38Uploads
14k+Views
29k+Downloads
Geography

KS3 Africa Scheme of Learning
Complete scheme of learning (12 lessons) aimed at KS3 focusing upon the continent of Africa. All lessons are fully resourced.
This scheme of work includes:
Use of Geographical skills to show how we will link to Africa through holidays.
Investigating the impacts of tourism in one country in Africa (Kenya) using a case study and suggest how the environment can be protected against mass tourism through eco-tourism.
Developing our enquiry skills by looking at where our food comes from.
Investigating the causes and effects of the food crisis in Africa and speculate on the possible long term impacts on the continent
Investigating how the conflict in various countries are causing problems socially and economically.
Investigating why people are moving from rural areas to urban areas in LIDCs and suggest the impact that this might have on the wider community.
Investigate the problems faced by the people living in squatter settlements
Investigating the possible solutions to the key problems in squatter settlements by using a case study to support your answer.

Population KS3 Scheme of Learning
This is a fully resourced 9 lesson scheme of learning based on the module of population and aimed at KS3. The scheme of learning includes:
Lesson 1: Why is the world’s population distribution uneven?
Lesson 2: Why is overpopulation a challenge?
Lesson 3: What factors influence population growth?
Lesson 4: How does the Demographic Transition Model show population change?
Lesson 5: How can we study the population structure of a country?
Lesson 6: What are the challenges and opportunities created by an ageing population?
Lesson 7: What are the challenges and opportunities created by immigration?
Lesson 8: What are the challenges created by rural-urban migration?
Lesson 9: Should refugees be allowed access to the UK?

Asia KS3 Scheme of Work
This is a complete KS3 scheme of work of 13 lessons focusing upon the continent of Asia. The scheme of work includes the following:
Asia is a wealthy continent. How far do you agree?
Locating Asia – map work (pupils need to learn the names and location of the continents as well as the names and location of countries within Asia)
Contrasting images of Asia to be given to pupils to instigate a discussion about the wealth of the continent.
Pupils answer the key question using the photographs and discussion as evidence.
GDP/GNI map of Asia and any commonly used measure of development.
Case Study: Japan
Location of Japan and the four major islands- map work
Japanese climate and physical features
Introduction- what is Japan like and how has it changed?
Japanese ecosystems- concentrate on one of: coniferous or deciduous woodland + flora and fauna adaptations.
Japanese industry- imports and exports (pie chart/bar chart must be used)
Population structure of Japan- ageing population and population pyramids
Should tourism in Asia be encouraged? Case Study: Thailand
Introduce tourism in an Asian country (Thailand)
Look at the changing number of tourists visiting the country (graph interpretation) – are there reasons that explain the fluctuating number? e.g.
Asian tsunami 2004
Pupils need to investigate the pros and cons of tourism and then be able to justify their decision as to whether they think tourism should be encouraged or not?
What are the characteristics of tropical rainforests?
Describe the distribution of tropical rainforests around the world
Understand the that the rainforests grow in layers (shrub layer, under canopy, canopy and emergent) and the reasons for this
Pupils need to be aware that animals and plants have adapted to life in the rainforest and have different characteristics depending on the layer they live in.
Do we need to protect tropical rainforests?
Pupils need to understand the importance of tropical rainforests to both humans and the environment
The causes of the destruction of the rainforests needs to be investigated both the human and natural causes
Pupils need to be able to link together the causes of the destruction and the consequences this has.

Are the monsoon rains in India always a negative?
This is a fully resourced lesson based upon the monsoon rains in India. The lesson includes the following:
• What are monsoon rains?
• Classifying the effects of monsoon rains into positive and negative as well as social, economic and environmental.
• Pupils need to consider whether they only create challenges and answer the key question.
Bundle

KS3 Schemes of Work/Learning Bundle
A bundle of some of my schemes of work to save you some cash! Included is:
KS3 Asia SOW
KS3 Afroca SOW
KS3 River Landscapes SOW
KS3 Using our Natural Environment SOW
KS3 Population SOW

What are the different types of volcanoes?
This is a fully resourced lesson focusing upon the types of volcanoes around the world. The lesson includes:
• Describing the distribution of global volcanic activity (specifically make links to Pacific Ring of Fire)
• Showing pupils images of a shield and composite volcano and ask them whether all volcanoes are the same.
• Pupils need to be able to identify and explain similarities and differences between the volcanoes. Shape, type of eruption and consistency of lava are the main differences.

KS3 Asia Scheme of Learning
This is a full scheme of learning aimed at KS3 focusing upon the continent of Asia. All lessons are fully resourced and are ready to print and use immediately!
This scheme of work includes:
Lesson 1: Where is Asia and what countries belong to Asia?
Lesson 2: Do tsunamis always create the same level of challenges for the countries involved?
Lesson 3: Does tourism create more challenges or opportunities for the host country?
Lesson 4: Do the monsoon rains in India only cause challenges for the country?
Lesson 5: Should tropical rainforests be protected?
Lesson 6 Why is there global uneven development?
Lesson 7: What factors contribute to a country’s level of development?
Lesson 8: What challenges does rapid urban growth create?
Lesson 9: What are the advantages and disadvantages of building a dam?

What damage do earthquakes cause?
This is a fully resourced lesson focusing upon the cause and impacts of the Nepal earthquake in 2005.

Should people live in areas of volcanic activity?
This is a fully resourced lesson based upon a key question of whether people should live in areas of volcanic activity. Pupils will assess and investigate a range of sources provided to be able to make a judgement on the key question of the lesson.

What causes tropical storms around the world?
This is a fully resourced lesson based upon tropical storms and their causes. The lesson includes:
• Pupils firstly need to know that tropical storms can also be known as hurricanes, cyclones and typhoons. The names change depending upon where in the world they occur.
• Pupils describe the distribution of tropical storms using a map.
• Pupils need to be aware of the conditions needed for tropical storms to occur (warm oceans over 27 degrees Celsius)
• Pupils then need to sequence the steps to explain the formation of a tropical storm.

Do tsunamis always create challenges?
This is a fully resourced lesson focused upon whether tsuanmis create challenges for countries. The lesson includes:
• Defining a tsunami
• Investigaing the cause of a tsunami
Case studies: Japanese Tsunami 2011 and Asian (Boxing Day) Tsunami 2004
• Comparing the social, economic and environmental effects of each tsunami

Should tropical rainforests be protected?
This fully resourced lesson focuses upon whether tropical rainforests should be protected whilst also exploring additional information about tropical rainforests. The lesson includes:
• Distribution/location of tropical rainforests
• Use sources to discover why rainforests are of value/important to both people and the planet and how human activity is threatening them
• Consider the methods used to manage the threats /conserve the rainforests.

River Landscapes KS3 SOW
This scheme of work is aimed at KS3 and based around river landscapes. This scheme of work includes the following:
How does the hydrological cycle work?
What are the key terms and processes associated?
What is the hydrological cycle and how does it work?
Include: key terms of precipitation, condensation, ground-water flow, surface-water flow, evaporation, impermeable and permeable rock.
What are the different kinds of geomorphological processes?
Processes of erosion- hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition and solution
Processes of weathering- biological, chemical and mechanical (freeze thaw)
Processes of mass movement- slumping and sliding
Processes of transportation- traction, saltation, suspension and solution
What are the long and cross profiles of a river?
Pupils need to recognise the different shapes for both the long and cross profile diagrams of a river valley.
Identify the difference between the upper, middle and lower courses of a river including the valley shape and river channel.
How do geomorphological processes lead to the formation of river landforms?
The formation of river landforms (waterfall, gorge, V-shaped valley, floodplain, levee, meander, oxbow lake)
Case Study: River Tees Location of The River Tees
Key features found in the upper, middle and lower course.
Human activities found along the upper course of The River Tees (sheep farming, Cow Green Reservoir and tourism in Middleton) and the impact that this has had on the landscapes.
Human activities found along the lower course of The River Tees (Tees Barrage and meander straightening) and the impact that this has had on the landscapes.

The Big Dry Knowledge Organiser
A detailed but compact knowledge organiser based upon the case study of the Big Dry in Australia.
This organiser includes:
Location
Background Information
Causes
Effects/Consequences
Responses

Andros Barrier Reef Knowledge Organiser
A compact but detailed knowledge organiser based upon the case study of the Andros Barrier Reef. This organiser includes:
Location
Background Information
Value
Threats
Management
Bundle

Knowledge Organiser Bundle
A bundle of knowledge organisers as part as OCR A 9-1 GCSE Geography Paper 1/2. It includes:
Andros Barrier Reef
Ethiopia- a country study
Peruvian Amazon
Rio de Janeiro- a study of a city in a EDC
The Big Dry- drought case study

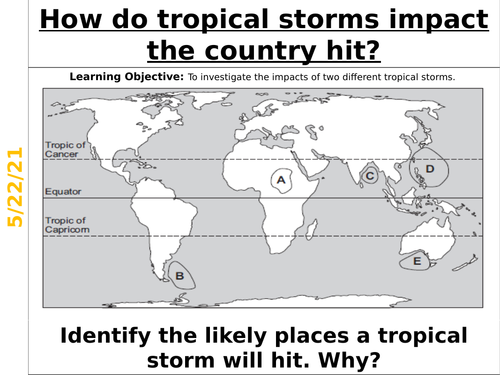
How do tropical storms impact the country hit?
This is a fully resourced lesson based upon the impacts of tropical storms on the countries that they hit. The lesson includes comparing the impacts of Hurricane Katrina of 2005 and Cyclone Nargis of 2008. Categorising of impacts are organised through ‘pizza toppings’.

What is Geography?
A fully editable lesson introducing students into what is Geography?
The lesson includes:
Circle map task
Defintions
Categorising types of Geography
Plenary- categorising elements of Geography through images

Student Friendly Command Words
Student friendly commands words for OCR A GCSE Geography.
I have this in my exercise books and as a display as a constant reminder.

Year 6 Transition Work 2023- Geography
I have created a Geography transition work book for Year 6 students to complete to aid the transition to secondary school. This will support students with the key skills needed to progress.