524Uploads
220k+Views
119k+Downloads
All resources

Halloween maze game
Using directions to guide pupils through a maze from the haunted house back to their home
In this fun Halloween maze game for kids, students will give each other instructions so that they can successfully navigate a Halloween table maze. This activity provides an engaging and practical way to test KS1 students’ maths knowledge as they will need to use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction, and movement.
This is one of a set of resources developed to support the teaching of the primary national curriculum. They are designed to support the delivery of key topics within maths and science. This resource focuses on developing understanding of geometric directions and involves giving verbal instructions to allow learners to successfully complete a table maze.
Clear instructions and correct vocabulary are important to ensure that the learners know how to complete the maze. This activity could be used as a starter or main activity to introduce geometry, position, and direction.
This activity needs to be carried out in pairs. One member of the pair will give instructions, the other will use those instructions to navigate the maze. The learner being given the instructions must wear a blindfold.
Tools/resources required
Projector/Whiteboard
Make a maze with tables or use masking tape or other suitable method of marking out the maze layout.
Blindfolds
The engineering context
When engineers program robots they need to be very clear in their instructions to avoid any confusion. For example, the Mars Rover must follow very detailed instructions to help it move safely on the planet and send back pictures.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity students will be able to follow a set of verbal instructions to successfully navigate a maze, they will understand the importance of clear instructions when instructing others and they will be able to use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Parachuting presents
How to make a toy parachute activity.
In this Christmas STEM activity, kids will use items found at home to make two parachutes and test which one is faster. They will learn about gravity, air resistance and more.
Download the STEM activity sheet for free. If you’re up for an extra activity, help our present find its way back to Santa’s sleigh through the maze.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Winter scavenger hunt
**This is a great outdoor activity for kids to learn about the change of seasons and the natural environment around them. **
The free printable activity sheets are provided for children aged 5 to 14. There is a wide variety of wildlife and plant life for kids to spot while wandering through the woodland or countryside looking for items to match the pictures. Along with the pictures, there are science questions and ideas for children to think about.
This scavenger hunt helps children develop their scientific knowledge by encouraging them to observe and identify different species of plants, animals, and insects. This can help students learn about ecosystems, food chains, and animal adaptations, among other topics.
It promotes gentle physical activity and fitness by encouraging children to walk while searching for items on their lists.
It will give children the opportunity to learn about the science of winter, including animal adaptations, weather patterns, and seasonal changes. They are also a great way of fostering a sense of teamwork and collaboration as kids work together to find and collect all the items.
The science context
Winter scavenger hunts can create engaging and interactive learning experiences that encourage curiosity, observation skills, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of scientific concepts. It allows children to become active participants in their own learning, igniting their passion for science and cultivating the next generation of scientific thinkers.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of the activity, kids will have gained a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the role that science plays in understanding it. The activity can also help to teach geography lessons by encouraging kids to explore different landscapes and geographical features, such as rocks and bodies of water.
We have a choice of three different winter scavenger hunt games for you to download, for 3-6, 5-11 and 11-14 year olds. Each game asks a series of questions, so there is also a corresponding answer sheet to download. Make sure the participants wrap up warm!
Going for a walk on or around Christmas? Please do share your pictures of what you find on your winter scavenger hunts with us on social media on Facebook and Twitter using our #SantaLovesSTEM hashtag. You can also send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Animal graphics project
Learn about simple mechanisms and make an animal that moves in this fun and creative activity for kids!
Students will use templates to help them cut out the parts for a DIY cardboard animal, and they will make the parts of a simple mechanism using cams and linkages, which will be attached to a round shaft made from a skewer; This will allow the legs of the animal to move up and down slowly.
This activity could be used as a main lesson activity to teach learners about simple mechanisms and how the direction of motion can change from rotary to reciprocating.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to support the delivery of key topics within science and design and technology, which could be carried out individually or in pairs. The teacher presentation could be left on the whiteboard as a supporting guide as they do this. Learners may need assistance cutting the cardboard to ensure the cuts are accurate.
As an optional extension activity, learners could add their own designs to their animal’s body and legs. Keeping the white paper template stuck to the legs allows them to be decorated as desired.
Tools/resources required
Card tubes
Wooden skewers
Glue sticks/ glue
sticky tack
Cardboard
Brass split pin fasteners
The engineering context
Mechanisms are used in almost every moving product, ranging from trains and cars to washing machines and door handles that must be pushed down to open, see-saws and scissors. They either transmit motion or change it in some way, increasing or decreasing its strength, quality, or type.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to understand that a linkage and cam can create movement, they will be able to make an amazing animal from graphics materials, and they will be able to use cams and linkage to make the legs move on the amazing animal.
Download the Animal graphics project activity sheet for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Christmas emoji
Design an emoji that reflects the festive season in this fun graphics activity
In this fun and creative activity, learners will use the theme of the festive season to design an emoji. They will think about what the festive season means to them and list their favourite things about this time of year. They will then use this list to sketch initial ideas for their own emoji before producing a final design that could be used on a phone or computer.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use the theme of the Christmas period to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, and Engineering.
This activity could be used as a main lesson activity to teach about sketching skills, following a brief and the use of modern communications technologies. It could also be used as part of a wider scheme of learning focusing on the design process or as a one-off transition activity.
Resources required
A round coin (e.g. two pence or ten pence)
A4 or A3 paper
Graph paper (or sheet from the resource)
Pencils, coloured pencils, paints and/or felt tip pens
A fine-liner pen for detailing on sketches
A pair of compasses or round object to draw large circles (e.g. a drinking cup or mug)
The engineering context
The development of ideas is fundamental to the work of the engineer working to solve a problem. To be able to work to a brief is the start of all engineering problem-solving activities.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will know the purpose of emojis, they will be able to understand how to design an emoji using a given theme, and they will be able to sketch with confidence!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved U.K. nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your emojis with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Jingle bells density science experiment
In this this fun Christmas STEM experiment, we see the effect that density has on objects and make some jingle bells dance!
Download the STEM activity sheet below for free. If you’re up for an extra activity, help our jingle bell finds its way back to the Christmas tree in our maze.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Make a homemade paper cone Christmas tree
Get kids thinking about 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional shapes, as well as faces, edges and vertices.
In this easy activity we are going to make paper cone Christmas trees which are fun to decorate and make a great centrepiece for any Christmas table.
Download the STEM activity sheet below for free, And if you’re up for an extra activity, try our wordsearch where you look for words used in the experiment to increase sticky learning.
Please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Microwaves and health
Explore the risks associated with exposure to microwaves
Living in a highly technological world, where access to information and entertainment is at our fingertips, the Inform and Entertain Me topic is a gateway to engage and introduce students to the principles and technology that form the basis for communication devices that are used in our everyday lives.
Activity info, teachers’ notes and curriculum links
This engaging activity allows students to explore the hazards and risks associated with exposure to microwaves. A microwave monitor is used to measure the microwave radiation from a microwave oven and a working mobile phone at a range of distances.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Download the activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
And please do share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation

Christmas cracker jokes
Use a net to make a booklet, adding funny cracker jokes and designs to the pages where needed in this festive activity for kids.
This activity could be a main lesson to teach learners how to use nets to make useable objects. It could also be used as one of several activities within a wider scheme of learning focusing on understanding the use of nets in maths.
The testing of the jokes could be linked with learning in English, as they involve writing and oral expression of the cracker jokes.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use Christmas themes to support the teaching of the primary National Curriculum. They are designed to support the delivery of key topics within maths and design and technology. This resource focuses on the use of a net to make a small booklet of funny cracker jokes, and these could be used as an alternative to the corny jokes often found in Christmas crackers!
Nets are important as they allow 3D objects to be made when folded.
Making the booklet:
Step 1 – Download the That’s a Cracker activity sheet. Identify the solid and dotted cutting lines.
Step 2 – Add the Christmas jokes.
Step 3 – ⚠ Safely cut out the booklet net using scissors.
Steps 4a and 4b – Fold the booklet as directed.
Step 5 – Now test out the jokes on friends!
As an optional extension activity, students could create and add their own designs and jokes to the booklet pages.
How long will this activity take?
This activity will take approximately 40-60 minutes to complete.
The engineering context
Engineers must regularly use mathematics knowledge and skills as part of their everyday job. They use nets to make scale models of buildings and other structures, as well as packaging for other products.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will know that graphics products can be made from nets, they will be able to add text to a graphic product, and they will be able to make a booklet from a net.
Download all the Christmas cracker jokes activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your classroom highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

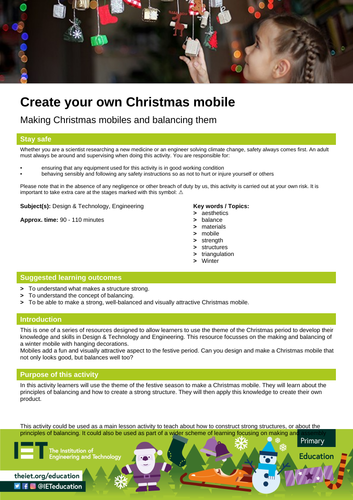
Create a Christmas mobile
Get creative with crafts this Christmas and build a beautiful mobile inspired by the winter holidays
A versatile lesson for teaching about constructing robust structures and the principles of balance. It can be incorporated into a broader curriculum on design and technology, emphasising making and assembly skills.
Learners will be encouraged to collect a variety of natural materials that they can use to craft a Christmas mobile. This homemade mobile will make a great sustainable Christmas decoration for the home or classroom.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow students to use the theme of the Christmas period to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, and Engineering.
The IET Education resource: Homemade Christmas decoration can be combined with this activity to create one of the hanging ornaments.
The time and resources required for this activity will vary depending on the types and quantities of decorations. We recommend using one of the following suggestions to make your mobile:
Fir/pine cones - Cones that have been collected previously and allowed to dry out are the best. They take paint well if dry and can look effective with decoration. Keep the hanging loops long.
Small fir trees - These are simple to construct.
Clay star - This will be a heavy element for the mobile. The impact of different weights on the mobile should be considered. Bolts do not have to be used if not available.
Pipe cleaner star - Learners may need additional assistance with measuring the length of the pipe cleaner to split it into five.
Using natural materials will give a unique, designer effect, but shop-bought decorations can be mixed in if time is short.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to understand what makes a structure strong, they will be able to understand the concept of balancing, and they will be able to make a strong, well-balanced and visually attractive Christmas mobile.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your inspiring creative crafts with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.
https://education.theiet.org/primary/teaching-resources/create-your-own-winter-mobile/

Make salt dough Christmas decorations
In this Christmas STEM activity, kids can make their own decorations using salt dough, in any shape they like!
They can even paint them and unlike normal baked goods, they will last a very long time.
Baking is a great way for kids to learn about science and maths in a fun and rewarding way, so get your aprons on!
Download the STEM activity sheet and watch our video for step-by-step instructions. If you’re up for an extra activity, help our ornament find its way back to the Christmas tree in our maze.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Make electric dough
In this fun science activity for kids, students will make play dough that can insulate or conduct electricity.
Make colourful dough with salt and another with sugar to find out which one will work! Through this process they will learn about conductors and insulators. Students will also learn about ionic bonding.
This is a resource that encourages learners to have fun with science. An activity sheet is available to download for free.
We have also included a bonus wordsearch using terminology from the activity to promote sticky learning.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your experiment highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM

Best Christmas wrapping paper experiment
Evaluate strength and durability of materials that Santa could use as wrapping paper
This fun and festive activity is suitable for 5-11-year-olds and will take approximately 1-2 hours to complete.
What equipment will you need?
At least six different types of wrapping paper. You can use more if you like (try and find ones which feel and look different, such as shiny metallic paper or tissue paper.),
Some tape for wrapping,
A large bin liner or a Christmas sack if you have one
Five bricks/ large stones of equal size. (It works best if they aren’t perfectly smooth or round.)
How to do it
Step 1 – Wrap up each brick or stone with a different piece of wrapping paper. These will be your ‘presents’.
Step 2 – Put them all in the sack together.
Step 3 – Ask an adult to act as Santa and shake the sack for 30 seconds as though carrying it around. You could sing Christmas songs while you are doing it.
Step 4 – Take each ‘present’ out and look at it carefully. Record any changes in the wrapping paper on a results sheet. These are your observations.
Step 5 – Put them all back into the sack and get your helper to shake them again.
Step 6 – Complete step 5 another three times (if your presents survive the shaking!). Record any changes each time.
Once you have determined which paper would be best, you could write a letter (or even a poem) to Santa to let him know how you tested the paper and which paper you think he should use. You can also look at packaging materials to see which protects items delivered by courier or the post the best.
For full instructions, download the worksheet and lesson plan for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your experiment highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Make a woven bag
Use recycled materials to produce a basket/bag that can be used to store small items or presents for Christmas.
In this fun activity for Key Stage 2, students will develop their knowledge and understanding of the weaving process and how it can be applied to make products. This is a challenging exercise that requires dexterity.
This activity could be used as a main lesson activity to teach about the skills and techniques associated with making textile products using weaving. It could also be used as part of a wider scheme of learning focusing on environmental issues within design and technology.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use the theme of the festive season to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, and Engineering.
Recycling helps to reduce the number of new materials we need to make products. Your challenge is to use recycled paper to make a great-looking and strong woven storage basket for Christmas.
Download our free activity sheet for a step-by-step guide on how to make your own woven bag!
Tools/resources required
Recycled paper
Scissors
PVA glue
Skewer or dowel
Empty card box
The engineering context
Engineers must understand the environmental impact of the designs they produce and how their carbon footprint can be reduced, for example, by using recycled or reused materials more.
Structural engineers must understand how to utilise weaker materials to create more robust structures, such as using rope to make bridges.
Weaving is an essential skill for textile designers and engineers.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to apply the process of weaving to create a basket, understand how strong structures can be created from weaker materials, and understand the benefits of using recycled materials to make products.
Download the Make a woven bag activity sheet for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Sustainable lighting design
Design and make a sustainably powered light
This fun engineering project for KS3 will allow students to embrace sustainable engineering as they learn to combine scientific principles with artistic flair to craft their unique and planet-friendly light.
This activity could be used as a main lesson to teach about the benefits of using renewable energy and how it can help solve social problems. It could also be used as part of a wider scheme of learning focussing on sustainability and the 6Rs (rethink, refuse, reduce, reuse, recycle, repair).
Approximately 1 billion people worldwide, or 15% of the total population, have no access to mains electricity. How could a lamp be powered for children living in these conditions to enable them to read and study at night?
What you will need
Hi-bright light emitting diodes (LEDs).
Block connectors with two pin connections at either end, or solder and soldering equipment.
Insulation tape.
Red and black wires or crocodile clips.
A low power DC generator/motor (a motor working in reverse acts as a generator).
Pre-made or purchased turbine blades to attach to the generator.
The engineering context
Engineers bear a social and ethical obligation to consider the environmental impact when addressing design challenges. Understanding how to generate greener energy is imperative for aspiring electrical or electronic engineers, given that the renewable energy sector is one of the rapidly expanding industries in the field of engineering.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to understand what is meant by, and the need for, renewable energy. They will be able to design and make a sustainably powered light, and they will understand how wind turbines work.
Download the free activity sheet!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable so that you can tailor them to your students and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, helpful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation

Halloween multiplication and division activity
Scaling activity to change the size of items
By applying mathematical knowledge and solving problems involving scale factors, we can manipulate scaled-up or scaled-down drawings.
In this fun STEM activity for KS2, students will learn how to change the scale of items, by doubling or halving the size and drawing them to a new scale. This is an engaging and practical exercise through which students will gain a deeper understanding of multiplication and division and how they are useful methods to change the scale of items.
This is one of a set of resources developed to support the teaching of the primary national curriculum. They are designed to support the delivery of key topics within maths and science. This resource focuses on the use of multiplication and division in the context of scaling an item to either double or half its size.
This versatile activity could be used as a main lesson activity to teach learners how to work out scale or to reinforce understanding of multiplication and division. It could also be used as one of several activities within a wider scheme of learning focusing on the use of maths to understand ratio and proportion. Additionally, it could support the development of drawing skills in art.
This is a Halloween-themed exercise that could be done as individuals or in pairs. Students will first use a grid to scale up a drawing of a pumpkin into a larger grid. Once this is completed, students will scale down a drawing of a ghost into a smaller grid. By utilising multiplication and division, students will gain valuable skills in the scaling of items.
This activity will take approximately 40-60 minutes to complete.
Tools/resources required
Halloween Multiplication and Division Activity… Worksheets
Pencils
Erasers
The engineering context
Structural engineers work with architects to help design most houses, hospitals, office blocks, bridges, oil rigs, ships and aircraft. They make scaled down drawings for each structure.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity students will know how multiplication can be used to work out scale, they will be able to scale drawings back to their original size by either scaling up or scaling down and they will be able to solve simple problems in scaling contexts i.e., 2 times larger or 2 times smaller.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Chromatography Christmas tree
**This Christmas STEM activity lets students create Christmas tree decorations in a new way, using chromatography! **
Students will use coffee filters, washable felt tips and a few other items to learn about mixtures, pigments and more!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM

Water treatment systems
Investigate the salinity of different water samples
Water is crucial to human life, but it can also be a killer.
Drinking or cooking water contaminated with micro-organisms or chemicals is a leading cause of disease and death across the world. Poor facilities for the disposal of sewage and other waste water can quickly lead to the spread of dangerous diseases.
Activity info, teachers’ notes and curriculum links
In this practical activity students investigate the salinity of three different water samples using a multimeter. Students first calibrate their salination probe and test the salinity of their solutions. Students can be asked to suggest how errors might have appeared in their results and what could be done to minimise or eliminate them.
This activity can be used as an extension to the ‘Filtering water’ activity.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Download the activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources (including film clips!) are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
And please do share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation

Changing perceptions with design
Developing a marketing and branding campaign for Pure Water
An essential part of a product’s identity is the logo that is used to represent it. In this activity, students will work on developing a ‘marketing and branding’ campaign for a drinking water product by Pure Water. The campaign will need to design the overall package for the scheme, including logos, slogans, adverts, podcasts, posters etc. As a class, brainstorm what the essential criteria are for an effective logo. Then participants generate a range of ideas select their best idea and develop this in a suitable form.
Activity info, teachers’ notes and curriculum links
This activity requires participants to apply understanding of creative thinking, product development and graphic design to a design and technology context.
Download the free activity sheet!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download and are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
Please do share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation
Tools/resources required
Projector/whiteboard
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales.
To watch the ‘Pure water’ video, please visit the IET Education website.

Robotics poster
Primary classroom poster looking at how the design of the Mars Curiosity enables it to explore the planet Mars effectively.
Download the single poster here or order a full set of posters for free from the IET Education website.