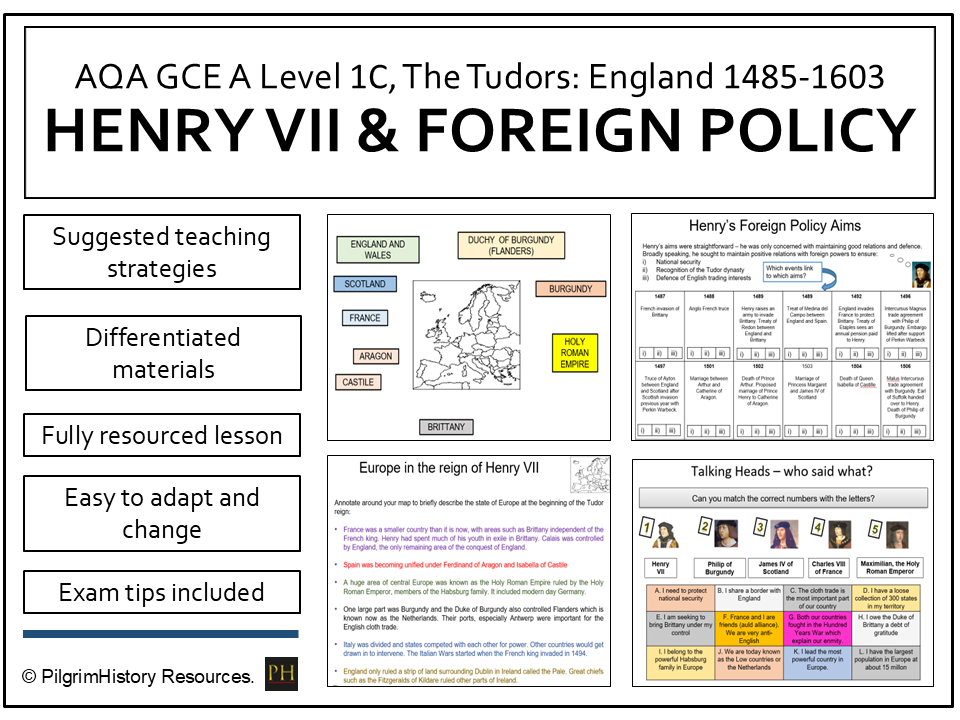
Pilgrim History's Shop
I am a History Teacher with a love for producing high quality and easily accessible history lessons, which I have accumulated and adapted for over 20 years of my teaching career. I appreciate just how time consuming teaching now is and the difficulty of constantly producing resources for an ever changing curriculum.