Acid-base titrations OCR AS Chemistry
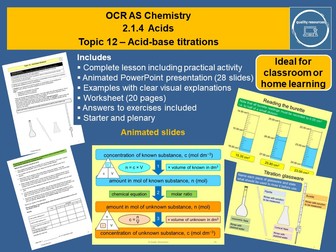
<p>This complete year 12 resource on acid-base titrations includes the practical procedure and calculations for titrations as well as details of evaluating experiments. It features a 28 slide interactive PowerPoint that illustrates the concepts in a lively, visual and systematic way. The resource includes a starter, learning checks, clearly explained examples of calculations, a practical activity with evaluation and a plenary. A 20 page worksheet includes a variety of structured and unstructured calculations and answers to all exercises. Ideal for the classroom or blended learning, this resource could be used to present the topic, or for revision, extension or consolidation.</p>
<p>This lesson is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following sections:<br />
Module 2 – Foundations in chemistry<br />
Part 1 – Atoms and reactions<br />
2.1.4 – Acids (part)</p>
<p><strong>Content covered:</strong><br />
• Titration and uses<br />
• Standard solution<br />
• Glassware and procedure for titration with detailed hints for technique<br />
• Reading burette<br />
• Recording titration results and calculating the mean<br />
• Titration calculations<br />
• Examples of structured and unstructured calculations<br />
• Revision of calculations involving masses and volumes<br />
• Practical titration activity<br />
• Evaluation of titration experiment<br />
• Uncertainties and calculating % uncertainties<br />
• Procedural errors</p>
<p>Duration: 2 lessons</p>
<p><strong>Please review!</strong></p>
<p><strong>Links</strong><br />
Previous topic: Topic 11 – Acids and bases (free resource)<br />
<a href="https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/acids-and-bases-ocr-as-chemistry-12747201">https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/acids-and-bases-ocr-as-chemistry-12747201</a><br />
Next topic: Topic 13 – Redox<br />
<a href="https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/redox-ocr-as-chemistry-12409890">https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/redox-ocr-as-chemistry-12409890</a></p>
<p><strong>Related topics</strong><br />
Topic 8 − Moles and concentration of solutions<br />
<a href="https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-and-concentration-of-solutions-ocr-as-chemistry-12391026">https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-and-concentration-of-solutions-ocr-as-chemistry-12391026</a><br />
Topic 9 – Moles and reactions<br />
<a href="https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-and-reactions-ocr-as-chemistry-12404411">https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-and-reactions-ocr-as-chemistry-12404411</a><br />
Bundle − Moles, masses, concentrations, gas volumes and reactions<br />
<a href="https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-masses-concentrations-gas-volumes-and-reactions-12404451">https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/moles-masses-concentrations-gas-volumes-and-reactions-12404451</a></p>