66Uploads
14k+Views
19k+Downloads
Featured resources

Cause and course of WW1 Edexcel iGCSE revision lesson
This will take more than one lesson and could be used as a home work activity for content revision.
There are answer sheets in the same format as the worksheets. As this is a revision activity, the answers do not go into all of the details of the textbook.
This should be an easy plug and play lesson.

iGCSE Edexcel Cause and course of WW1 (paper 1 - A1)
This series of lessons follows the iGCSE Edexcel History, paper 2 (A1) The origins and course of the First World War, 1905–18.
18 content lessons plus two exam lessons.
Each lesson uses the textbook, but there are reading alternatives too.
Lessons follow the specification published by Edexcel and included:
1.1 The alliance system
1.2 Economic and imperial causes of war
1.3 Military causes of war
2.1 Moroccan Crises
2.2 Crises in the Balkans
2.3 Balkan nationalism and Serbian rivalry
2.4 Assassination to war
3.1 Schlieffen Plan and reasons for its failure
3.2 Trenches and reasons for deadlock
3.4 Somme
3.5 Passchendaele
3.6 Haig
4.1 German threat at North Sea
4.2 U-boats
4.3 Gallipoli (2 lessons)
5.1 Ludendorff Offensive
5.2 Hundred Days
5.3 Cause of Germany’s defeat
2 exam lessons
Lessons include relevant exam questions with mark schemes
There is a learning check list for the students
There is also a learning checklist that matches up specification topic with exam questions.
There are two lessons that focus on the examination.
o One for B question. Examples, work for students to mark and then one to complete.
o One for C question. Example answers, work for students to mark and then one to complete.

America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877 (iGCSE history, Edexcel, paper 2, B1)
This is a series of lessons that cover Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (iGCSE) in History, paper 2, B1 America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877.
• Each lesson begins with knowledge recall that is self-assessed.
• Relevant past exam questions are included, with mark schemes, for each lesson (where applicable).
• There is a Personalised Learning Checklist (PLC) that breaks the specification down into its constituent parts and tracks what exam questions have been asked for each topic. This reveals what topics seem to be asked multiple times and allows students to practice those questions.
• No textbook is required. Printable reading materials provided.
Lesson titles include:
1.1 Tensions between large and small states
1.2 The significance of Shay’s Rebellion
1.3 The Connecticut Compromise
1.4a Founding Fathers – federalism
1.4b Founding Fathers - Bill of Rights
1.5 Constructionists
1.6 Jefferson’s Presidency
2.1 opposition to westward expansion
2.2a Louisiana Purchase
2.2b Transcontinental Treaty
2.2c Annexation of Texas
2.3 Missouri Compromise
2.4 Indian Removal Act
2.5 Settling the West
2.6 California Gold Rush
3.1 Compromise of 1850
3.2 Kansas–Nebraska Act
3.3 Economic origins of the division between Union and Confederacy
3.4 Causes of the American Civil War
4.1 The Civil War and Union victory
4.2 Role of military leadership
4.3 Naval blockade
4.4 Political leadership
4.5 The Emancipation Proclamation
4.6 Gettysburg, Vicksburg, and march through Georgia
4.7 Destruction of the Sothern economy
5.1 John and Reconstruction
5.2a Freedmen’s Bureau, Southern response and Black Codes
5.2b Civil Rights Acts and Amendments
5.3 Failure of Grant’s Peace Policy

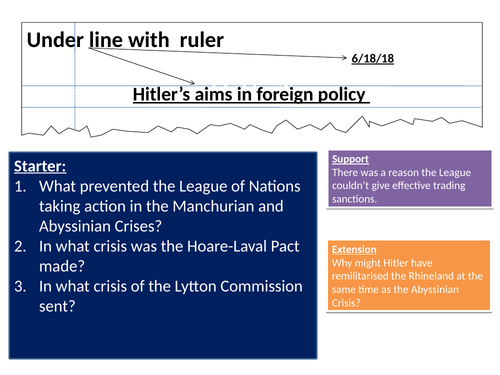
Hitler's aims in foreign policy
Hitler’s aims in foreign policy.
Use for IGCSE.
No textbook required.

East Germany, 1958-90 (Edexcel iGCSE history, paper 2, A5)
This is a series of lessons that cover the iGCSE Edexcel History paper 2 (A5) East Germany, 1958-90.
Previous exams from 2019 to 2023 have been used throughout the lessons. I have matched them up by topic and included the mark scheme after. The exclusion of 2024 exams means you will be able to use this for any mock exams.
A learning checklist is included. This gives you an overview of the content and when it has been examined.
No textbook is required. All lessons come with readymade reading that is referenced in the lesson ppts.
1.1 Origins of the Berlin Wall
1.2 Ulbricht and Khrushchev
1.3 The impact of the Wall on East Berliners, security and escapes.
2.1 Economic stabilisation and emigration
2.2 New economic system and socialism
2.3 Comecon and economic problems
2.4 The nature of state control
2.5 Propaganda and censorship
2.6 Support and Eastern Bloc
3.1 Daily life in Eastern Berlin
3.2 Changing role of women
3.3 Honecker and the development of a GDR identity
3.4 the importance of sport
4.1 Relations with West Germany
4.2 Relaxation of travel rules
5.1 Gorbachev
5.2 Key events of 1989
5.3 the end of the GDR
I’m in the process of making units of work for all of the iGCSE Edexcel Hsitory options. But for now, the ones with the
Paper 1 Depth studies
1 The French Revolution, c1780–99
2 Development of a nation: unification of Italy, 1848–70
3 Germany: development of dictatorship, 1918–45
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12923243
4 Colonial rule and the nationalist challenge in India, 1919–47
5 Dictatorship and conflict in the USSR, 1924–53
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12939702
6 A world divided: superpower relations, 1943–72
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13085657
7 A divided union: civil rights in the USA, 1945–74
8 South Africa: from union to the end of apartheid, 1948–94.
Paper 2 : Investigation and Breadth Studies
A1 The origins and course of the First World War, 1905–18
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12882315
A2 Russia and the Soviet Union, 1905–24
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12911138
A3 The USA, 1918–41
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13084089
A4 The Vietnam Conflict, 1945–75
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13149998
A5 East Germany, 1958–90.
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13151559
B1 America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13139147
B2 Changes in medicine, c1848–c1948
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13034136
B3 Japan in transformation, 1853–1945
B4 China: conflict, crisis and change, 1900–89
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-13030617
B5 The changing role of international organisations: the league and the UN, 1919–c2011
B6 The changing nature of warfare and international conflict, 1919–2011
B7 The Middle East: conflict, crisis and change, 1917–2012
B8 Diversity, rights and equality in Britain, 1914–2010.

The Vietnam Conflict, 1945–75 (Edexcel iGCSE history, paper 2, A4)
This is a series of lessons that cover the iGCSE Edexcel History paper 2 (A4) the Vietnam Conflict, 1945-75.
Previous exams from 2019 to 2023 have been used throughout the lessons. I have matched them up by topic and included the mark scheme after. The exclusion of 2024 exams means you will be able to use this for any mock exams.
A learning checklist is included. This gives you an overview of the content and when it has been examined.
No textbook is required. All lessons come with ready made reading that is referenced in the lesson ppts.
Series of 24 lessons:
1.01 Origins of the First Indochina War
1.02 The tactics of General Giap
1.03 Search for a diplomatic solution
1.04 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu
2.01 Geneva Conference & Domino Theory
2.02 South and North Vietnam
2.03 Ho’s policies to unite Vietnam, NLF & Ho Chi Minh Trail
2.04 response of the USA
2.05 Fall of Diem and Gulf of Tonkin
3.01 Second Indochina War
3.02 Operation Rolling Thunder
3.03 televised war - Khe Sanh
3.04 televised war – Tet
3.05 Televised war - The Battle of Hue
4.01 Failure of peace talks
4.02 Cambodia and Laos
4.03 Relations with China
4.04 Vietnamisation and withdrawal by 73
4.05 the effects of Ford’s diplomatic response
5.01 Effect of war on civilians in Vietnam
5.02 US response to Guerilla war
5.03 Hearts & minds, My Lai, and Phoenix
5.04 US media coverage
5.05 Fulbright Hearings (1971)

Edexcel GCSE Crime and punishment in Britain, c1000–present (unit of work)
This is a series of 27 lessons that covers Edexcel’s Crime and punishment in Britain, c1000–present.
• AfL is included.
• All starter activities are self assessed, excluding the first lesson.
• Lessons are matched up with their relevant exam questions from the SAMs to 2022.
• Mark schemes are included where they have been used.
• The origins of the exam questions are clearly marked and mark schemes included.
• Where there is printing to do, it is in a separate document and clearly labeled.
These lessons are plug and play. They have been designed for other people to open the PowerPoint and begin teaching.
The list of lessons are below. I have included where Exam Qs have been matched with content.
Lessons:
Introduction to Crime and Punishment
Anglo-Saxon Crimes in Britain
Anglo-Saxon Law enforcement and punishment
Norman Crime
Norman law enforcement and punishment - 2019, Q5; 2022, Q5
Later Middle ages crime - SAM, Q5
Case study – Church
1500-1700 context of time period
1500-1700 Crime - 2018, Q4; 2021, Q5
1500-1700 law enforcement and punishment - 2020, Q4; SAM, Q6
1500-1700 Gunpowder Plot
1500-1700 Mathew Hopkins
1700-1900 Crime - 2022, Q3; 2019, Q6
1700-1900 Tolpuddle Martyrs.
1700-1900 Bow Street Runners 2018, Q5
1700-1900 Metropolitan Police
1700-1900 Views on punishment
1700-1900 Prison reform SAM, Q4
1700-1900 Pentonville prison - 2018, Q6
1700-1900 Robert Peel
1900-present Crime - 2021, Q4, Q6; SAM, Q3
1900-present Changing definitions of crime
1900-present Law enforcement - 2020, Q3 Q6; 2019, Q4
1900-present punishment - death penalty
1900 – present - punishment - prisons - 2022, Q4; 2021, Q3; 2018, Q3
1900- present - Conscientious objectors - 2019, Q3
1900-present Derek Bentley
You will need the Pearson Edexcel GCSE (9-1) Crime and punishment through time, c1000–present. ISBN is 978 1 292 12736 1.
This unit of work does not include the Whitechapel unit.
Bundle

Edexcel Cold War Lessons and resources
Bundle covers the entire Period Study.
Includes exam questions and mark schemes
Printable resources included
AfL includes answers on the next slide.

Edexcel Cold War Key Topic 1
This is a series of 10 lessons (with a ppt with all the exam Qs for this section) that follows Edexcel History Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91. Exam questions are included within the lessons and in a separate ppt for revision.
You don’t need to published textbook with this series of lessons, but it can easily be substituted in.
Lessons in total with resources to print:
introduction to Cold War
Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam
Impact of the atomic bomb, telegrams, and Soviet satellite stats
Truman Doctrine
Cominform, Comecon, and NATO
Berlin Crisis
Significance of arms race and Warsaw Pact
Hungarian uprising (causes and Khrushchev’s response)
International reaction to invasion
A ppt with all the exam Qs (up to 2022) with mark schemes for key topic one.
An overview lesson with worksheet to accompany
Every lesson starts of with 5 recall questions with the answers
Past exam questions and mark schemes are included in the lessons
Exam questions with the mark scheme are included
Each activity had an AfL activity, often with answers
Possible to use the published textbook or to use the resources provided.

British Empire (unit of work)
This scheme of work focuses on how imperialism has developed over time with a focus on the development of India and scramble for Africa.
These lessons are easily adaptable and followed with clear instructions and a scheme of work
This unit of work includes:
10 lessons, plus assessment
A written SoW. Learning objectives are linked to suggested learning activities.
Where there is reading, there is a choice of reading ages to use.
There are 10 lessons int he unit of work, plus one assessment:
What was the British Empire?
Motives for imperialism
East India Company
Cause of EIC taking over India
Indian rebellion
Impact of empire on Britain
Berlin conference
Scramble for Africa
Contemporary interpretation of Empire
Preassessment lesson
Assessment
Where there is reading to complete there is a choice of reading age of 14 or 11. The reading age has been determined using the Flesch-Kincaid readability test* and all reading comes with five comprehension questions that can be self-assessed.
There are opportunities for pupils to peer assess and self assess using the success criteria provided.
Flesch-Kincaid readability test* has been used to determine the reading age of each piece of text
The Flesch-Kincaid reading method is a readability test designed to assess the complexity of written text. It was developed by Rudolf Flesch and J. Peter Kincaid in 1975 and has since become one of the most widely used methods to determine the readability of texts in English. The Flesch-Kincaid reading method calculates the reading ease and grade level of a piece of writing based on two primary factors: average sentence length and average number of syllables per word

English Civil War (unit of work)
This is a source-based SoW that focuses on the causes and course of the English Civil War. The SoW is broken into ten lessons:
Gunpowder Plot
Primary source 1
Charles I and Parliament
Primary source 2
Start of the English Civil War
Causes of the English Civil War
Events of the English Civil War
Execution of Charles I
Primary source 3
Assessment (source based assessment.
Where there is reading to complete (lessons 1, 3, 5, 7, 8) there is a choice of reading age of 12 or 10. The reading age has been determined using the Flesch-Kincaid readability test* and all reading comes with five comprehension questions that can be self-assessed.
There are opportunities for pupils to peer assess their own PEE paragraphs using the success criteria provided.
This unit of work includes:
• Ten lessons. Five of these lessons have a comprehension-based reading activity targeted at reading age 12 or ten, depending upon the ability of the group.
• All lessons have blooms related to learning objectives.
• A SoW that links learning activities to the learning objectives. There is also an intention statement.
• A knowledge organiser that is editable.
• While the assessment lesson is a source based it can easily be edited into causation.
The Flesch-Kincaid reading method is a readability test designed to assess the complexity of written text. It was developed by Rudolf Flesch and J. Peter Kincaid in 1975 and has since become one of the most widely used methods to determine the readability of texts in English.The Flesch-Kincaid reading method calculates the reading ease and grade level of a piece of writing based on two primary factors: average sentence length and average number of syllables per word

Edexcel Cold War Key topic 2
This is a series of lessons that follows the Edexcel P4 Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91.
You don’t need the text book with this series of lessons but it can easily be substituted in.
7 lessons included with printable resources.
The Rufugee problem in Berlin
The Berlin Wall
Cuba (Bay of Pigs)
The Cuban Missile Crisis
Prague Spring ( 2 lessons)
Key Topic 2 overview lesson with worksheet
All exam questions and mark schemes relevant for Key topic 2 in one ppt.
All exam questions for this Key Topic are included (SAMs to 2022). Mark schemes included.
AfL activities included with answers after.
Each lessons starts off with recall activity (answers on the next slide).
Self assessment is included in the lesson.
Very Little editing required.

US involvement in the Vietnam War, 1954-75
Edexcel Key topic 3, option 33.
9 lessons, including an introduction lesson. The lessons include all the relevant past exam questions. These include 2018, Q3a; 2019, Q2; 2020, Q2&3.
I have also included an exam map.
There is printing for lesson 2. The rest of the printing is in a booklet.
To complete these lessons you will need the *Edexcel GCSE (9-1) History (The USA, 1954-1975: conflict at home and abroad) textbook. ISBN 978-1292127323

iGCSE History (CIE) Germany, 1918-45 (Depth Study B)
iGCSE History, depth study: B) Germany, 1918-45. 26 lessons to teach.
No textbook is required.
Printing is clearly titled with each lesson or can be printed as booklet. Easy to adapt to use whatever textbook you have.
Past exam questions (paper 1 and 4) are included at the end of each lesson where relevant with the mark schemes.
Exam map is included to show the bullet point from the spec and the year it was tested.
Lesson titles:
1.1 Revolution and Republic
1.2 Reactions to the ToV (2019, P4, Q4)
1.3 The Weimar Constitution
1.4a Threats from the left and the right (5 relevant exam Qs)
1.4b Economic problems and Ruhr (2021, 11a; 2019, 11b)
1.5 Economic problems and hyperinflation (3 relevant exam Qs)
1.6 Stresemann Economic achievements (2021, P1, 11b)
1.7 Stresemann abroad
1.8 Cultural achievements of the Weimar Republic
1.9 How stable was the Weimar Republic
2.1 Early years of Nazi Party
2.2 Munich Putsch (3 relevant exam Qs)
2.3 Roles of Hitler and other Nazi leaders
2.4 Great Depression
2.5 Reasons for Nazis rise to power (2022, P1, 11b)
2.6 Hitler takes power
2.7 Reichstag Fire (3 relevant exam Qs)
3.1 Steps to dictatorship (3 relevant exam Qs)
3.2 Control and repression (2022, P1, 12a)
3.3 Culture and mass media (6 relevant exam Qs)
3.4 Economic policies including rearmament (3 exam Qs)
4.1 Social policies (4 exam Qs)
4.2 Antisemitism & final solution (2020, P4, Q2)
4.3 Persecution of minorities (2023, P1, 12a)
4.4 Opposition to Nazi Rule (2022, 12b; 2020, 12c)
4.5 Impact of WW2 on Germany (3 exam Qs)

iGCSE History (CIE) the United States, 1919-41 (depth study D)
This is a unit of 22 lessons that covers Cambridge (CIE) iGCSE History depth study D: The United States, 1919-41.
Read information is provided with the lessons and is clearly labelled.
Each lessons starts off with 5 recall questions that are self assessed on the next slide.
The lessons have past exam questions at the end of the lesson with the mark scheme on a separate slide.
Exam map is provided so you can see the most assessed topics.
Lesson titles:
1.0 America in the early 20th century
1.1 & 1.4 Causes of Boom
1.2 government policies cause of Boom
1.3 Old industries
1.5 Decline of agriculture
2.1 Roaring 20s
2.2 Film and media
2.3 Prohibition and organised crime (printing at end)
2.4a Immigration
2.4b The Palmer raids and Red Scare
2.5 African Americans and KKK
2.6 Women and flappers
3.1a Wall St. Crash
3.1b Great Depression and causes
3.2 Impact of the Great Depression - 2 lessons
3.3 Hoover’s reaction to GD
4.1 Election
4.2 Roosevelt
4.3 New Deal legislation
4.4 Opposition to the New Deal
4.4b Radical criticism
4.5 Strengths and weaknesses of the ND

CIE Cambridge IGCSE History The First World War, 1914–18
Series of lessons that covers iGCSE history, CIE Cambridge, paper 1, Depth study A, The First World War, 1914–18 (World War One, WW1)
Relevant exam questions, with mark schemes, are included at the end of lesson
Exam Map shows what is on the spec and when it was examined. This allows you to easily find exam Qs by topic.
Section 2 (To what extent was it a world war?) has never been examined, but it’s on the spec, so lessons included.
All resources are provided so no textbook is required:
1.1 Schlieffen Plan
1.2 Why did the Schlieffen Plan fail
1.3 Stalemate
1.4 Trench warfare
1.5 New weapons and methods
1.6 Verdun
1.7 Somme
2.1 British Empire on the Western Front
2.2 the war in Africa
2.3 Contribution of Japan
2.4 The Arab revolt
3.1 German threat in North Sea
3.2 Gallipoli Campaign
3.3 Eastern front and Russia leaves
3.4 The impact of war on civilian populations
4.1 Ludendorff Offensive & defeat of Germany
4.2 Hundred Days
4.3 Conditions in Germany towards the end of the war
4.4 The Armistice

Cause of WW1 (unit of work) KS3
This is a Key Stage 3 scheme of work that aims to develop knowledge and a casual understanding of the Frist World War. There are seven lessons included, plus an assessment:
What was WW1?
Militarism
Alliances
Imperialism
Nationalism
Assassination and July Crisis
What caused WWI?
Assessment
Also, included is a knowledge organiser. There are 30 questions designed for pupils to use to self-study at home. These are then tested in every lesson until lesson 7. Included on the knowledge organiser is also a timeline of events and a list of keywords sorted into alphabetical order.
Starter activities are knowledge recall with elf assessment.
There are clear opportunities for peer assessment with examples of WWW and EBI that pupils are able to use.
Group work, individual work, and teacher-led learning are included as a part of the scheme of work.
Reading materials are included in the lesson. Militarism and alliances include a choice of reading that is at reading age 10 or 12. Both include self assessment.

Edexcel Cold War Key Topic 3
This series of lessons follows Edexcel’s Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91. There are printable information sheets, but this can be esily substituted with the textbook.
Seven lessons in total with resources to print.
Invasion of Afghanistan and Carter
Detente (2 lessons)
Second Cold War
Gorbachev’s new thinking (2 lessons)
Fall of the Berlin Wall
Collapse of the SU and end of Warsaw
KT3 over view lessons with worksheet
KT3 exam questions with mark schemes
Every lesson starts of with 5 recall questions with the answers
Exam questions with the mark scheme are included
Self assessment is included.
Mark schemes are included on the ppts to make peer assessment easy.
Each each question relevant to KT3 is included in the exam question ppt. It is clear what part of th spec each exam question is referring to.

What was the Industrial Revolution?
This is a stand alone lesson that explores the key themes of the Industrial Revolution.
Link to FULLY RESOURCED SoW here https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12888896
Learning objectives:
identify changes from 1750 to 1900.
describe the changes that took place from 1750 to 1900.
Explain the impact of change over 150 years.
There is printing for this lesson. AfL is included. This includes the answers to the activities.