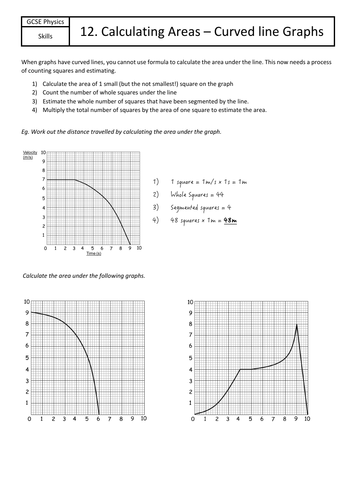
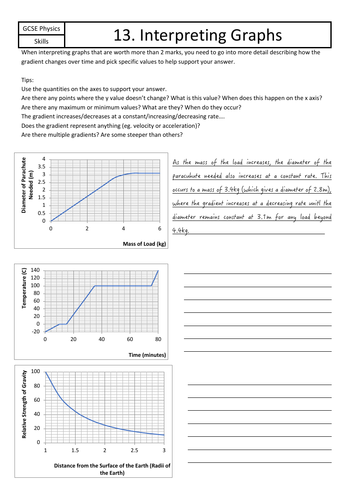
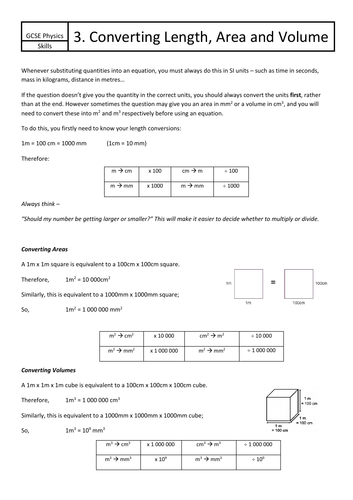
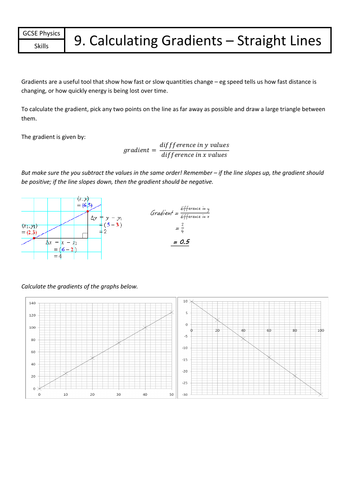
Jordan Bell Physics
Complete worked solutions and answers to the popular online problems on the Isaac Physics website. Full GCSE Topic Booklets including comprehensive notes, activities, structured questioning with practical skills. Each booklet comes with Summary Questions and Extension Questions that involve deep-thinking to challenge the most-able. Resources can be purchased individually, or bundles can be purchased where all individual resources are in one package.