524Uploads
214k+Views
114k+Downloads
All resources

Halloween treasure hunt
Using coordinates, angles and directions to locate pirate treasure on a map
In this exercise learners will look at different methods to find position and direction on a map. They will learn how to use coordinates and bearings using angle and distance. They will work with a pirate treasure map and a series of worksheets to work out where the treasure is. Differentiated worksheets are available, allowing the learners to progress from using simple coordinates and vector coordinates to polar coordinates using bearings with angles and distances.
This is one of a set of free STEM resources developed to support the teaching of the primary national curriculum. They are designed to support the delivery of key topics within maths and science. This resource focuses on position and direction using vector and polar coordinates, with the theme of a pirate treasure map.
This activity could be used as a main lesson activity for KS2, to teach learners how to use coordinates and angles. Further number skills may be used to work out map scale and distances.
This exercise could be carried out as individuals or in pairs. The learners will find buried treasure on a pirate map, using various methods to find position and give direction.
Students will follow the instructions on the ‘Treasure Hunt’ worksheet and add the positions and lines of direction on the Treasure Map using a ruler and pencil.
The worksheets are progressive; The first worksheet uses coordinates, the second uses vector coordinates and the third worksheet uses polar coordinates.
This activity will take approximately 40-60 minutes to complete.
Tools/resources required
Activity and worksheets
Protractors (360 degree)
Rulers
Pencils/Coloured pencils/Pens
Erasers
The engineering context
When planning to build new stadiums and large industrial sites, civil engineers need a good understanding of map reading skills to make sure that the buildings are built in exactly the right place. Engineers use special equipment to get the bearings and distance correct.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity students will be able to describe a position on a map or grid, they will be able to give directions to a specific point on a map or grid using vector coordinates and they will be able to give directions to a specific point on a map or grid using polar coordinates.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Circuits and symbols poster (secondary)
Secondary classroom poster showing basic components and symbols in a circuit.
Download the single poster or order a full poster set for free from the IET Education website.

Electromagnetic spectrum
Compare different types of electromagnetic waves
The electromagnetic spectrum is a fundamental part of our universe, influencing everything from the warmth of sunlight to the functionality of our electronics.
This activity delves into different types of electromagnetic waves and their everyday applications. It ties into key concepts like the electromagnetic spectrum, infra-red, wave, and frequency.
By investigating the technology used in the Nintendo Wii and designing an interactive ‘tag’ game, students will enjoy a hands-on, practical approach to learning.
As part of the ‘Time for a game’ scheme of work, this activity provides an electronics systems context for students to explore infrared technologies. Other activities include Inputs and outputs of design and Binary numbers.
This is one of a set of resources developed to support the teaching of the secondary national curriculum, particularly KS3. It has been designed to support the delivery of key topics within mathematics and design and technology (DT).
Activity: Compare different types of electromagnetic waves
This is an engaging activity in which students investigate the technology used in the Nintendo Wii, exploring infrared communication. They can then apply this knowledge and understanding into the design of an interactive ‘tag’ game.
Download our activity overview and PowerPoint presentation for a detailed lesson plan for teaching students how to compare different types of electromagnetic waves.
The engineering context
Learning about the electromagnetic spectrum introduces them to principles critical to electrical and telecommunications engineering, such as understanding wave behaviour and frequencies.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will gain a solid understanding of how light and infrared travel as waves. They will comprehend the electromagnetic spectrum and its applications, as well as understand the link between frequency and wavelength. Furthermore, this activity nurtures critical thinking and independent investigation skills, providing a broader understanding of communication methods and technologies.
Download our activity sheet and related teaching resources
The activity sheet includes teachers’ notes, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
Please do share your highlights with us @IETeducation.

How polar animals keep warm
A simple and fun science experiment about insulation, to see how blubber keeps penguins, whales, polar bears and seals warm in the North Pole.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use the theme of the festive period to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, Science, Mathematics and Engineering.
In this activity, students will construct a straightforward model of a polar animal and use this to investigate how they keep themselves warm. They will understand how well a layer of blubber can insulate an animal and how the heat loss is reduced against an uninsulated animal.
This is a versatile activity that could serve as a main lesson activity to teach about insulation and heat transfer. It could also be used as part of a wider scheme of learning, focusing on how animals react to the world around them.
This activity could be carried out in pairs or small groups. The teacher presentation covers the main activity on slides 1 to 11, and the subsequent slides are extension work and links.
Resources required
An empty margarine tub
A full margarine tub
A large flat dish
Warm water
Cold water with ice
A thermometer
A stopwatch or smart watch timer
Graph paper
Pencils and differently coloured pencil crayons
The engineering context
Engineers must be able to investigate the natural world to understand how it works. This allows them to design solutions that benefit and learn from the environment, such as suits for divers that can keep them warm.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to understand how polar animals keep warm in very cold conditions, they will be able to understand what blubber is and how it helps polar animals to survive, and they will be able to record experiment data using tables and graphs.
Download the How polar animals keep warm activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho please do share your experiment highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Make a snow globe
This is a craft activity that all children can enjoy. Using an empty jam jar, children can make a snow globe with biodegradable glitter and a few other items from around the home or classroom.
Our step-by-step guide is simple to follow, making it a great STEM project for children. It is an enjoyable hands-on activity promoting creativity and stimulating imagination. It can be used as a craft project for the home or as a main lesson activity in school for the festive season. As well as teaching design creativity, there are potential curriculum links with the Art department and STEAM-based activities.
What you will need
Clean jam jar or mason jar (no labels) with a tightly fitting lid
Biodegradable glitter
Christmas decoration or festive ornament – make sure it’s waterproof and small enough to fit in the jar
Water
Glue gun and glue stick (or waterproof glue – a tube of clear, silicone sealant will do)
Glycerine or light corn syrup
The engineering context
Building a snow globe is a hands-on learning experience that combines art and science. It’s not only a fun winter craft activity for children, but it can also help to develop their STEM skills. While making a snow globe, children will develop their practical skills and learn about science and engineering concepts such as viscosity.
Suggested outcomes
This STEM craft activity will teach creativity and problem-solving skills. Children can experiment with different arrangements of objects, types of jar, and glitter distribution to create their desired scene. This process encourages them to think critically, make aesthetic choices, and find solutions if things don’t go as planned. It’s also an opportunity for them to express their individuality and explore their artistic side. The use of biodegradable glitter can also teach learners about sustainability and environmental issues.
The activity sheets are available to download for free.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
You can download our step-by-step instructions below as either a classroom lesson plan or PowerPoint presentation. You can also watch our video tutorial to find out how to make a snow globe. If you’re up for an extra activity, try our number fun activity as well.
And please do share your handmade snow globes with us on social media on Facebook and Twitter using our #SantaLovesSTEM hashtag. You can also send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Maths for D&T poster
Secondary classroom poster where your students can find out about the equations and formulae needed for D&T.
Download the single poster or order the full set of posters for free from the IET Education website.

Smart and modern materials
The new materials changing the way we live
Discover and explore the new materials changing the way we live with our Smart and modern materials activity.
The development of new materials with incredible properties are changing the way we live: from LCD TVs to super light airliners, these materials have quickly found their way into pretty much all of the modern technology around us.
Activity info, teachers’ notes and curriculum links
In this practical lesson, students conduct different tests on a selection of materials and identify each one from its properties. The tests include Eureka cans, electrical circuits, and other interesting investigations to test the density, hardness, magnetic and conductive properties of materials. This activity can be tailored to include tests that best investigate the properties of the materials you have available.
Download the activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download and are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
Please do share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation
Tools/resources required
Resources required for class:
Samples of 8 to10 different materials, with more than one sample of each if possible. All the samples should be able to fit in the available eureka cans
Access to accurate weighing scales
Safety glasses.
Resources required per team:
HB pencil, copper coin*, knife**, iron nail, small steel file
Eureka can and an accurate measuring cylinder
A magnet
Powerpack/battery pack, 3 leads, light bulb and holder, crocodile clips
A pad of sticky notes.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales.
To watch the ‘Nature reinvented’ video, please visit IET Education website.

Dress the elf activity
Design a new uniform for Santa’s elves while learning about maths combinations
In this engaging Christmas elf activity, students will use multiplication to determine the possible wearing combinations with a set number of clothing items. Children will have a lot of fun selecting outfits for their elves to wear and fostering their creativity and mathematics skills. It allows pupils to take a practical approach to applying multiplication.
This activity is one of a series of accessible STEM resources designed to allow learners to use Christmas themes to support the teaching of the Primary National Curriculum. These resources support the delivery of key topics within maths and science.
A version of this resource without a Christmas theme is available from the IET Primary website titled Fantastic Fashion.
Tools/resources required
Coloured crayons/pencils
Sticky tack, double sided sticky tape, glue sticks
Safety scissors
Thin card for printing the Dress-the-Elf activity sheet.
The engineering context
Understanding combinations is vital to how engineers work out how to make things at the best cost. A bicycle has many parts, so an engineer will work out the best combination of parts to keep the production costs down.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to write and calculate statements for multiplication, they will be able to solve a contextual problem using multiplication, and they will understand how to determine the number of wearing combinations possible using a dress-the-Elf activity.
The History of Christmas Elves
We can trace the history of Christmas elves to European folklore and traditions. In Scandinavian countries, elves known as “nisse” or “tomte” were believed to be small, mischievous creatures who lived on farms and brought good luck to the household. Over time, these elves became associated with the Christmas season and took on a more benevolent role as helpers of Santa Claus. The popular image of Christmas elves as cheerful, industrious beings with pointy hats and pointed ears emerged in the 19th century, thanks to stories and illustrations. Today, Christmas elves are synonymous with Santa’s workshop, assisting in toy-making and spreading holiday cheer.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable so that you can tailor them to your students and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, helpful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Energy transfer
Explore energy transfer and energy efficiency using wind turbines
The concept of energy transfer is brought to life in this activity, showing students how the kinetic energy of wind can be harnessed to power homes and businesses. Windmills and wind turbines are based upon the principle of trying to create a shape where air flow causes the maximum possible change in kinetic energy. The hands-on nature of this task, which involves modifying a basic wind turbine to generate electricity, will appeal to students’ curiosity and creativity.
This is one of a set of resources developed to support the teaching of the secondary national curriculum, particularly KS3. It has been designed to support the delivery of key topics within science and design and technology (DT).
Tools/resources needed
Electric fans
Turbines at 5 angles (Most blades can be bought as kits, or partial kits can be purchased where students can build their own blades)
Wires
Rulers
Crocodile clips
Voltmeter
Ammeter or multimeter
Model Generator
Activity: Explore energy transfer and energy efficiency using wind turbines
This activity gives students the opportunity to explore how the energy efficiency of turbines is directly affected by their design (shape and angle, which can be determined through the study of aerodynamics).
The engineering context
This activity provides a real-world context, introducing students to the principles of aerodynamics and energy efficiency in engineering design. As they explore how the shape and angle of turbine blades affect energy conversion, they’re learning vital principles relevant to fields such as renewable energy engineering, mechanical engineering, and environmental engineering.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students should be able to describe how energy is transferred using turbines and explain the importance of efficiency in devices. They will have designed an investigation to determine the relationship between efficiency and turbine design (shape and angle). Students will also have developed critical thinking skills as they control variables and analyse results to improve accuracy. In addition, they’ll gain a broader understanding of renewable energy resources, highlighting the need to develop alternative ways to generate electricity.
Download our activity sheet and related teaching resources
The activity sheet includes teachers’ notes, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
Please do share your highlights with us @IETeducation.

Halloween maze game
Using directions to guide pupils through a maze from the haunted house back to their home
In this fun Halloween maze game for kids, students will give each other instructions so that they can successfully navigate a Halloween table maze. This activity provides an engaging and practical way to test KS1 students’ maths knowledge as they will need to use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction, and movement.
This is one of a set of resources developed to support the teaching of the primary national curriculum. They are designed to support the delivery of key topics within maths and science. This resource focuses on developing understanding of geometric directions and involves giving verbal instructions to allow learners to successfully complete a table maze.
Clear instructions and correct vocabulary are important to ensure that the learners know how to complete the maze. This activity could be used as a starter or main activity to introduce geometry, position, and direction.
This activity needs to be carried out in pairs. One member of the pair will give instructions, the other will use those instructions to navigate the maze. The learner being given the instructions must wear a blindfold.
Tools/resources required
Projector/Whiteboard
Make a maze with tables or use masking tape or other suitable method of marking out the maze layout.
Blindfolds
The engineering context
When engineers program robots they need to be very clear in their instructions to avoid any confusion. For example, the Mars Rover must follow very detailed instructions to help it move safely on the planet and send back pictures.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity students will be able to follow a set of verbal instructions to successfully navigate a maze, they will understand the importance of clear instructions when instructing others and they will be able to use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.

Parachuting presents
How to make a toy parachute activity.
In this Christmas STEM activity, kids will use items found at home to make two parachutes and test which one is faster. They will learn about gravity, air resistance and more.
Download the STEM activity sheet for free. If you’re up for an extra activity, help our present find its way back to Santa’s sleigh through the maze.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Make an exploding snowman
Students will learn about the effects of chemical reactions while making an exploding snowman in this fun, science experiment for kids.
In this activity, students will use the theme of Christmas to make a card model of a snowman and mix the bicarbonate and vinegar to see the effects of the reaction.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use the theme of the Christmas period to develop their knowledge and skills in Science and Engineering.
This activity could be used as a main lesson to teach learners about chemical reactions when one or more substances are changed to a different substance. It could also be used to explain foams as liquids or solids containing gas bubbles.
Small 50g containers are best for this activity. The teacher may either bring in small plastic bottles or get the learners to bring in the bottles/containers.
Teachers should ensure that covers are placed on work surfaces, or trays are used to prevent spills and catch the exploding liquid.
The products of the reaction are relatively safe, though caution should be taken not to get splashes in the eyes, and clothes should be protected. The exploding mixture produced can be disposed of by washing it down the sink with plenty of water.
Equipment required
A zip-lock bag (sandwich bag size is great to start off with)
Permanent markers
Baking soda
White vinegar
Kitchen roll
The engineering context
Engineers use chemical reactions to help solve a number of problems. For example, rocket engineers mix chemicals together to make a reaction that powers a space rocket.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to make an exploding snowman using bicarbonate and vinegar, and they will be able to understand that a reaction is when one or more substances are changed to a different substance.
Download the Make an exploding snowman activity sheet for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your experiment highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Why do snowflakes have 6 sides?
Learn the science of snowflakes and why they always have 6 sides in this fun Christmas STEM activity
Our free resource designed to allow learners to use the theme of the Christmas period to develop their knowledge and skills in Mathematics, Design and Technology and Science. This lesson focuses on the science behind snowflakes and polar charge.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your snowflake highlights with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM

How does Santa's sleigh fly?
In this fun and festive activity, students will explore drag, thrust, gravity and lift forces to design and craft their own sleigh for Santa.
Download the How does Santa’s sleigh fly? activity sheets for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your sleigh designs with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.

Pulleys - forces in motion
Calculate tension force using pulleys
In this practical activity two objects are connected via a string that passes over a pulley; then they are released from rest. Participants are tasked to use their knowledge of mechanics to predict the time taken for the heavier object to fall to the ground and the greatest height reached by the lighter object? Once each participant has made their calculations, complete the experiments, and compare to the predictions.
This practical is designed to be easily set up and carried out in a maths classroom using simple equipment. It will help students to understand the mechanics topic of kinematics and constant acceleration equations in AS and A level Mathematics.
The video features the equipment needed and the practical procedure. The teacher notes contain additional guidance on carrying out the activity, sample calculations and suggested points for discussion, as well as an indication of some relevant real-life applications.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download and are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs. Links to stream and download the videos can be found resources section below.
Tools/resources required:
Board
2 cup hooks
2 washing line pulleys
Long piece of string with 3 loops in it
3 different masses, e.g. different coloured plasticine
Pencil
Ruler
Tape measure/plumb line
Protractor
Kitchen scales
Sticky tape
And please do share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation
To watch a video about pulleys, please visit the IET Education website.

Cybersecurity poster
Secondary classroom poster where your students can find out about cybersecurity and how it affects the world we live in.
Download the single poster or order a full set of posters for free from the IET Education website.

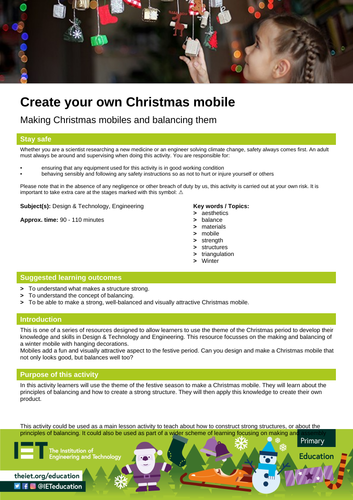
Create a Christmas mobile
Get creative with crafts this Christmas and build a beautiful mobile inspired by the winter holidays
A versatile lesson for teaching about constructing robust structures and the principles of balance. It can be incorporated into a broader curriculum on design and technology, emphasising making and assembly skills.
Learners will be encouraged to collect a variety of natural materials that they can use to craft a Christmas mobile. This homemade mobile will make a great sustainable Christmas decoration for the home or classroom.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow students to use the theme of the Christmas period to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, and Engineering.
The IET Education resource: Homemade Christmas decoration can be combined with this activity to create one of the hanging ornaments.
The time and resources required for this activity will vary depending on the types and quantities of decorations. We recommend using one of the following suggestions to make your mobile:
Fir/pine cones - Cones that have been collected previously and allowed to dry out are the best. They take paint well if dry and can look effective with decoration. Keep the hanging loops long.
Small fir trees - These are simple to construct.
Clay star - This will be a heavy element for the mobile. The impact of different weights on the mobile should be considered. Bolts do not have to be used if not available.
Pipe cleaner star - Learners may need additional assistance with measuring the length of the pipe cleaner to split it into five.
Using natural materials will give a unique, designer effect, but shop-bought decorations can be mixed in if time is short.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to understand what makes a structure strong, they will be able to understand the concept of balancing, and they will be able to make a strong, well-balanced and visually attractive Christmas mobile.
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please do share your inspiring creative crafts with us @IETeducation! #SantaLovesSTEM.
https://education.theiet.org/primary/teaching-resources/create-your-own-winter-mobile/

Make salt dough Christmas decorations
In this Christmas STEM activity, kids can make their own decorations using salt dough, in any shape they like!
They can even paint them and unlike normal baked goods, they will last a very long time.
Baking is a great way for kids to learn about science and maths in a fun and rewarding way, so get your aprons on!
Download the STEM activity sheet and watch our video for step-by-step instructions. If you’re up for an extra activity, help our ornament find its way back to the Christmas tree in our maze.
And please do share your learning highlights and final creations with us on social media @IETeducation #SantaLovesSTEM or send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Winter scavenger hunt
**This is a great outdoor activity for kids to learn about the change of seasons and the natural environment around them. **
The free printable activity sheets are provided for children aged 5 to 14. There is a wide variety of wildlife and plant life for kids to spot while wandering through the woodland or countryside looking for items to match the pictures. Along with the pictures, there are science questions and ideas for children to think about.
This scavenger hunt helps children develop their scientific knowledge by encouraging them to observe and identify different species of plants, animals, and insects. This can help students learn about ecosystems, food chains, and animal adaptations, among other topics.
It promotes gentle physical activity and fitness by encouraging children to walk while searching for items on their lists.
It will give children the opportunity to learn about the science of winter, including animal adaptations, weather patterns, and seasonal changes. They are also a great way of fostering a sense of teamwork and collaboration as kids work together to find and collect all the items.
The science context
Winter scavenger hunts can create engaging and interactive learning experiences that encourage curiosity, observation skills, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of scientific concepts. It allows children to become active participants in their own learning, igniting their passion for science and cultivating the next generation of scientific thinkers.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of the activity, kids will have gained a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the role that science plays in understanding it. The activity can also help to teach geography lessons by encouraging kids to explore different landscapes and geographical features, such as rocks and bodies of water.
We have a choice of three different winter scavenger hunt games for you to download, for 3-6, 5-11 and 11-14 year olds. Each game asks a series of questions, so there is also a corresponding answer sheet to download. Make sure the participants wrap up warm!
Going for a walk on or around Christmas? Please do share your pictures of what you find on your winter scavenger hunts with us on social media on Facebook and Twitter using our #SantaLovesSTEM hashtag. You can also send them via email to IETEducation@theiet.org to be featured in our online gallery.

Make a woven bag
Use recycled materials to produce a basket/bag that can be used to store small items or presents for Christmas.
In this fun activity for Key Stage 2, students will develop their knowledge and understanding of the weaving process and how it can be applied to make products. This is a challenging exercise that requires dexterity.
This activity could be used as a main lesson activity to teach about the skills and techniques associated with making textile products using weaving. It could also be used as part of a wider scheme of learning focusing on environmental issues within design and technology.
This is one of a series of free STEM resources designed to allow learners to use the theme of the festive season to develop their knowledge and skills in Design and Technology, and Engineering.
Recycling helps to reduce the number of new materials we need to make products. Your challenge is to use recycled paper to make a great-looking and strong woven storage basket for Christmas.
Download our free activity sheet for a step-by-step guide on how to make your own woven bag!
Tools/resources required
Recycled paper
Scissors
PVA glue
Skewer or dowel
Empty card box
The engineering context
Engineers must understand the environmental impact of the designs they produce and how their carbon footprint can be reduced, for example, by using recycled or reused materials more.
Structural engineers must understand how to utilise weaker materials to create more robust structures, such as using rope to make bridges.
Weaving is an essential skill for textile designers and engineers.
Suggested learning outcomes
By the end of this activity, students will be able to apply the process of weaving to create a basket, understand how strong structures can be created from weaker materials, and understand the benefits of using recycled materials to make products.
Download the Make a woven bag activity sheet for free!
All activity sheets and supporting resources are free to download, and all the documents are fully editable, so you can tailor them to your students’ and your schools’ needs.
The activity sheet includes teacher notes, guidance, useful web links, and links (where appropriate) to the national curriculum in each of the four devolved UK nations; England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
Oh ho ho, and please share your classroom learning highlights with us @IETeducation.