497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
All resources

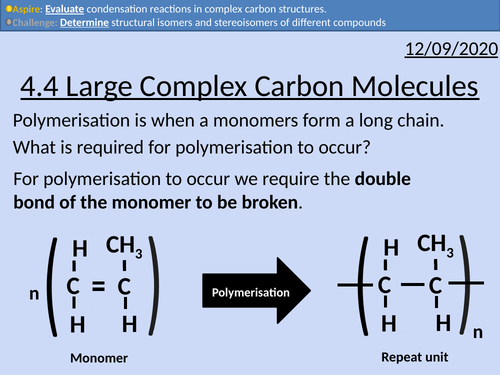
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

OCR Applied Science: 4.1 Principles of Carbon Chemistry
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Alkanes as saturated hydrocarbons containing single C-C and C-H bonds
• Alkenes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C=C double bond
• Alkynes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C ≡ C triple bond
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four members of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
• Aldehydes and ketones as organic compounds containing the C=O group
• Name and draw the structural formulae of the first four aldehydes and the first two ketones
• Alcohols as organic compounds containing the OH group
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four alcohols
• Conversion of alcohols to form aldehydes and ketones is classified as an oxidation reaction
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four carboxylic acids
• Reaction of carboxylic acids with an alkali, to include full equations using structural formulae
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the four C4H8O2 esters
• How an ester can be made from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol

A level Chemistry: Combined Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.6 Combined Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

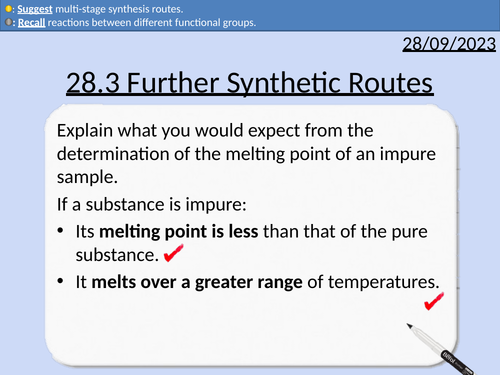
A level Chemistry: Further Synthetic Routes
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

GCSE Physics: Floating and Sinking
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.5 Floating and Sinking
Content Covered:
Balanced Forces
Rearranging equations
Mass and weight
Gravitational field strength
Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Difference in pressure causing up thrust
Combining two equations
Worked solutions
Exam Style Questions
Problems with answers
Demonstration

GCSE Physics: Wave Velocity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.2 Wave Velocity.
Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Simple experiment for the speed of sound
Speed of sound experiment with microphones and oscilloscope.
Ripple tank demonstration and explanation
The speed equation
Measuring distance and time
Echoes
Definition of mechanical waves
Water waves as a transverse waves
Converting from cm, mm, and km into m.
Definition and equation for frequency.
Wave speed equation

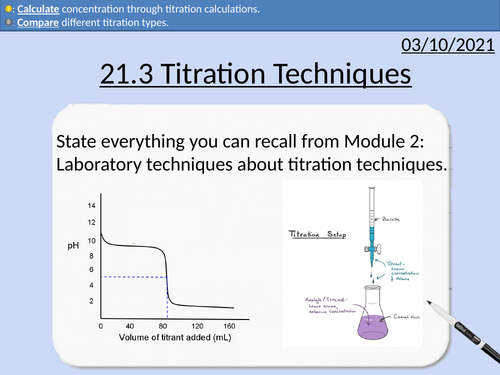
OCR Applied Science: 21.3 Titration Techniques
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
3.1 Titration techniques on consumer products
• Acid-base titration (e.g. limescale removers, eco-disinfectants)
• Precipitation titration (e.g. contact lens saline solution)
• Redox titration, (e.g. bleach, tooth whitener; vitamin C tablets).
• Complexometric titrations (e.g. Milk of Magnesia)
Including explanation and activities on:
Titration calculations
Moles and molar mass
Rearranging Equations
State symbols
Significant Figures
Comparing Data
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.3 Respiration
All resources for B1.3 Respiration GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is an exothermic reaction
The structure of mitochondria
ATP and its uses
Why blood flow increases to muscles when exercising
Conditions for anaerobic respiration
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in mammals
Lactic acid and its affects.
Oxygen debt
Comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration in mammals.
Anaerobic respiration in plants - fermentation.
Fermentation word equation and symbol equation.
Exam questions.
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Amines, Amino Acids, and Polymers
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
27.1 Amines
27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
27.3 Condensation Polymers
Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons
Amines being derived from ammonia (NH3)
Classifying amines as primary, secondary, and tertiary
Naming amines
Naming ammonium salts
Amines neutralisation reactions with acids
Preparation of aliphatic amines
Preparation of aromatic amines
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers
Recap of addition polymerisation
Identifying monomers and repeat units from condensation polymers
Polyesters and ester links
Polyamides and amide links
Polyesters and polyamides formed from one monomer
Polyesters and polyamide formed from two monomers
Alkali hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Acid hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Circular Motion
OCR A level Physics: Thermal Physics apart of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.1 The Particle Model
All resources for P1.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.2 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.2 What happens in cells?
All resources for B1.2 What happens in cells? GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells.
DNA is packaged into a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes shared from their parents.
Genes are sections of DNA that code for physical characteristics.
The structure of DNA.
DNA is comprised of monomers called nucleotides.
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base.
There are four organic bases: Adenine, A. Thymine, T. Cytosine, C. Guanine, G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA.
The role of proteins and AI
Proteins as polymers
Explaining transcription
mRNA and complementary bases
Explaining translation
Enzymes are made of protein.
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction without being used up themselves.
Enzymes and the lock and key hypothesis.
Enzymes breaking down and bonding substrates.
Enzymes-catalysed reactions
Rate of reaction
Denaturing of enzymes and the active site
Optimum temperature and optimum pH for enzymes
Definition of concentration
Increasing concentration of enzymes and substrates
Saturation of substrates
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.1 Cell Structures
All resources for B1.1 Cell Structures GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell
Labeling a light microscope
Defining magnification and resolution.
Explaining why stains are used for light microscope.
Calculating total magnification, objective lens magnification and eyepiece lens magnification.
Calculating actual size, magnification, and magnified size of objects.
Converting from from micrometre (µm) to millimetres (mm)
Rearranging equations
Comparing sizes of different cells
Using standard form
Using SI prefixes (nano, micro, milli, kilo, mega)
Comparing electron microscopes and light microscopes.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 26 Nuclear Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
26.2 Binding Energy
26.3 Nuclear Fission
26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Materials
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Materials.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Hooke’s Law to Young Modulus.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Work, Energy and Power
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from conservation of energy to derivations for kinetic energy.
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
28.1 Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
28.2 Further Practical Techniques
28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds
Defining an electrophile
Substitution reactions
Nitration of Benzene
Reaction mechanisms
Halogenation of Benzene
Common Halogen Carriers
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
Acyl Chloride
Acylation Reactions of Benzene
Reactivity of Alkenes and Arenes
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene
Naming positions on the aromatic ring
Activating groups and deactivating groups
2-and-4-directing and 3-directing groups
ortho-and-para directing and meta directing groups
Two-step synthesis routes for benzene using directing groups.
Nitration of benzene
Halogenation of benzene
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of benzene