497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
All resources

OCR AS level Physics: Moments and Equilibrium
OCR AS level Physics: Moments and Equilibrium is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Power and Efficiency
OCR AS level Physics: Power and Efficiency is a part of the Module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

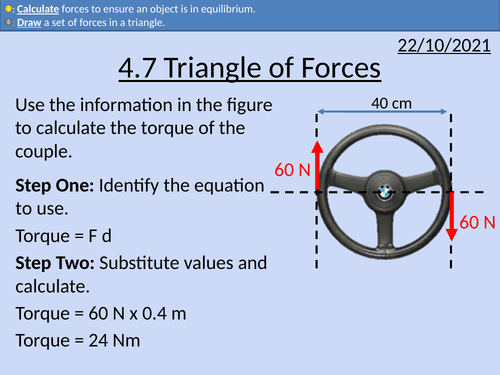
OCR AS level Physics: Triangle of Forces
OCR AS level Physics: Triangle of Forces is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Density and Pressure
OCR AS level Physics: Density and Pressure is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

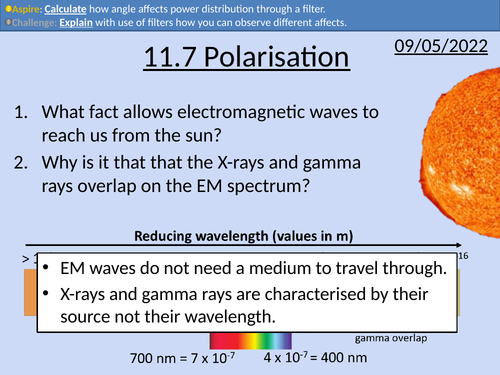
OCR AS level Physics: Polarisation
OCR AS level Physics: Polarisation is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

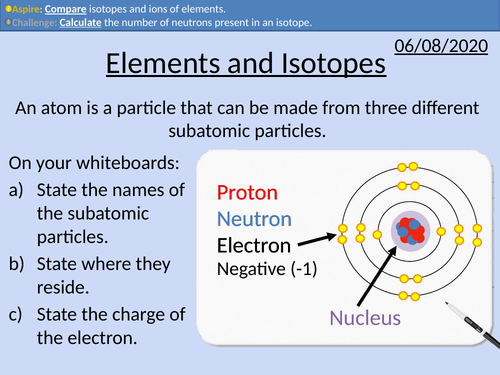
GCSE Chemistry: Isotopes and Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definitions of elements, isotopes, and ions
• State mass number, atomic number, and chemical symbols
• Calculate the number of neutrons
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.1 The Particle Model
All resources for P1.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model

OCR Applied Science: 1.1 The Atom
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
nucleus contains protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons
relative masses and charges
nuclear and atomic diameters
nucleon number, proton number and isotopes
proton number defines the type of atom
nuclear notation
attractive and repulsive forces within the nucleus

OCR Applied Science: 2.1 Mixtures and Alloys
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Types of mixtures to include solutions, colloids and suspensions
Difference between colloids and suspensions in terms of particle size
Uses of common colloids in nature and medicine
Types of colloids to include aerosols, emulsions, foams, gels and sols
Significance of colloids in nature and medicine
Alloys as mixtures of metals
The character and features of alloys
Uses of common alloys to include amalgam, solder, bronze, titanium alloy

GCSE Chemistry: Filtration and Crystallisation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for solution, solute, solvent, insoluble, soluble.
The technique of filtration
The technique of crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Filled outer shells result in more stable electronic structures.
• The electronic configuration ionic compounds
• Models of giant ionic structures

GCSE Chemistry: Bond Energies and Energy Changes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of bond energies
• Calculating bond energies per mole
• Calculating change in bond energies in reactions
• Determining if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic from the change in bond energy.

GCSE Chemistry: Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition for exothermic and endothermic
• Examples of exothermic and endothermic reactions
• Practical procedure for NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
• Determining if experimental evidence show a exothermic or endothermic reaction

GCSE Chemistry: Group 0 - Noble Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Properties of Noble gases
• Trends and anomalies in Group 0 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 0 Noble gases
• Electron configuration of Group 0 Noble gases
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
All resources for P4.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Group 7 - The Halogens
Halogen Displacement Reactions
Group 0 - The Noble Gases
The Transition Metals
Reactivity of Elements

GCSE Physics: Wave Velocity & Water Waves
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.2a Wave Velocity & Water Waves. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Definition of mechanical waves
Water waves as a transverse waves
Converting from cm, mm, and km into m.
Definition and equation for frequency.
Wave speed equation
Rearranging equations
Ripple tank demonstration and explanation

OCR AS Chemistry: Properties of Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.1 Properties of Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Comparing pi-bond (π-bond) and sigma bonds (σ-bonds).
Aliphatic alkenes and alicyclic arrangements of molecules
s, p, d orbitals for electrons
Trigonal planar shape of alkanes leading to 120 degree bond angle.

OCR AS Physics: Electrical Energy & Power
OCR AS Physics: Electrical Energy & Power is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Derive three equations for electrical power
Applying electrical power equations
Create a circuit diagram to calculate power
Base units for V A and W.

OCR AS Physics: Potential Dividers
OCR AS Physics A: Potential Divider is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Application of the ratio of resistances
Application of the potential divider circuit
Deriving the potential divider equation
Rearranging the potential divider equation

GCSE Physics: Specific Latent Heat
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.4 Specific Latent Heat
Presentation covers
Changes of State - Phase changes
Interactive Graph
Equation with example
Questions with solutions for SLH equation
Exam style question with answer