497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
All resources
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.2 Powering Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.

GCSE Physics: Energy Sources
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.1 Energy Sources
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides,
Waves,
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal

GCSE Physics: Radiation and the body
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.2.1 Radiation and the body
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Background radiation definition
Sources of background radiation
Contamination and irradiation
Medical examples of irradiation - X-rays, sterilisation, gamma knife
Medical examples of contamination - Tracers
Half-life and penetration power for radioactive tracers.

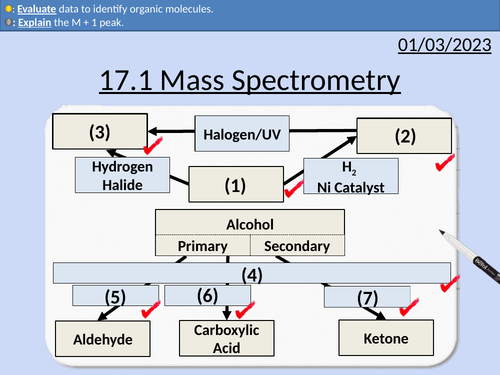
OCR AS Chemistry: 17.1 Mass Spectrometry
OCR AS Chemistry: 17.1 Mass Spectrometry
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Molecular ions M+
M + 1 peak
Fragment ions
Identifying molecules from a mass spectrum

OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Absorb infrared radiation increasing vibrations
What determines the magnitude of vibration
Fingerprint region
Identifying peaks
Bundle

OCR AS Chemistry: Module 4 Organic Chemistry
This bundle includes all PowerPoint lessons for Module 4 Organic Chemistry.
All PowerPoints are whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
Basic concepts of organic chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Nomenclature of organic compounds
Representing the formulae of organic compounds
Isomerism
Introduction to reaction mechanisms
Alkanes
Properties of the alkanes
Chemical reactions of the alkanes
Alkenes
Properties of the alkenes
Stereoisomerism
Reactions of alkenes
Electrophilic addition in alkenes
Polymerisation in alkenes
Alcohols
Properties of alcohols
Reactions of alcohols
Haloalkanes
The chemistry of haloalkanes
Organohalogen compounds in the environment
Organic Synthesis
Practical techniques in organic chemistry
Synthetic routes
Spectroscopy
Mass spectrometry
Infrared spectroscopy

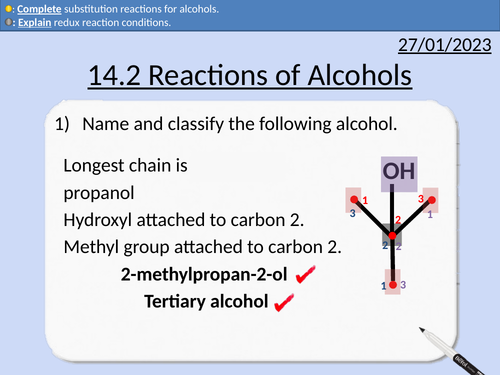
OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14.2 Reactions of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

GCSE Physics: Radiation and Temperature
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.4 Radiation and Temperature
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.

GCSE Physics: Inside our planet
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.5 Inside our planet
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
S and P waves
Structure of the Earth
Reflection, absorption, and refraction of waves
Sonar to map the ocean floor
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8 Global Challenges
All resources for P8 Global Challenges GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted
Structure of the solar system
Nuclear Fusion
Evolution of large stars
Evolution of Sun like stars
Gravitational force and force from nuclear fusion
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
S and P waves
Structure of the Earth
Reflection, absorption, and refraction of waves
Sonar to map the ocean floor
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.3 Beyond Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted
Structure of the solar system
Nuclear Fusion
Evolution of large stars
Evolution of Sun like stars
Gravitational force and force from nuclear fusion
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
S and P waves
Structure of the Earth
Reflection, absorption, and refraction of waves
Sonar to map the ocean floor

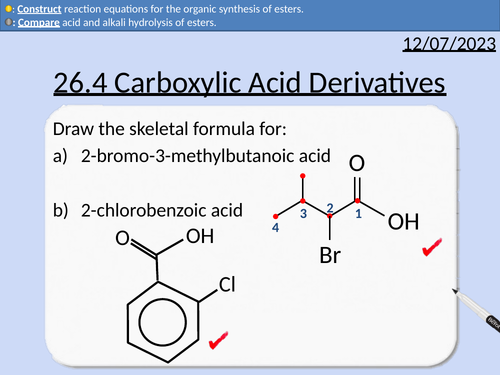
A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming acyl chlorides
Naming acid anhydrides
Naming esters
Esterification
Acid hydrolysis of esters
Alkali hydrolysis of esters
Producing acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids
Producing carboxylic acids from acyl chlorides
Producing esters from acyl chlorides and phenols
Primary, secondary, and tertiary molecules
Producing primary amides from acyl chlorides
Producing secondary amides with acyl chlorides
Producing esters and carboxylic acids wirh acid anhydride
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds
Defining an electrophile
Substitution reactions
Nitration of Benzene
Reaction mechanisms
Halogenation of Benzene
Common Halogen Carriers
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
Acyl Chloride
Acylation Reactions of Benzene
Reactivity of Alkenes and Arenes
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene
Naming positions on the aromatic ring
Activating groups and deactivating groups
2-and-4-directing and 3-directing groups
ortho-and-para directing and meta directing groups
Two-step synthesis routes for benzene using directing groups.
Nitration of benzene
Halogenation of benzene
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of benzene

A Level Chemistry: The Chemistry of Phenol
OCR A level Chemistry: 25.3 The Chemistry of Phenol
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene

A Level Chemistry: Introducing Benzene
OCR A level Chemistry: 25.1 Introducing Benzene
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds

A Level Chemistry: Carbonyl Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.1 Carbonyl Compounds
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The carbonyl group
Differentiating between aldehydes and ketones
Naming aldehydes and ketones
Oxidation of aldehydes
Electronegativity and polar bonds
Electrophiles, nucleophiles, and nucleophilic addition reactions
Reducing carbonyl compounds with sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (NaH4)
Primary and secondary alcohols from carbonyl compounds
Reacting carbonyl compounds with hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (NaBH4)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (HCN)
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Amines, Amino Acids, and Polymers
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
27.1 Amines
27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
27.3 Condensation Polymers
Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons
Amines being derived from ammonia (NH3)
Classifying amines as primary, secondary, and tertiary
Naming amines
Naming ammonium salts
Amines neutralisation reactions with acids
Preparation of aliphatic amines
Preparation of aromatic amines
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers
Recap of addition polymerisation
Identifying monomers and repeat units from condensation polymers
Polyesters and ester links
Polyamides and amide links
Polyesters and polyamides formed from one monomer
Polyesters and polyamide formed from two monomers
Alkali hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Acid hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters

A level Chemistry: Amines
OCR A level Chemistry: 27.1 Amines
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons
Amines being derived from ammonia (NH3)
Classifying amines as primary, secondary, and tertiary
Naming amines
Naming ammonium salts
Amines neutralisation reactions with acids
Preparation of aliphatic amines
Preparation of aromatic amines

A level Chemistry: Further Practical Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.2 Further Practical Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube

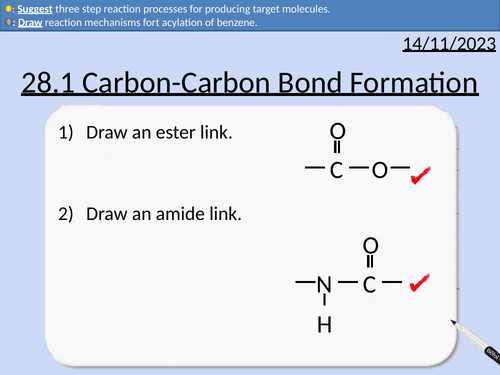
A level Chemistry: Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride