484Uploads
144k+Views
63k+Downloads
Chemistry

GCSE Chemistry: Reactions of Acids
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Identifying metals on the periodic table
• Predicting the salt formed in acid metal reactions.
• Predicting the salt formed in acid carbonate reactions.
• Conservation of mass and state symbols

GCSE Chemistry: Electrolysis of Water
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pure water being made partially of ions (hydrogen and hydroxide).
• PANIC convention for electrodes
• OILRIG convention for redox reactions
• Electron transfers at electrodes
• Half-equations for anode and cathode
• Balancing half-equations

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Cations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Flame tests for lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, and copper.
Electron energy levels and emitting radiation.
Precipitate tests for iron(II)), iron(III), copper(II), calcium, and zinc.

OCR AS Chemistry: Structural Isomerism
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.4 Structural Isomerism
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition for Structural Isomers
Moving functional group to form isomers
Aldehydes and ketones being structural isomers
Skeletal formula and structural formula

OCR AS Chemistry: Properties of Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.1 Properties of Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Comparing pi-bond (π-bond) and sigma bonds (σ-bonds).
Aliphatic alkenes and alicyclic arrangements of molecules
s, p, d orbitals for electrons
Trigonal planar shape of alkanes leading to 120 degree bond angle.

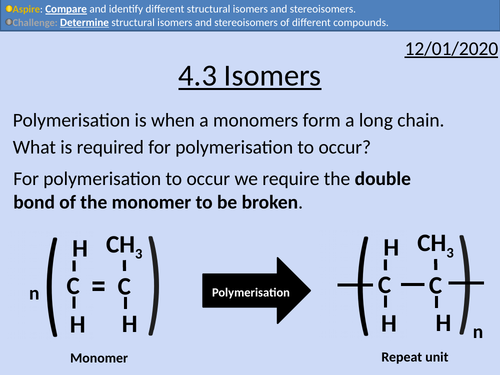
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.

OCR AS Chemistry: Electrophilic Addition in Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.4 Electrophilic Addition in Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electrophile molecules
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanisms for addition reaction of alkenes and hydrogen halides
Carbocations and stability
Markownikoff’s Rule
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Haloalkanes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Haloalkanes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Naming Haloalkanes
Classifying Haloalkanes (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanism for hydrolysis
Rates of reactions for hydrolysis
Reaction conditions for hydrolysis
Definitions for CFC (Chlorofluorocarbons) and HCFC (Hydachlorofluorocarbons)
Creation of ozone
Depletion of ozone with CFCs
Reaction steps including initiations and propagation

OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming Haloalkanes
Classifying Haloalkanes (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanism for hydrolysis
Rates of reactions for hydrolysis
Reaction conditions for hydrolysis

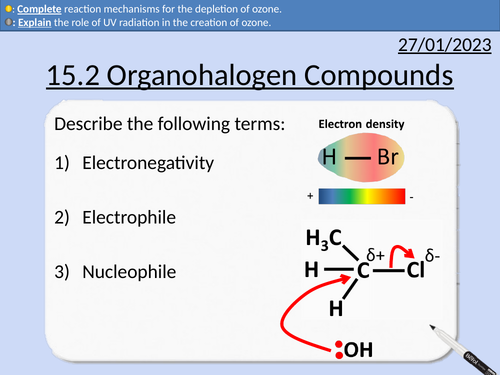
OCR AS Chemistry: Organohalogen Compounds
OCR AS Chemistry: 15.2 Organohalogen Compounds and the Environment
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definitions for CFC (Chlorofluorocarbons) and HCFC (Hydachlorofluorocarbons)
Creation of ozone
Depletion of ozone with CFCs
Reaction steps including initiations and propagation
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Naming alcohols
Classifying alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Polar and non-polar molecules
Explaining physical properties of alcohols compared to alkanes
Volatility
Solubility
Melting points
Chain length and London forces
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

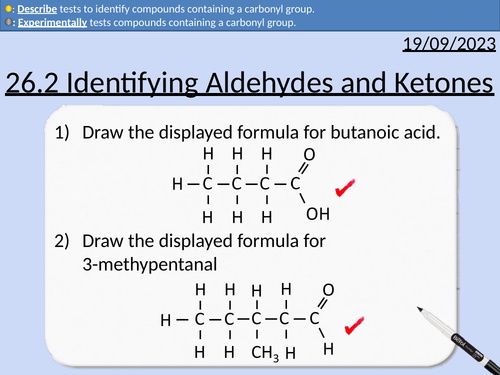
A level Chemistry: Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.2 Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Testing for Carbonyl Groups
Brady’s reagent - 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine - 2,4-DNP
Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones
Tollen’s reagent - silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia
Bundle

OCR A Level Chemistry: Module 6 Organic Chemistry and Analysis
This bundle includes all PowerPoint lessons for Module 6 Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All PowerPoints are whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
C25 Aromatic Chemistry
Introducing Benzene
Electrophilic substitution Reactions
The Chemistry of Phenol
Directing Groups
C26 Carbonyls and Carboxylic Acids
Carbonyl Compounds
Identifying Aldehydes and ketones
Carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acid derivatives
C27 Amines, Amino Acids and Polymers
Amines
Amino acids, amides and chirality
Condensation Polymers
C28 Organic Synthesis
Carbon-carbon bond formation
Further Practical Techniques
Further Synthetic Routes
C29 Chromatography and Spectroscopy
Chromatography and functional group analysis
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
Interpreting NMR Spectra
Combining Techniques
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.1 The Particle Model
All resources for P1.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model

OCR Applied Science: 6.2 Physico-chemical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Structure of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Properties of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Forces and bonds of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Phase diagrams – interpreting and calculating changes.
Sublimation and phase diagrams.

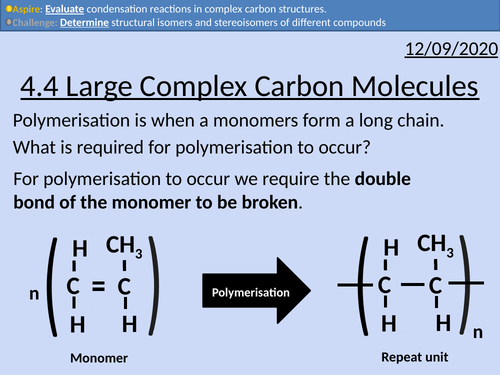
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

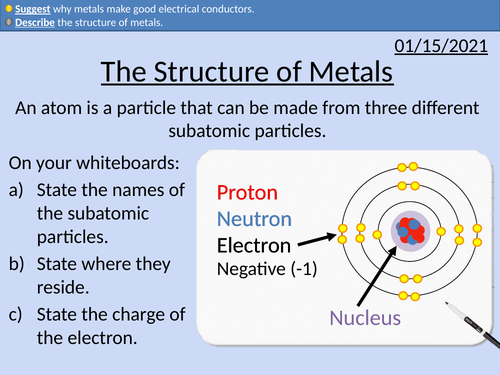
GCSE Chemistry: The Structure of Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State a use for metals
• Describe the structure of metals
• Why metals make good electrical conductors.
• Metals on the periodic table

GCSE Chemistry: Group 1 - Alkali Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Alkali Metals
• Properties of Alkali Metals
• Trends and anomalies in Group 1 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 1 Alkali Metals
• Electron configuration of Group 1 Alkali Metals
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
All resources for P4.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Group 7 - The Halogens
Halogen Displacement Reactions
Group 0 - The Noble Gases
The Transition Metals
Reactivity of Elements

GCSE Chemistry: Biological Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Proteins as polymers and amino acids as monomers
Carbohydrates and simple sugars
Comparing simple sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose) with complex carbohydrates (starch).
DNA as a polymer and nucleotides as monomers
Structure of nucleotides (phosphate group,
a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base).
Base pairing in DNA and hydrogen bonds