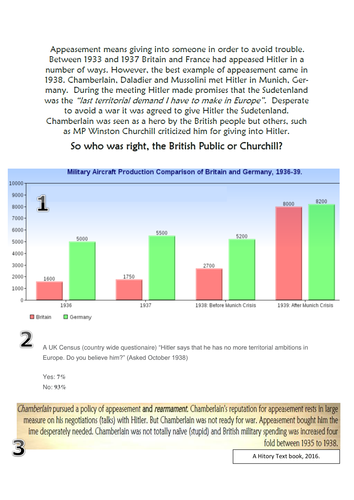
Mike Morley's Shop
I have been a teacher for 8 years and am currently working in Dubai as a History teacher and Head of Year. I put a lot of effort into creating my premium resources and will not upload them until I am confident the lesson will be graded at least a good if not outstanding. Please contact me if you have any queries, questions or concerns about my resources. Regards