
Learning checklist clearly highlights the topics that are assessed most often
I have used Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History: A World Divided: Superpower Relations, 1943-72 Student Book ISBN: 9780435185442 to plan the series of lessons. You, or your students, will need that text book.
Lessons included:
1.1 Communism vs capitalism
1.2 Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam
1.3 USSR & E. Europe and attitudes of Stalin and Truman
2.1 Soviet expansion in Eastern Europe. Churchill and the ‘iron curtain’
2.2a Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan
2.2b Cominform (1947), Comecon (1949), NATO (1949)
2.3 Berlin Crisis (1948-49)
3.1 Korean War
3.2 Hungary & peaceful coexistence
3.3 international reaction to Soviet invasion
3.4 significance of arms race and Warsaw Pact
4.1 U2 incident and Summit Conferences
4.2 Causes and effects of Berlin Wall
4.3 Effects of the Berlin Wall
4.4a Cuba Bay of Pigs
4.4b Cuban Missile Crisis
5.1 The Thaw
5.2 SALT and treaty

iGCSE Edexcel The USA, 1918-41 History, (paper 2 - A3)
This is a series of lessons that cover the iGCSE Edexcel History paper 2 (A3) The USA, 1918-41.
The Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History The USA, 1918-41 Student Book (ISBN 978-0435185459) has been used throughout the ppts. You, or your students, will need access to this book.
Previous exams from 2019 to 2023 have been used throughout the lessons. I have matched them up by topic and included the mark scheme after. The exclusion of 2024 exams means you will be able to use this for any mock exams.
A learning checklist is included. This gives you an overview of the content and when it has been examined.
22 Lessons include:
1.0 America in the early 20th century
1.1 The economic benefits of the First World War
1.2 Causes of Boom
1.3 Old industries
1.4 Leisure industry
1.5 Women and flappers
2.1 attitudes and policies towards immigration
2.2 The Palmer raids and Red Scare
2.3 Sacco and Vanzetti
2.4 African Americans and KKK
2.5 Morals & values and Monkey Trial
2.6 Prohibition and organised crime
3.1a Wall St. Crash
3.1b Great Depression and causes
3.2 Hoover’s reaction to GD
3.3 Impact of the Great Depression - 2 lessons worth of work
4.1 Roosevelt
4.2 Second New Deal
4.3 Impact of Second New Deal
4.4 Rural electrification and Pros & cons of New Deal
5.1 Opposition to the New Deal
5.2 Radical criticism

iGCSE Edexcel Russia and the Soviet Union, 1905–24 (Paper 2 - A2)
This is a unit of lessons that iGCSE Edexcel History. This is for paper 2 and is (A2) Russia and the Soviet Union, 1905-24. The unit has been squeezed into 24 lessons. Where there is a relevant exam question, it has been included at the end of the lesson with the mark scheme:
1.1 Tsarist rule in Russia
1.2 1905 Revolution
1.2 exam questions (2a June 2021,a & 2r June 2019, c)
1.3 The first four dumas
1.4 Stolypin’s & Goldfield (2. 20 Nov a & 2a Nov 21, a)
2.1 Effects of WW1 on Russia
2.2 Influence of Rasputin
2.3a February Revolution - 2 lessons
2.3b army mutiny, Abdication & government (2a. June 2021, a)
3.1a Problems with the provisional government (2a June 2022, b&c)
3.1b the impact of the Petrograd Soviet
3.2a Lenin and the Bolsheviks (2r. June 2019, a)
3.2b Kornilov Revolt
3.3a Reasons for the success of the Bolsheviks
3.3b Lenin and Trotsky (2AR. June 2022, b&c)
4.1a Decrees and assembly (2. Nov 2020, Qa)
4.1b Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (2a. June 2021, b&c)
4.2 Sides and events of the Civil War (2AR. June 2022, a)
4.3 Reasons for the Bolshevik victory
5.1 War communism
5.2 The Kronstadt Naval Mutiny (2r. November 2020, a)
5.3a New economic policy
5.3b Opposition to the NEP (2. Nov 2020, Qb ;2a. June 2022, a)
5.4 Lenin’s achievements to 1924
Each lesson begins with five recall questions that are self assessed on the next slide.
There are three learning objectives for each lesson. These are displayed at the bottom of each slide.
This Unit of work uses the textbook that has been published by the exam board.
Title: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History: The Soviet Union in Revolution, 1905–24 Student Book
ISBN: 978-0435185435

iGCSE China: conflict, crisis and change, 1900–89 (Edexcel paper 2 - B4) history
igcse China (Edexcel paper 2 - B4)
This is a series of lessons that covers Edexcel’s iGCSE history B4 China: conflict, crisis and change, 1900-89.
Relevant previous exam questions are at the end of each lesson, along with the mark scheme.
Where printing is needed, this has been included as a separate document.
The lessons are squeezed into 25 lessons:
1.0 China in the 20th century
1.1 Boxer Uprising & late Qing Reforms
1.2 the causes, events, results of 1911 revolution (2.2020 Nov, a)
1.3 China under the Warlords
1.4 CCP, United Front, Soviet Union
1.5 Emergence of Chinese Communist Party
1.6 Northern Expedition, Shanghai mass (2b, June 2021, b)
2.1 The Long March (2r. June 2019 a)
2.2 War with Japan 1937-1945
2.3 Key features of the Civil War 1946-49 (2br. June 2022, b)
2.4 Cause of success (2b June 2021, Ci; 2br. June 2022, B)
3.1 Changes in agriculture (2r. June 2019; 2. 2020 Nov, b)
3.2 & 3.6 Changes in industry (2b June 2022, Cii)
3.3 Changes in the role of women (2b June 2022,a)
3.4 Political Changes
3.5 The Hundred Flowers Campaign
3.7 USSR influence (2b June 2022 Ci)
4.1 Causes of Cultural Revolution
4.2 Key features of the Cultural Revolution.
4.3 Impact of cultural revolution (2. 2020 Nov, Cii; 2br. June 2022, Cii)
4.4 Sino-Soviet split (2. 2020 Nov, Ci)
5.1 The rise and fall of ‘Gang of Four’ (2b. Nov 2021, b)
5.2 Changes under Deng (2b June 2021, Cii; 2r Nov 2020 Cii; 2br June 2022)
5.3 Deng’s opposition (2b Nov 2021; 2. Nov 2020; 2r Nov 2020)
5.4 Student opposition and Tiananmen Sq 1986-89 (2b June 2021, a; 2b June 2022, b)
• You/ your students will need Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History: Conflict, Crisis and Change: China, 1900–1989 Student Book (ISBN 978-0435185374) as many of the lessons use this textbook.
• Each lesson begins with knowledge recall that is self-assessed.
• Relevant past exam questions are included, with mark schemes, for each lesson. So, you will teach the lesson and, at the end of the lesson are past exam questions (where applicable).
• There is also a Personalised Learning Checklist (PLC) that breaks the specification down into its constituent parts and tracks what exam questions have been asked for each topic. This reveals what topics seem to be asked multiple times and allows students to practice those questions.

Cambridge IGCSE History B
iGCSE Cambridge (CIE) History Core Content B
This is a series of lessons that covers Core content: Option B
The twentieth century: international relations from 1919
This is the Cambridge iGCSE History (CIE)
• Each lesson starts with five recall questions that are self assess (answers are on the next slide)
• The lessons cover the spec for Core Content B, Cambridge iGCSE, for exams in 2024, 2025, and 2026
• Clear learning objectives in each lesson.
• NO TEXTBOOK is required for these lessons, but that does occasionally you need to print the materials that come with the lessons.
Lessons included:
1 Was the Treaty of Versailles fair?
1.1 aims of the Big Three
1.2 Treaty of Versailles
1.3 Political impact of ToV on Germany
1.4 Economic and social impact of ToV on Germany
1.5 Contemporary opinions about ToV
2 To what extent was the League of Nations a success
2.1 Structure of the League of Nations
2.2 Success and failures of the LoN
2.3 LoN’s humanitarian work
2.4a Manchuria (events and causes)
2.4b Manchuria (consequences)
2.4c Manchuria source questions
2.5a Abyssinian Crisis (events and causes)
2.5b Abyssinian Crisis Abyssinian consequences
2.5c Abyssinian source Qs
3 How far was Hitler’s foreign policy to blame for the outbreak of war in Europe in 1939?
3.1 Hitler’s Aims in foreign policy
3.2 Rhineland, Saar and rearmament
3.3 Spanish Civil War and Anti-Conmintern Pact
3.4 Appeasement and Rome-Berlin Axis
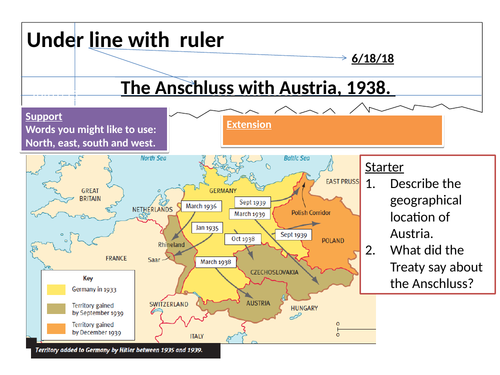
3.5 Anschluss
3.6 Sudetenland and Munich Agreement
3.7 Nazi-Soviet Pact
3.8 Why did peace collapse?
4 Who was to blame for the Cold War?
4.1 End of WW2
4.2 Yalta
4.3 Potsdam
4.4 Soviet expansion
4.5 USA’s reaction to Soviet expansion
4.6Berlin blockade and airlift
4.7 NATO and Warsaw
4.8 Who was to blame for the Cold War?
5 How effectively did the United States contain the spread of communism?
5.1 Causes of the Korean War
5.2 Events of the Korean War
5.3 Cuban Crisis
5.4 consequences of the Cuban Crisis
5.5 Vietnam
5.6 Involvement in Vietnam war
5.7 Events of the Vietnam War
5.8 Causes of the Vietnam War
5.9 Summary of Vietnam
6 How secure was the USSR’s control over Eastern Europe, 1948–c.1989?
6.1 Hungary
6.2 Resistance Czechoslovakia
6.3 Comparing and contrasting resistance in Hungary and Czechoslovakia
6.4 Berlin Wall
6.5 Poland and solidarity
6.6 Gorbachev

iGCSE Edexcel Germany: development of dictatorship: 1918-45 (paper 1, option 3)
This is a series of 24 lessons that covers the iGCSE Edexcel paper 1 Germany: development of a dictatorship. Where there is a relevant previous exam question, it has been included at the end of the lesson, including the mark scheme:
1.1 Establishment of Weimar Republic (1a. June 2022 a)
1.2 Reactions to the ToV (1a. November 2021 a)
1.3 Challenges from the left and right (1. November 2020 ci)
1.4 Economic problems and Ruhr (1. June 2019 a)
1.5 Hyperinflation (1a. June 2021 ci)
2.1 Stresemann at home (1r. November 2020 a)
2.2 Stresemann abroad (1. June 2019 b; 1. November 2020 b; 1a November 2021 ci)
2.3 How stable was the Weimar Republic
3.1 Hitler’s early career in politics
3.2 Munich Putsch (1a. November 2021 b)
3.3 Reorganisation of the Nazi Party, 1924-28 (1. June 2019 ci)
3.4 Great Depression (1a. June 2021 cii)
3.5 Nazi methods to win support & the role of the SA (1. November 2020 cii)
3.6 Events from 1932 to January 1933 (1a. June 2022 ci)
4.1 Steps to dictatorship
4.2a Nazi methods of control
4.2b Propaganda and censorship (1a. November 2021 (cii))
4.3 Social policies (1a. June 2021 a; 1a. June 2022 b)
4.4 Nazi racial policies (1r. November 2020 b)
4.5 Unemployment (1. June 2019 cii)
5.1 Nazi policies towards Jews
5.2 The Home Front (1. June 2021 b; 1a June 2022 cii)
5.3 Opposition to Hitler (1. November 2020 a; 1r November 2020 cii)
5.4 Hitler’s death and the end of the Third Reich
Each lesson begins with five recall questions that are self assessed using the answers on the next slide.
Included is a Personalised learning checklist. The spec is broken down into its smaller parts. Students can then RAG rate them. You will be able to see where topics align to exam questions on this document.
There are three learning objectives for each lesson. These are displayed at the bottom of each slide.
I have used the published textbook. If you don’t have it, you can easily swap out the page numbers for a different one. Textbook you need: Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History Development of Dictatorship: Germany 1918-45 Student Book *ISBN: 978-0435185381

AQA: First World War 1894-1918 entire unit
These lessons have been designed to be easy to follow.
Lessons follow the AQA (BA) Conflict and tension: The First World War, 1894–1918 , and include the following 26 lessons
Part one: The causes of the First World War
1.01 The alliance system (2022, Q3)
1.02 Moroccan Crises (S1, Q3)
1.03 Crisis in the Balkans (2018, Q3)
1.04 Splendid isolation
1.05 Wilhelm foriegn policy (2022, Q1)
1.06 European rearmament
1.07 Slav nationalism and Austro-Serbian rivalry
1.08 Assassination
1.09 July Crisis
1.10 cause of WW1
Part two: The First World War: stalemate
2.01 Schlieffen Plan & Belgium
2.02 Trenches and Marne (2020, Q3)
2.03 military tactics and technology
2.04 Verdun
2.5 Somme (S2, Q2)
2.06 Passchendaele
2.07 Haig
2.8 Gallipoli (2018, Q1)
2.09 War at sea
Part three: Ending the war
3.01 Russia leaves (2019, Q1)
3.02 USA enters WW1 (S2, Q1)
3.03 tactics and technology (2019, Q2)
3.04 Ludendorff Offensive (2021, Q4; S2, Q3)
3.05 Hundred Days
3.06 end of WW1 (2022, Q2)
3.07 Cause of Germany’s defeat (2018, Q2; 2020, Q4)
The lessons use the Oxford Conflict and Tension: First World War 1894-1918 book (9780198429005); HOWEVER, there is an alternative for every time the textbook has been included. You will just need to print the reading sheets.
The lesson clearly displays where an exam question has been used and includes the mark scheme.
All comprehension activities have the answers included on the next slide.
Lessons include links to YouTube for engagement.

Henry VIII's Reformation (unit of work - KS3)
Six lessons, plus assessment.
- Lesson 1: What was the Reformation?
- Lesson 2: Henry VIII’s Great Matter
- Lesson 3: Break with Rome
- Lesson 4: Religious transformation of England.
- Lesson 5: Wealth and power
- Lesson 6: Why did Henry VIII divorce Rome (assessment planning lesson)
- Lesson 7: Assessment
Most lessons include reading and links to engaging videos on YouTube.
Reading Packs
Three different reading packs (reading ages of 13, 10, and 8).
Answers are included for each reading pack to allow quick self-assessment.
SoW
A written SoW is included. The SoW breaks down each lesson into three learning objectives with activities connected to each objective. All activities are included on each PowerPoint. This unit includes self assessment, peer-assessment and teacher assessment at the final lesson.
This is a plug-and-play lesson. No additional planning is needed. Just print the reading packs. Where there is reading in a lesson the 13-year reading age has been included in the PowerPoint. It is easy to swap this out for the self assessment part of the lesson

Cause American Revolution (unit of work)
Causes of the American Revolution
These lessons have been designed to be plug and play. You could open the PowerPoint and begin teaching without any additional work.
#What’s Included?#
Seven lessons
Building an empire
Why go to America
American Revolution (including Boston Tea Party, Declaration of Independence, taxation without representation)
War of independence
Causes of the American Revolution
Causation lesson
Assessment
Knowledge organiser
The knowledge organiser is targeted at transferring key knowledge from short to long term memory.
Scheme of work
A written scheme of work that includes learning objectives along with suggested activities aligned to the learning objective.
A intention statement sets out the knowledge to be gained and also the importance of the second order concept of significance.
This topic is vital at KS3 for studying the American Civil War and later American units (like Civil War) at KS4.

iGCSE Edexcel revision lesson 3) Germany: development of dictatorship
Revision lesson for the iGCSE History paper 1 topic 3: Germany: development of dictatorship.
This lesson includes:
Power point with instructions, page numbers from the Published textbook (details below), self assessment.
You may need to zoom in and out of the powerpoint for the self assessment OR simply print off the answer sheet I have included.
There is an A3 sheet with the entire unit it. Again, you want want to print this as septerate pages.
Also included is a learning checklist. This is a list of what the spec says needs to be taught. Students then RAG rate it. There is a list of where to find exam questions for each section too.
This should be a plug and play lesson. It has been designed for an hour’s lesson but may take more depending on the ability of your children.
Textbook you need: Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) History Development of Dictatorship: Germany 1918-45 Student Book *ISBN: 978-0435185381
*

iGCSE Edexcel USSR, 1924-53 History (paper 1, option 5)
This is a series of lessons designed to meet the needs of learners completing Edexcel’s iGCSE Paper 1 (5) Dictatorship and conflict in the USSR, 1924 – 53
The spec squeezed into 24 lessons:
1.1 The Soviet Union in 1924
1.2 The rivals for leadership (1. Nov 2020, a)
1.3 Strengths & weaknesses of Stalin and Trotsky (1. June 2019, a)
1.4 Stalin’s steps to power (1a. June 2021 Ci; 1r. Nov. 2020 Ci)
2.1a Reasons for industrialisation
2.1b Nature of industrialisation
2.1c successes and failures of industrialisation
2.2a Collectivisation (1. June 2022 Ci; 1a. Nov 2021a)
2.2b Opposition to collectivisation
2.2c Success and failures of collectivisation (1a June 2021 b; 1r Nov 2020 Cii)
3.1 Purges and causes (1. June 2019, Ci; 1r. Nov 2020, a)
3.2a & c Key features and impact of the purges of the 1930s (1a. June 2021 a)
3.2b Control of the population
3.2d Purges armed forces (1a. June 2022 b; 1a. Nov 2021 Ci)
3.3 Cult of personality, censorship, propaganda
3.4 Education and the Soviet interpretation of history
4.1 Town & countryside (1. June 19, Cii; 1a. June 22, Cii; 1a. Nov 21, b)
4.2 Different experience of social groups (1r. Nov 2020 b)
4.3 Changes in education (1. November 2020, Cii)
4.4 Persecution of ethnic minorities (1. June 2019, Cii)
5.1a Soviet setbacks and survival (1. June 2019, b; 1. November 2020, Cii; 1a. June 21 Cii)
5.1b Stalingrad (1a June 2022 a)
5.2 Post-war
Each lesson starts with 5 recall questions that can be self assessed on the next slide.
Clear instructions for each activity
The textbook approved by the exam board (978-0435185466) has been used, along with some printable materials that compliment the textbook~
Learning objectives are clearly displayed on each slide
The titles of the PPT clearly indicate where an exam question has been used.
-All exam questions have mark scheme on the next slide.

iGCSE Edexcel Cause and course of WW1 (paper 1 - A1)
This series of lessons follows the iGCSE Edexcel History, paper 2 (A1) The origins and course of the First World War, 1905–18.
18 content lessons plus two exam lessons.
Each lesson uses the textbook, but there are reading alternatives too.
Lessons follow the specification published by Edexcel and included:
1.1 The alliance system
1.2 Economic and imperial causes of war
1.3 Military causes of war
2.1 Moroccan Crises
2.2 Crises in the Balkans
2.3 Balkan nationalism and Serbian rivalry
2.4 Assassination to war
3.1 Schlieffen Plan and reasons for its failure
3.2 Trenches and reasons for deadlock
3.4 Somme
3.5 Passchendaele
3.6 Haig
4.1 German threat at North Sea
4.2 U-boats
4.3 Gallipoli (2 lessons)
5.1 Ludendorff Offensive
5.2 Hundred Days
5.3 Cause of Germany’s defeat
2 exam lessons
Lessons include relevant exam questions with mark schemes
There is a learning check list for the students
There is also a learning checklist that matches up specification topic with exam questions.
There are two lessons that focus on the examination.
o One for B question. Examples, work for students to mark and then one to complete.
o One for C question. Example answers, work for students to mark and then one to complete.

Industrial Revolution SoW, KS3 (change and continuity)
This is seven lesson scheme of work, plus an assessment that focuses on the change and continuities of the Industrial Revolution. There is an additional lesson called What was the Industrial Revolution that is listed on TES that accompanies this SoW.
Each lesson contributes towards answering the question of how far was the Industrial Revolution a turning point?
There is an additional lesson that can be found here https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12888894 for FREE.
Steam engine (peer assessment at end).
Factory life
Agricultural revolution (group work lesson)
Urbanization
Transport (peer assessment)
Resistance to change
Pre-assessment lesson
Assessment
• There is a knowledge organiser included that is editable.
• Each lesson starts off with recall questions from the knowledge organiser. This is self assessed.
• Each lesson has three learning objectives.
• Lessons 5 and 1 have opportunities for peer assessment. The peer assessment slide has examples of WWW and EBI.
• Each lesson has an opportunity for peer assessment.
• All lessons, excluding agricultural revolution lesson, have a choice of reading age 12 or 10.
This has designed to be a plug and play style of lessons. No additional planning is needed, but all resources are editable.

Cause and course of WW1 Edexcel iGCSE revision lesson
This will take more than one lesson and could be used as a home work activity for content revision.
There are answer sheets in the same format as the worksheets. As this is a revision activity, the answers do not go into all of the details of the textbook.
This should be an easy plug and play lesson.

Cambridge iGCSE Russia, 1905 – 41 (depth study C)
This Unit of work covers the Cambridge (CIE) iGCSE Depth study C) Russia, 1905 – 41.
28 lessons are included.
Exam questions have been matched up to topics and are at the end of the ppts with the mark schemes.
Each lesson has three learning objectives.
No specific textbook needed. All printable materials are included.
Lessons covers the entire spec and include:
1.1 Tsarist rule in Russia
1.2 1905 Revolution
1.3 Attempts at reform
1.4a Effects of WW1 on Russia
1.4b Influence of Rasputin
1.5 March 1917 Revolution
2.1 Provisional Government
2.2 Failure of the Provisional Government
2.3a Lenin and the Bolsheviks
2.3b Bolshevik seizure of power
2.4a Civil War
2.4b Reasons for the Bolshevik victory
2.4c War communism
2.5a The Kronstadt Naval Mutiny NEED MULTIFLOW
2.5b New economic policy
2.6 Lenin’s death
3.1 Reasons for Stalin’s emergence as leader by 1928
3.2 Stalin’s use of Terror
3.3 Propaganda and official culture
3.4 the Purges
4.1 Causes of the modernisation of Soviet economy
4.2a five-year plans
4.2b Successes and failures of the 5 year plans
4.3a Collectivisation
4.3b opposition to collectivisation
4.3c Successes and failures of collectivisation
4.4 Different experience of social groups
4.5 Women int he USSR

America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877 (iGCSE history, Edexcel, paper 2, B1)
This is a series of lessons that cover Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (iGCSE) in History, paper 2, B1 America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877.
• Each lesson begins with knowledge recall that is self-assessed.
• Relevant past exam questions are included, with mark schemes, for each lesson (where applicable).
• There is a Personalised Learning Checklist (PLC) that breaks the specification down into its constituent parts and tracks what exam questions have been asked for each topic. This reveals what topics seem to be asked multiple times and allows students to practice those questions.
• No textbook is required. Printable reading materials provided.
Lesson titles include:
1.1 Tensions between large and small states
1.2 The significance of Shay’s Rebellion
1.3 The Connecticut Compromise
1.4a Founding Fathers – federalism
1.4b Founding Fathers - Bill of Rights
1.5 Constructionists
1.6 Jefferson’s Presidency
2.1 opposition to westward expansion
2.2a Louisiana Purchase
2.2b Transcontinental Treaty
2.2c Annexation of Texas
2.3 Missouri Compromise
2.4 Indian Removal Act
2.5 Settling the West
2.6 California Gold Rush
3.1 Compromise of 1850
3.2 Kansas–Nebraska Act
3.3 Economic origins of the division between Union and Confederacy
3.4 Causes of the American Civil War
4.1 The Civil War and Union victory
4.2 Role of military leadership
4.3 Naval blockade
4.4 Political leadership
4.5 The Emancipation Proclamation
4.6 Gettysburg, Vicksburg, and march through Georgia
4.7 Destruction of the Sothern economy
5.1 John and Reconstruction
5.2a Freedmen’s Bureau, Southern response and Black Codes
5.2b Civil Rights Acts and Amendments
5.3 Failure of Grant’s Peace Policy