497Uploads
168k+Views
71k+Downloads
Chemistry

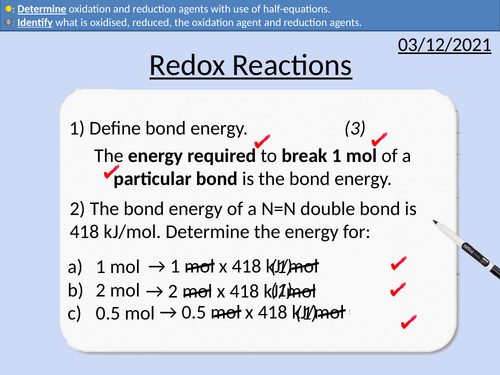
GCSE Chemistry: Redox Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Oxidation and reduction reactions for oxygen
• Identification of oxidation and reduction agents
• Oxidation and reduction reactions for electrons
• Half equations to determine oxidation and reduction
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
29.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
29.4 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
29.6 Combined Techniques
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.
Nuclear Spin
Resonance
Tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Chemical Shift ẟ
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift ẟ / ppm
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

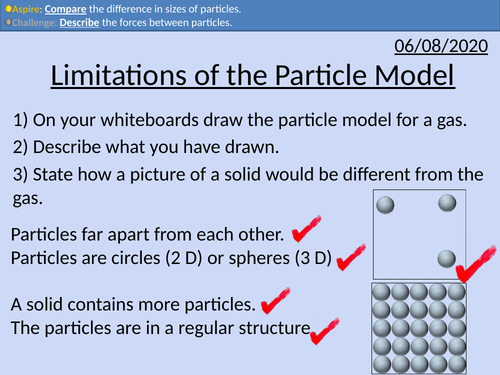
GCSE Chemistry: Limitations of the Particle Model
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Describing the limitations of the model: lack of forces between particles, size of particles, and space between the particles.
• Mathematically comparing sizes and distances of particles

GCSE Chemistry: Alkenes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Unsaturated hydrocarbons
• Comparing alkanes and alkenes
• Mnemonic device for naming alkenes
• General formula for alkenes
• Completing addition reactions for alkenes

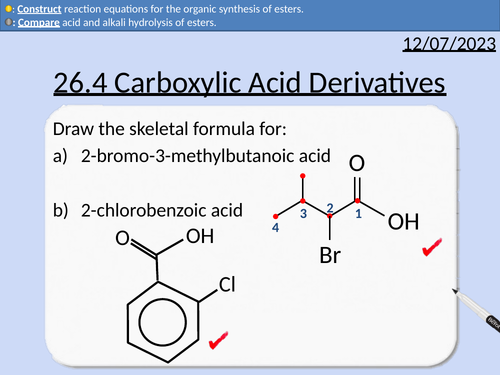
A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming acyl chlorides
Naming acid anhydrides
Naming esters
Esterification
Acid hydrolysis of esters
Alkali hydrolysis of esters
Producing acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids
Producing carboxylic acids from acyl chlorides
Producing esters from acyl chlorides and phenols
Primary, secondary, and tertiary molecules
Producing primary amides from acyl chlorides
Producing secondary amides with acyl chlorides
Producing esters and carboxylic acids wirh acid anhydride
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds
Defining an electrophile
Substitution reactions
Nitration of Benzene
Reaction mechanisms
Halogenation of Benzene
Common Halogen Carriers
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
Acyl Chloride
Acylation Reactions of Benzene
Reactivity of Alkenes and Arenes
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene
Naming positions on the aromatic ring
Activating groups and deactivating groups
2-and-4-directing and 3-directing groups
ortho-and-para directing and meta directing groups
Two-step synthesis routes for benzene using directing groups.
Nitration of benzene
Halogenation of benzene
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of benzene

A Level Chemistry: Carbonyl Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.1 Carbonyl Compounds
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The carbonyl group
Differentiating between aldehydes and ketones
Naming aldehydes and ketones
Oxidation of aldehydes
Electronegativity and polar bonds
Electrophiles, nucleophiles, and nucleophilic addition reactions
Reducing carbonyl compounds with sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (NaH4)
Primary and secondary alcohols from carbonyl compounds
Reacting carbonyl compounds with hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (NaBH4)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (HCN)
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Amines, Amino Acids, and Polymers
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
27.1 Amines
27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
27.3 Condensation Polymers
Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons
Amines being derived from ammonia (NH3)
Classifying amines as primary, secondary, and tertiary
Naming amines
Naming ammonium salts
Amines neutralisation reactions with acids
Preparation of aliphatic amines
Preparation of aromatic amines
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers
Recap of addition polymerisation
Identifying monomers and repeat units from condensation polymers
Polyesters and ester links
Polyamides and amide links
Polyesters and polyamides formed from one monomer
Polyesters and polyamide formed from two monomers
Alkali hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Acid hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters

A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The Carboxyl Group and polarity of bonds.
Naming carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids as weak acids
Reactions of carboxylic acids with:
Metals
Metal oxides
Alkali
Carbonates
Changing solubility of carboxylic acids in water due to carbon chain length.
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
28.1 Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
28.2 Further Practical Techniques
28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

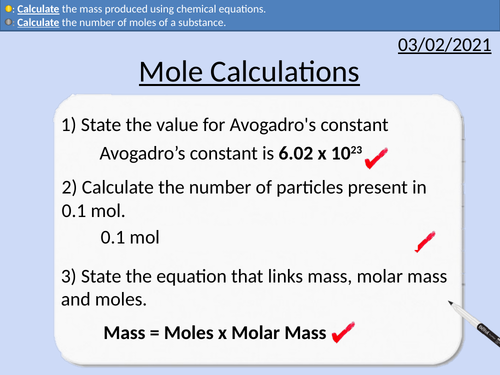
GCSE Chemistry: Mole Calculations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Rearranging Equations
• Stoichiometry as relative abundances
• Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Formula Mass and Molar Mass
• Calculating the number of moles present
• Conservation of mass

OCR AS Chemistry: Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.2 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Aliphatic, alicyclic, and aromatic compounds.
Naming organic compounds
Drawing organic compounds
Functional Groups
Alkane
Alkene
Alkyne
Alcohols
Haloalkane
Aldehyde
Ketone
Carboxylic Acid
Ester
Amine
Nitrile

OCR AS Chemistry: Structural Isomerism
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.4 Structural Isomerism
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition for Structural Isomers
Moving functional group to form isomers
Aldehydes and ketones being structural isomers
Skeletal formula and structural formula

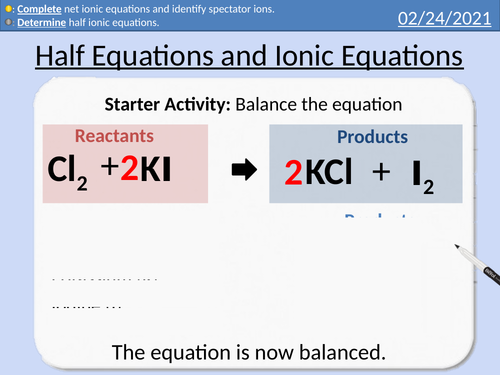
GCSE Chemistry: Half Equations and Ionic Equations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Precipitation in chemical reactions
• Definition of ions
• Ionic Half equations
• Dot and cross diagrams for electron structure
• Introduction to full ionic equations and net ionic equations
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C3.1 Introducing Chemical Reactions
Resources for C3.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Formulae of elements and molecules
Formulae of ionic compounds
Conservation of mass
Chemical Equations
Half equations and ionic equations
The mole
Mole calculations

GCSE Chemistry: Instrumental Methods of Analysis
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Jobs in Environmental Chemistry
Definition of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Advantages of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Gas Chromatography and Chromatograms
Mass Spectrometer and Relative Atomic Mass
Identifying a molecule with use of a mass spectrum

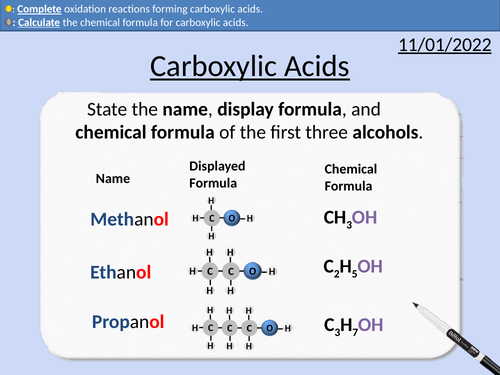
GCSE Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Functional groups of carboxylic acids, alcohols, alkanes, and alkenes.
• Mnemonic device for naming carboxylic acids
• General formula for carboxylic acids
• Drawing the structural formula for carboxylic acids
• Carboxylic acids as weak acids and
• Acid reactions with bases, metals, and carbonates
• Oxidation reactions from alcohols to carboxylic acids

OCR AS Chemistry: Polymerisation of Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.5 Polymerisation of Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Monomers and repeat units
Addition Polymerisation for:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Environmental Concerns from polymers including:
Combustion of polymers
recycling PVC
biogradeable bioplastics
photodegradable polymers
feedstock recycling

A Level Chemistry: Introducing Benzene
OCR A level Chemistry: 25.1 Introducing Benzene
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds

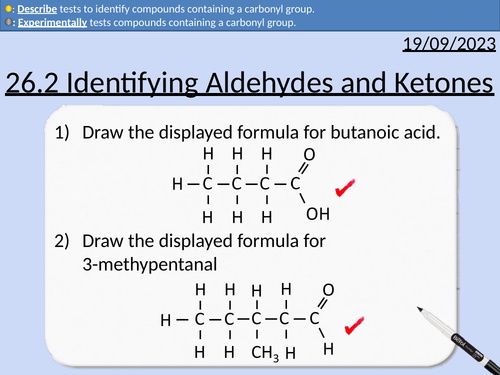
A level Chemistry: Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.2 Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Testing for Carbonyl Groups
Brady’s reagent - 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine - 2,4-DNP
Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones
Tollen’s reagent - silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia