404Uploads
119k+Views
40k+Downloads

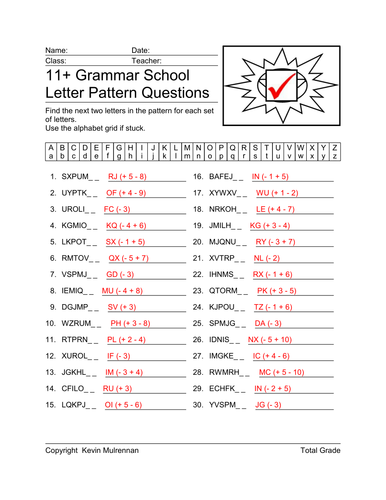
11+ Verbal Reasoning Questions Letter Patterns Vol 2
Another 100 worksheets on volume 2. I've included more questions per sheet and for some I have omitted the alphabet grid. I have designed 100 worksheets on letter patterns for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 100 worksheets provided on a cd. Letter patterns is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. Introduce some logic and problem solving skills to students with the Letter Patterns worksheet. Sets of letters related in some way are displayed. Students must find the next two letters in the pattern for each set of letters. You can see an answer sheet in my picture with the answers in red.

100 Worksheets Addition Maths Easy at Start Hard at the End
100 worksheets on addition.
I’ve used a nice big font.
They start off easy then get progressively harder.
Answer sheets provided for all worksheets.

Teaching Resources 100 worksheets Literacy Wordsearch KS2 English Language
I have designed 100 worksheets on Literacy word searches for primary school children. A wide variety of words used. Plenty of different directions to keep the kids guessing. I have used common English words. Ideal for 11+ preparation. Ideal for Literacy. Ideal for people learning English. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

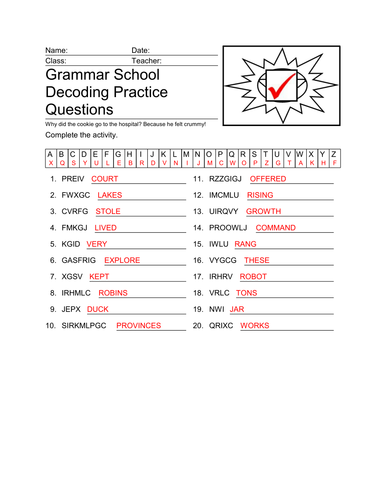
11+ Verbal Reasoning Decoding Vol 1 Maths KS2
I have designed 100 worksheets on decoding numbers for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 100 worksheets provided on a cd. Decoding is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. The Decoding worksheet helps to reinforce spelling and problem solving skills for students. The letters of each word are replaced with other letters or numbers based on a pattern. Students must translate the words and spell them correctly. You can see an answer sheet in my picture with the answers in red.

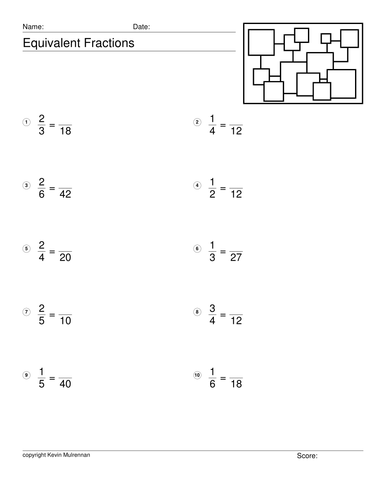
Equivalent Fractions 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths
100 worksheets with answers.
20 per sheet.
Pupils have to write the equivalent fractions.

Number Order 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics KS1
100 worksheets with answers on Number Order.
Pupils have to put the numbers in the correct order.
There are at least 10 sets of numbers per sheet.
A nice little time filler.

Simplifying Fractions 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics KS2
100 worksheets on simplifying fractions.
Answer sheets provided.
A good time filler or homework.

Time Passages 100 worksheets with Answers Maths Telling the Time
I have designed 100 worksheets on time passages for primary school children. They have to draw the time hands on the clocks on the sheets. What time will it be? - There are two clocks . The first clock shows a time, the second clock is blank. A question like "What time will it be in 2 hr and 20 min?" appears below the clocks. The student draws the answer on the second clock. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

500 Latin Wordsearches Word Searches Cambridge Latin Course
500 word searches on the first book of the Cambridge Latin course.
Answers provided.
The block of text has different shapes. There’s even some colour ones if you are feeling extravagant and can afford the ink!
Great for rainy Friday afternoons.

Teaching Resources worksheets Area Perimeter Mathematics
I have designed 100 worksheets on calculating area and perimeter for primary school children. There is a wide variety of difficulty. Some sheets just require area, some perimeter, some a mixture of the two. In some rectangles are used, others have triangles. You can use your professional judgement to choose the appropriate sheet. Answer sheets are provided for all worksheets.

1000 Questions Advanced Addition Maths Mathematics KS2
1000 questions on advanced addition.
Pupils write the answers directly on the sheets. There are different numbers of digits that they can add up.
Answers all provided.

Harry Potter Puzzles Crosswords Word Searches J K Rowling
Puzzles for Harry Potter.
Great for Friday afternoons when the kids go mad.
Sample clues.
ACROSS
A person who is born to magic parents but has
no magic ability.
Hooded dark arts creatures who at one time
followed Voltemort.
The wizarding world’s main newspaper.
The day a person dies and becomes a ghost.
A very powerful dark wizard who killed James
and Lily Potter.
Fifth year exam for students of the Hogworts
Academy.
An expensive broom that Sirius buys for
Harry.
The train that takes Hogworts students to and
from the school.
Nearly Exhausting Wizarding Test.
Buttery drink which can be bought by
students in Hogsmeade.

Remembrance Day World war 1 History Teaching Materials Plans Resources KS2 History
I’m now retired from teaching after decades in the classroom.
I’d like to help the younger generation.
One aspect I don’t miss is Sundays. Trying to fill in planning grids that were rarely used or looked at. What a nightmare!
So I’ve put together my teaching plans, powerpoints, adobe pdf files etc from the various schools I was in.
Feel free to adapt for your planning grid.
In it are lesson plans, powerpoints, questions etc.
You get:
9 pdf files 19 powerpoints 16 word files
example text in pp
Remembrance Day 2010
LO: Understand why and what we remember.
Recognise how important Year 5’s job is.
Examine some sources of information about the first and second world wars.
Each year the nation expresses its unequivocal support for The Royal British Legion’s charity work through the Poppy Appeal.
The emphasis this year is the need to help the Afghan generation of the Armed Forces and their families - today and for the rest of their lives.
What is the Poppy Appeal?
What is Remembrance Sunday?
The Sunday nearest to November 11 when those who died in World War I and World War II are commemorated.
In 1900 (how many years ago?) there were
five great, powerful nations in Europe:
Britain France RussiaAustria-Hungary Germany
These countries had empires and armies.
Between 1900 and 1914 tension and arguments began to cause trouble.
The five main countries began an ‘arms race’, they were trying to amass troops, weapons and war ships.
Remember that powerful country called Austria-Hungary? The heir to the Austrian Hungarian throne was a man called Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated – this caused lots of trouble between the five rival nations.
Britain declared war on 4th August
1914.
Article on the assassination of the Archduke.
The total number of casualties, both military and civilian, were about 37 million. 16 million deaths. 21 million wounded. About 1.1million British troops died.
Major hostilities of World War I were formally ended at the 11th hour of the 11th day of the 11th month of 1918.
Lest we forget…

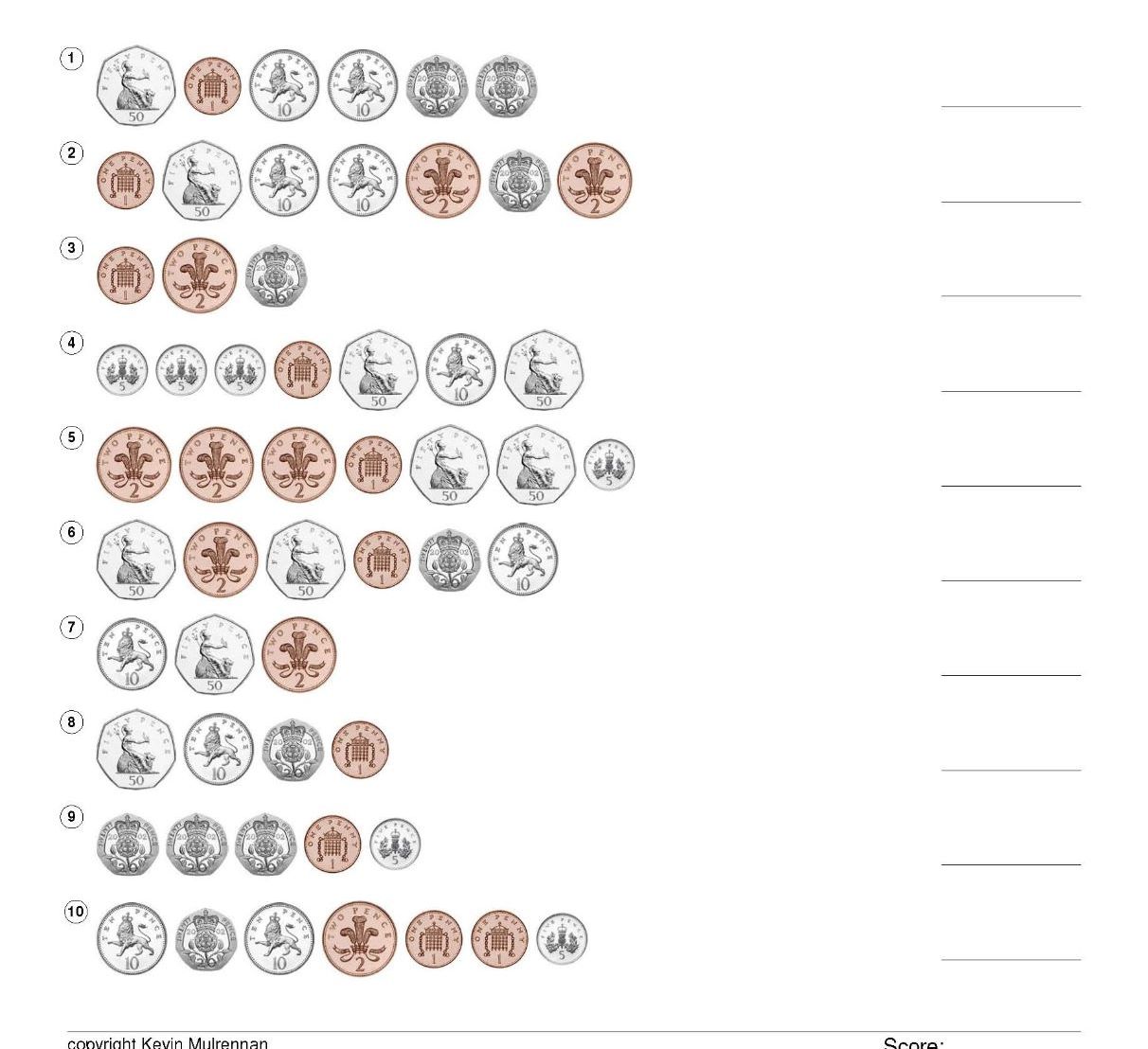
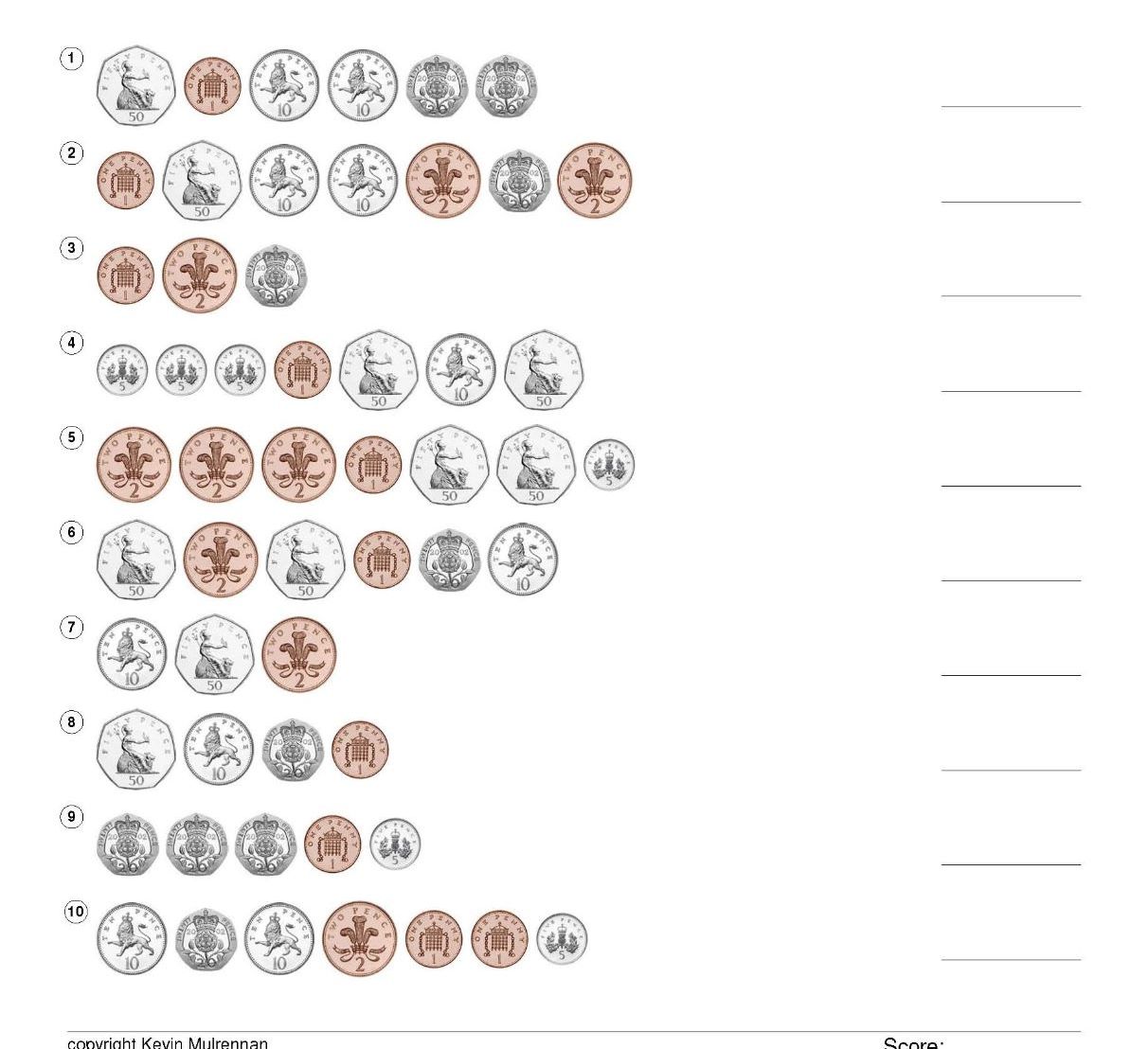
Euro Coins European Worksheets 500 Questions Mathematics Counting KS1 KS2
500 questions on counting up Euro coins.
5 worksheets with 100 questions each.
There are little pictures of the coins and the pupils have to add them up and write the answers on the sheet.
Bundle Sale

Bundle Coins Worksheets KS2
Bundle.
100 Worksheets on counting coins
Plus questions on Pythagoras and addition
Teaching Resources 100 worksheets Coins KS1 Teachers Counting KS1 KS2
100 Questions on Pythagoras Answers Provided
100 Worksheets Addition Maths Easy at Start Hard at the End
Bundle Sale

Decoding Bundle 200 Worksheets Verbal Reasoning
A bundle of worksheets.
200 worksheets on decoding,
Plus some great ones on Pythagoras.
I have designed 200 worksheets on decoding numbers for the 11+ non verbal reasoning questions. There are 200 worksheets provided on a cd. Decoding is an important aspect of the 11+ exams. Ideal for parents, pupils and tutors. Answer sheets provided. The Decoding worksheet helps to reinforce spelling and problem solving skills for students. The letters of each word are replaced with other letters or numbers based on a pattern.
Bundle Sale

Bundle Coins plus Across Down Subtraction and Addition
A bundle.
Coins worksheets plus ones on acoss down puzzles (subtraction and addition)
Teaching Resources 100 worksheets Coins KS1 Teachers Counting KS1 KS2
2
KS2 Mathematical Puzzles Across Down Subtraction
2
Maths Puzzles Across Down Addition 100 Puzzles Plus Answers
Bundle Sale

Year 4 Planning Complete Year's Planning Numeracy Literacy KS2 & Aesop Cloze Worksheets Bundle
Great mega bundle.
A complete year’s planning.
Plus great Aesop cloze worksheets.
Incredible value.
Please look at my shop for individual details.
Below is one as an example:
Planning for the Autumn term for year 4.
You get 160 mb of material so good value imo.
I taught mainly in Catholic schools so has a Catholic bent. But as we live in a multicultural society, this should be no problem.
You get planning for:
creative curriculum
Literacy
Numeracy
P.E. (some)
Science (some)
R.E. (Advent etc)
Loads of great lessons to ease your Sunday afternoons. Just cut and paste into your school template.
Bundle Sale

Fractions Worksheets Mega Bundle With Answers
A great bundle of fraction worksheets.
Includes:
Equivalent Fractions 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths
Half a million (500000) Fraction Questions Worksheets
Mixed Fractions Questions 100 Worksheets Maths
Bundle Sale

Bundle Coins Worksheets UK Euro Shopping
A good value bundle.
Fill in the worksheets on counting Euro coins, UK coins and a series of shopping questions that test knowledge of money etc.