39Uploads
5k+Views
2k+Downloads
Geography

End of term Geography quiz 2024
A seven round quiz with 10 questions per round, and answers (70 questions total). The rounds are mixed difficulty so it is suitable for all ages.
Rounds:
Unusual Geography
World food
Cultural Geography
Currency
World landmarks
Artists and bands
Famous explorers

CIE GCSE Geography paper 4 unit of work
This unit covers everything the students need to know for Cambridge IGCSE paper 4 (alternative to course work). It includes teaching material plus loads of real exam practice questions (and mark schemes) for each question.
Topics covered:
Human
Hypothesis and aims
Describing relationships between variables
Primary vs secondary data examples
Surveys
Questionnaires
**Weather **
Instruments
Types of clouds
Measuring rain
Plotting data
Stevenson screens
Rivers
Velocity
Channel cross section
Equipment
Cross section
**Coasts **
Equipment
Longshore drift
Velocity/direction
Beach transects

CIE IGCSE Geography Theme 2 revision booklet
A guided revision booklet covering Cambridge International GCSE Geography, Theme 2 The natural environment.
For each topic there are learning objectives, the ‘Bare Necessities’, key terms diagrams, and guided spaces to for students to complete.
This is a 51 page booklet covering:
Earthquake and volcanoes
Rivers
Coasts
Weather
Climate and vegetation
Plus a list of all of the recent 7 mark questions for Theme 1.

CIE GCSE Geography Theme 3 - All Lessons for Economic Development
This is a full set of high quality resources and includes power points, c resources, exam questions, skills questions (OS Maps). The lessons are varied with activities such as group work, pair work, research tasks etc. Ready to pick up and teach - no extra planning needed.
Covers:
3.1 Development
3.2 Food production
3.3 Industry
3.4 Tourism
3.5 Energy
3.5 Water
3.7 Environmental risks of economic development
Bundle

Cambridge IGCSE Geography - entire course (power points, activities etc.) for paper 1, 2 and 4)
These resources cover the entire Cambridge IGCSE Geography course, paper 1, paper 2 and paper 4 (alternative to course work).
These high quality resources are successfully tried and tested in the classroom, with excellent results.
This includes everything you need to download and go…not extra planning. Powerpoints, worksheets, assessments and revision guides all included.

SOW: Our Oceans for KS3 Geography (threats, exploration, conservation, plastic)
A complete 12 lesson scheme of work (plus assessment) fully resourced with power points and activities ready to go. Ready to pick up and teach.
Activities include (but not limited to)
card sorts
research
presentations
creative design
persuasive writing
Topics
introduction to the oceans
Ocean ecosystems
Coral bleaching
Ocean zones (plant and animal adaptations)
Oceans conservation and sustainability
Plastic and the oceans
Ocean exploration
Case study: the Maldives
Assessment
Some of these are double lessons, many have options to expand learning beyond.

CIE IGCSE Geography Theme 1 revision booklet
A guided revision booklet covering Cambridge International GCSE Geography, Theme 1 Population and Settlement.
For each topic there are learning objectives, the ‘Bare Necessities’, key terms diagrams, and guided spaces to for students to complete.
This is a 37 page booklet covering:
1.1 population dynamics
1.2 Migration
1.3 Population pyramids
1.4 Population density and distribution
1.5 Settlement and service provision
1.6 Urban settlements
1.7 Urbanisation
Plus a list of all of the recent 7 mark questions for Theme 1.

Booklet of all case studies: CIE GCSE Geography paper 1
A collection of all of the information students need to answer every 7 mark question on Cambridge IGCSE paper 1.
Includes:
Theme 1
A country which is over-populated.
A country which is under-populated
A country with a high rate of natural population growth.
A country with a low rate of population growth (or population decline)
An international migration.
A country with a high dependency ratio
A densely populated country or area (at any scale from local to regional).
A sparsely populated country or area (at any scale from local to regional).
Settlement and service provision in an area.
An urban area (including changing land use and urban sprawl).
A rapidly growing urban area in a developing country and migration to it.
Theme 2
An earthquake
A volcano
The opportunities presented by a river, the hazards associated with it and their management.
The opportunities presented by an area of coastline, the hazards associated with it and their management.
An area of tropical forest
Deforestation of a tropical rainforest
An area of dry desert
Theme 3
A farm or agricultural system
A country or region suffering from food shortages
An industrial zone or factory.
An area where tourism is important.
Energy supply in a country or area
Water supply in a country or area.
An area where economic development is taking place and causing the environment to be at risk.
Know a case study of a transnational corporation (TNC) and its global links.

CIE GCSE Geography Paper 2 - entire unit of work
These resources cover the entire Cambridge international GCSE paper 2 for map and graph skills.
It includes powerpoints, worksheets and exam practice. This is ready to download and teach - no extra planning needed.

Geography top trump cards
Printable country top trump cards - great for a reward in class, or for fast finishers!
32 countries, the cards include the population, area, GDP, life expectancy, and HDI.
Print double sided for professional looking top trumps card your students will love!
You can print as many sets as you need!

1.1 Population dynamics (Part 1 of CIE Theme 1)
Includes lessons, activties and exam practice questions for:
Describe and give reasons for the rapid increase in the world’s population.
Understand the causes and consequences of over-population and under-population.
Understand the main causes of a change in population size.
Know a country which is overpopulated and a country which is under-populated.
Give reasons for contrasting rates of natural population change
Know a case study of a country with high rate of natural population growth and a country with a low rate of population growth (or decline).
Full set of resources ready to pick and up and teach

Plastic Apocalypse: The Effects of Plastic Pollution on Our Oceans
This is a stand alone lesson, or can be used as part of a SOW on oceans or sustainability.
It covers:
An introduction into what plastic is.
True or false for surprising facts.
A card sort to show a time line of how single use plastic ends up in the oceans.
The impacts of plastic in the Oceans.
Extended writing: persuasive piece.
Full power point and resources ready to pick up and teach.

CIE GCSE Geography Theme 2 (The Natural Environment): All Lessons/ Entire SOW
Cambridge IGCSE Geography Paper 1, Theme 2.
This is a full set of high quality resources - power points, print outs, exam questions, all case studies. The lessons include engaging and varied activities such as group work, pair work, student presentations, research tasks, videos, debates, card sorts and more. Ready to pick up and teach - no extra planning needed.
2.1 Earthquakes
2.2 Volcanoes
2.3 Earthquakes
2.4 Rivers
2.5 Coasts
2.6 Weather
2.7 Climate and Natural Vegetation

1.5, 1,6, 1.7 Theme 1 CIE GCSE Geography full lessons (Settlement, urban settlements, urbanisation)
Full set of high quality resources - powerpoints, print outs, exam questions, skills questions (OS Maps)
Covers:
-settlement patterns
site and situation
settlement heirarchy
Population threshhold/sphere of influence
Problems in urban areas
Urban Sprawl
Regeneration
Causes and impacts of urbanisation (push and pull)
Case studies: settlement heirarchy (manchester), problems in urban areas (manchester), urbanisation (Rio)

ESS IBDP 8.3 : Solid domestic waste unit of work
Complete, high quality lessons covering environmental systems and societies unit 8.3: solid domestic waster. Ready to pick up and teach, no extra planning needed and exam practice included.
Different types of solid domestic waste
The abundance and prevalence of non-biodegradable pollution
The linear vs circular economy
Waste disposal options include landfills, incineration, recycling
and composting.

ESS (IBDP) 1.2 Systems and models unit of work
Full lessons for IB ESS topic 1: ready to pick up and teach - no extra planning needed.
Covers:
• A systems approach should be taken for all the topics covered in the
ESS course.
• These interactions produce the emergent properties of the system.
• The concept of a system can be applied at a range of scales.
• A system is comprised of storages and flows.
• The flows provide inputs and outputs of energy and matter.
• The flows are processes that may be either transfers (a change in location)
or transformations (a change in the chemical nature, a change in state or a
change in energy).
• In system diagrams, storages are usually represented as rectangular boxes
and flows as arrows, with the direction of each arrow indicating the direction
of each flow. The size of the boxes and the arrows may be representative of
the size/magnitude of the storage or flow.
• An open system exchanges both energy and matter across its boundary
while a closed system exchanges only energy across its boundary.
• An isolated system is a hypothetical concept in which neither energy nor
matter is exchanged across the boundary.
• Ecosystems are open systems; closed systems only exist experimentally,
although the global geochemical cycles approximate to closed systems.

KS3 Map skills full unit
This is a full unit of work, including any hand outs, for a year 7 or 8 unit of work on map skills. It covers one half term. It is based on the IB middle years programme framework, but it is suitable for any classroom. Includes assessments and marking rubrics.
Topics
compass directions
coordinates
scale (model building project)
relief
map symbols
fieldwork - conducting a school survey
critical thinking: can we trust maps?
Assessment: design a fictional map, with optional literacy link

3 Lesson Geography project for KS3: design a virtual fieldtrip
This is a three lesson project perfect for year 6, 7, 8 or 9 Geography. It includes a powerpoint with all of the needed instructions for each lesson, and a planning document for students to use.

ESS (IBDP) 8.2 Resource use and society unit of work
Entire unit of work for Environmental systems and societies topic 8.2: resource use in society. Full lessons ready to teach: no extra planning needed.
This resource covers:
Renewable natural capital can be generated and/or replaced as fast as it is
being used. It includes living species and ecosystems that use solar energy
and photosynthesis, as well as non-living items, such as groundwater and the
ozone layer.
• Non-renewable natural capital is either irreplaceable or can only be replaced
over geological timescales; for example, fossil fuels, soil and minerals.
• Renewable natural capital can be utilized sustainably or unsustainably. If
renewable natural capital is used beyond its natural income this use becomes
unsustainable.
• The valuation of natural capital can be divided into the following two
main categories.
• The impacts of extraction, transport and processing of a renewable natural
capital may cause damage, making this natural capital unsustainable.
• Natural capital provides goods (such as tangible products) and services (such
as climate regulation) that have value. This value may be aesthetic, cultural,
economic, environmental, ethical, intrinsic, social, spiritual or technological.
• The concept of a natural capital is dynamic. Whether or not something has
the status of natural capital, and the marketable value of that capital varies
regionally and over time and is infuenced by cultural, social, economic,
environmental, technological and political factors. Examples include cork,
uranium and lithium.

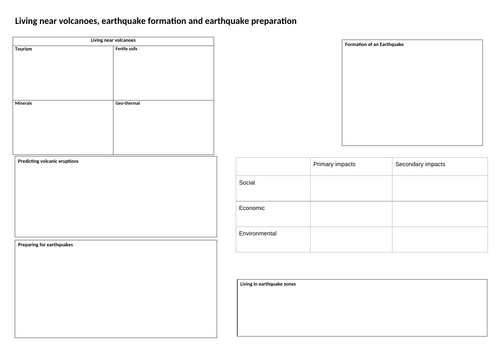
Blank GCSE knowledge organiser: Earthquakes
A guided revision resource - blank knoweldge organiser covering earthquake formation, living near earthquakes and earthquake preparedness.
As this is a free resource, if you find it useful it would be a great help if you could leave me a review! Thanks!