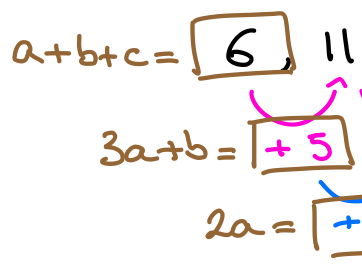43Uploads
19k+Views
8k+Downloads
All resources

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Functions
The following presentation was created for the Applications and Interpretations SL course following the order of teaching for the Kognity textbook but can also be used with the Pearson or Oxford textbook.
The PowerPoint goes through the following:
-what is a relation?
-domain and range
-set and interval notation
-vertical asymptotes
-what is a function?
-mapping diagrams
-vertical line test
-function notation
-forming equations from mapping diagrams
-linear models
-linear simultaneous equations
-inverse functions
-horizontal line test
-domain and range for inverse functions
-piecewise functions
Throughout the PowerPoint there are worked examples along with exercises for students. I have also included a few Desmos and Geogebra interactive links to help students get a better understanding of the concepts through visuals. At the end of each section I have included IB exam questions so students get get practice to the types and style of questioning they should expect to see when they write their exams.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Financial Mathematics
The following contains 4 PowerPoints covering the following topics:
Simple Interest
Compound Interest
Inflation
Depreciation
Loans
Annuities
Amortization
Each PowerPoint contains worked examples, student exercises and Past Exam questions. There are also links throughout to various YouTube explanations (eg. difference between simple interest and compound interest, what is amortization?, etc.), How to use the GDC examples, Desmos, and Geogebra interactives.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Arithmetic Sequences & Series
The Following presentation was created for the Applications and Interpretations SL course but can be used for any course such as A-levels that teach this topic. I have included exam question from both A-Level and the IB in the Presentation.
The PowerPoint goes through the following:
-linear sequences from GCSE
-the nth term formula
-embedded simultaneous equation problems
-inequality problems
-introduction to series and proof
-both forms of writing the sum formula
-sum problems involving inequalities
-sigma notation
-basic summation properties
Throughout the PowerPoint there are worked examples along with exercises for students. I have also included a few video exam solutions with videos going through addition examples for students. There is also a video explain how the Arithmetic Sum formula evolved. At the end of each section I have included IB exam questions so students get get practice to the types and style of questioning they should expect to see when they write their exams.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Chapter 4 - Dividing Up Space
The PowerPoint follows chapter 4 from the Oxford textbook. There are worked examples, student exercises and past paper exam questions for each section. I have also embedded links to various Youtube, GeoGebra and Desmos activities and visuals to help improve student understanding. The PowerPoint contains the following content:
recap piecewise functions
the number plane
distance between 2 points (2D & 3D)
midpoint (2D & 3D)
classifying triangles given coordinates
coordinate geometry in 3D space
gradients
different forms of an equation of a line
points of intersection
parallel and perpendicular lines
collinear points
perpendicular bisectors
shortest distance to a line

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Chapter 5 - Modelling Constant Rates of Change
The following PowerPoint covers the following topics following the Oxford textbook. Topics covered include:
Functions
* reation
* domain and range
* mapping diagrams
* number system
* set notation
* interval notation
* what is a function
* vertical line test
* function notation (numerical, graphical, and algebraic)
* finding equation of functions from a mapping diagram
Linear Models
* recap equation of a line
* rates of change
* simultaneous equations
* direct proportion
* inverse functions
* domain and range
* horizontal line test (one-to-one)
* finding inverse functions
Arithmetic Sequences
Arithmetic Series
* sigma notation
Simple interest
Modelling
Through the PowerPoint there are links to youtube videos, GeoGebra and Desmos interactives, and Desmos Classroom activities. The PowerPoint has worked examples, and student exercises. I have also put in past paper exam questions for each topic.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Chapter 3 - Representing and Describing Data
This PowerPoint follows the Oxford textbook.
The following content is covered throughout the PowerPoint. I have also added a few extra concepts which can be used in students Internal Assessments (IA). For example, I spend a little time looking at the skewness formula, different ways of calculating outliers, 1.5 x IQR or 2 X SD, skewness in box plots, etc.
Univariate data
* qualitative vs quantitative
* continuous vs discrete
* which representations are used for specific types of data
* primary and secondary data
* choosing a good sample
* sampling bias
* reliability vs validity
* skewness
Questionnaires
* biased questions
Measures of central tendency
* mean, meadian, mode
* outliers
* un-grouped and grouped
* how to use the GDC
* combined mean
Measures of dispersion
* range, quartiles, IQR, standard deviation
* normal distribution curve
* skewness
* different formulas for sample and population for SD
* how to use the GDC
* effects on mean and SD
Sampling techniques
Presentation of data
Bivariate data
* scatter graphs
* correlation
* introduction into the line of best fit (leading into chapter 6)
Throughout the PowerPoint there are worked examples and student exercises. There are also multiple links to various classroom and interactive activities using GeoGebra and Desmos Classrooms. As well, I have included links to certain Youtube videos to help with using the GDC.

Angry Birds: Quadratics Project
Here is a great activity to do as a group, pairs or individually. I haven’t created it but wanted to share it with others. This activity looks at quadratics given in different forms; table of values, graphically, in words, and in standard form. The idea is to see which birds hit the pigs. There are 5 versions of this activity which is great. Students don’t need to know about vertex form (completing the square) for this activity, but do need to understand that the axis of symmetry is half way between the roots.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Chapter 6 - Modelling Relationships
The following PowerPoint covers Chapter 6 from the Oxford textbook. Modelling Relationships: Linear Correlation and Bivariate Data. The Lesson contains various interactive activities such as Desmos Classroom for review exercises, Geogebra and Phet Simulations for showing line of best fit, least-squares, etc. There are also video links on how to used the GDC to find correlation and linear regression. The PowerPoint covers the following content below.
correlation review (from chapter 3)
finding correlation coefficient (PMCC)
discussion about covariance
interpreting PMCC
correlation and causation
coefficient of determination
line of best fit
interpolation and extrapolation
reliability
linear regression
residuals
piecewise functions
* step functions
All my PowerPoints have worked examples and exercises for students to complete. I have also added past paper questions in each section to get students accustom to the type and style of questions they will see on their exam. This PowerPower in particular comes with a Microsoft Teams quiz on Correlation and Linear Regression.

Time Series Assignment
Here is a short independent task looking at time series of population over time. It also creates discussion for curves of best fit.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation SL: Chapter 2 - Representing Space
The PowerPoint covers the complete content of Chapter 2 of the Oxford textbook. I have also added a few extension topics which build upon what students are learning and will be useful further in the course. Topics cover in the PowerPoint include:
The sine law
* the ambiguous case
The cosine law
Area of non-right angle triangles
Algebraic triangle problems
3D Problems involving non-right angle triangles
Area of sectors
Area of Segments
3D shapes
* surface area
* volume
* writing expressions
* algebraic problems
* capacity
There are also Past Paper questions embedded into the lesson along with various GeoGebra and Desmos interactive activities.

IB Maths Applications and Interpretation: Chapter 1 - Measuring Space
This PowerPoint follows the entire content for Chapter 1 of the Oxford textbook. Certain topics included are not in chapter 1 but builds on the skills students are currently learning in the chapter and will be useful later on. For example, for the simplifying indices topic I go a little further into writing indices in non-fractional form which is useful for when you teach derivatives. Conent covered through the PowerPoint include:
Measurements and Estimates
Rounding and Significant Figures
Upper and Lower Bounds
Measurement Error
Percentage Error
Basic Exponent Rules
* changing bases
* writing in non-fractional form
Standard form (scientific notation)
Right angle trigonometry
* Pythagoras
* proving right angle triangles
* algebraic problems
* SOH-CAH-TOA
* elevation and depression
* problems involving circles
* 3D problems
* problems involving special quadrilaterals
* angles between lines and planes
Arc Length
Throughout the PowerPoint you will find GeoGebra links (click the icon) as well as Past Paper questions. There are also worked examples and exercises for students to complete throughout the lesson.

IB Maths AI: Voronoi Diagrams
This complete lessons contains Desmos and GeoGebra interactives to demonstrate how to create voronoi diagrams, as well as examples. The lesson starts off with a review on finding equations of perpendicular bisectors then moves into a explorative task about voronoi diagrams. The lessons covers the following topics:
equation of a perpendicular bisector
how to construct a perpendicular bisector
key terminology used when constructing voronoi diagrams
how to construct a voronoi diagram with multiple sites
finidng centre of a circle using perpendicular bisectors of cords
finding locations of missing sites
nearest neighbour
adding new sites to a voronoi diagram
toxic waste dump problems (largest circle)
At the end this is a multiple choice quiz. There are also embedded link to Desmos Classroom activities. As well, throughout the PowerPoint there are worked examples and exercises and past paper exam questions for students to complete.

Linear Functions - Straight Line Graph Quizzes
The following are 5 quizzes created for online teaching through Microsoft Teams. All 5 quizzes are multiple choice, so self marking. The 5 quizzes cover the entire topic of linear functions which are as follow:
Straight Line Graphs; graphing, finding an equation, finding gradient, interpreting equation, rearranging equations (25 questions)
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines (19 questions)
Modelling Linear Functions – Real Life Graphs (14 questions)
Distance and Midpoint (10 questions)
Equations of Perpendicular Bisectors (5 questions)

IB Maths: Applications and Interpretation SL - Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Complete PowerPoints for Chapter 10 - Modelling Rates of Change: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, for the Oxford textbook. The PowerPowers can be used with other textbooks. PowerPoints are built around students learning the the following topics online, but can also be used to deliver in-class. PowerPoints have embedded links to video examples, Desmos activities, GeoGebra, and Casio GDC videos. The following is the topics that the 8 PowerPoints cover.
Geometric Sequences
Geometric Series
Compound Interest
Annuities
Amortization
Exponential Functions
Exponential Models
Exponential & Logarithmic Equations
There are also Past Paper questions in each section of the unit.

Bungee Barbie - Scatter Graphs and Line of Best Fit
This activity requires students to gather data to construct a scatter graph. After students have constructed the scatter graph they then have to find the equation of the line of best fit and use that to make a prediction of how many bands are needed for the bungee jump. Calculations will be off which lead to the discussion of interpolation and extrapolation and why maths in the real world does not always match up with theoretical predictions.
The PowerPoint comes with a worksheet that students will use to fill in. I have also attached an egg version. The activity will take at least 2 days. One day to gather their information and the second to test their predictions.

Embedded Linear Simultaneous Equations
30+ linear simultaneous equation problems. The PowerPoint starts with a quick recap on how to solve using either substitution or elimination. Most problems require students to transfer skills from other contexts in order to solve the problem. Problems include, linear and quadratic sequence, equations of quadratic graphs, angle properties, equation of a line, area and perimeter, index rules, HCF & LCM, pressure and density, etc.

Quadratic Sequences - Complete Lesson
The lesson looks at the differences between a linear and quadratic sequences graphically and focusing on finite differences, thus leading to the nth term. The lesson identifies two methods for finding the nth term of a quadratic sequence with multiple questions in different contexts. Questions also have students transferring skills from other topics such as area, solving equations, simultaneous equations, etc.
This lesson can also be used with AQA Further Maths students as the PowerPoint ens with limiting value of a sequence.

Common Factoring - Introductory Lesson
The Following lesson introduces the concept of common factoring through numerical calculators where students find quicker and easier ways to mental calculator sums through the use of common factoring. It then moves on to algebraic factoring with visual displays (algebraic tiles) and finishes with piecewise factoring. The idea is to move from piecewise factoring onto expanding double brackets.

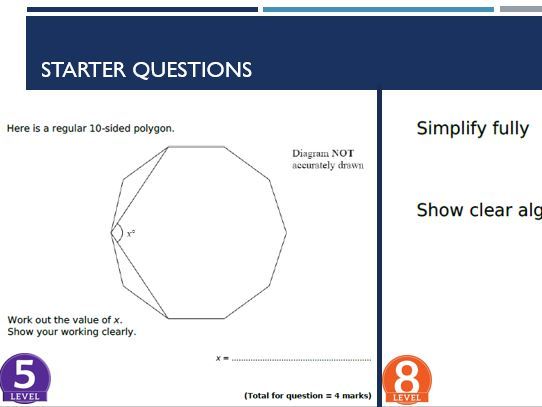
Higher GCSE Maths Starters (Target 5 - 9)
Th bundle contains 32 days worth of starters. Each stater comprises of 2 questions. One being of level 4 or 5 and the other of level 7 to 9. The idea is that students will practice both questions from the beginning and ending of the exam. I find higher level students tend to make mistakes early of in the exam and this allows them to practice these types of questions in class. Thus helping to improve results.

GCSE 9-1 Maths Digit Proofs
For those higher achieving students looking to get a grade 9. As proofs is new to the Edexcel specification, digit proofs is not common but has shown up on a Mock Exam.