11Uploads
2k+Views
15Downloads
English

What is Intelligence Anyway by Issac Asimov
I use this assignment with high school freshman at the start of the year to establish that there are myriad learning styles and methods of processing information.

Quick Write Paragraph Development Template
Use this template with rubric to help students develop their writing. It is sufficient for any writing prompt. Albeit formatted for a shorter writing piece, this practice allows students to continue their writing on the back of the page or another sheet of loose leaf.
To differentiate, lengthen the word count or alter the target objective of the prompt. Students are encouraged to learn the rubric so they are able to score themselves as well as their peers.

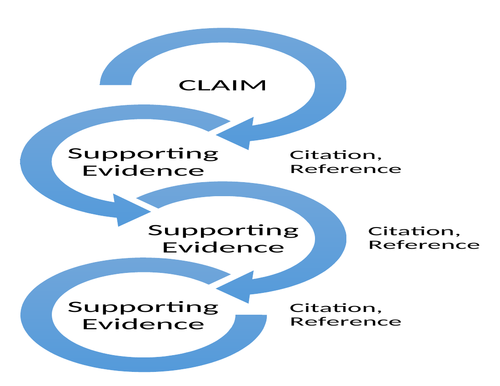
Poster-How to Make a Claim
This poster is for the secondary classroom. It is a simple flow chart of establishing a claim and supporting it with evidence.

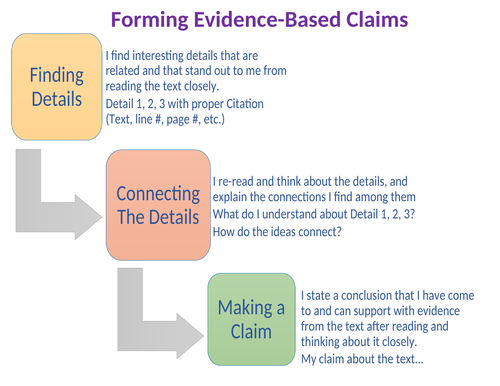
Forming Evidence Based Claims
This poster is for the secondary classroom. It best helps support student understanding of the parts of an argument. Finding details, connecting the details, and finally, making a claim. This flow chart can be discussed forwards or backwards as a way to achieve the creation of an argumentative position and the support of it.

KNQ Graphic Organizer: Know, New, Question
As an alternative to the KWL Chart (What do you KNOW, What do you WANT to know, What have you LEARNED), the KNQ Graphic Organizer (What do you KNOW about the subject, What is NEW about the SUBJECT, What QUESTIONS do you have) requires students to organize their information in a different way.
Some student don’t know what they WANT to know, so having them ask QUESTIONS at the end of the lesson can help them reflect of what they’ve learned and what may have been left out. Instead of what a student has LEARNED about the subject, they can examine what is NEW information they have acquired through the lesson. Finally, establishing what students KNOW is always good pedagogical practice as a diagnostic assessment.
The KNQ practice can be used to assess student reading comprehension, lesson engagement and understanding or thematic content in a unit. As a lesson assessment, this tool can help gage next steps and gaps in learning.

Pre Reading: Kaffir Boy
These resources are used in high school English Language Arts courses. They are great for Global History, however, if the English teacher uses these as a supplement to what the Social Studies teacher is doing, it will reinforce relevant information.
Students begin responding independently to the Anticipation Guide. They share out as time permits. In small groups, students are given a portion of the Apartheid background information. The teacher should cut them into strips. Each group should read and discuss the content of their passage. The teacher can opt to use a discussion protocol, in this case, they can use the Literature Circle Roles attached (basic). Once students have shared out, they JIG-SAW the information by making connections between passages. They self assess using the rubric.

Annotation Slides
Annotation is a supremely useful skill and reading strategy to use in order to better understand and discuss what you have read. Students require repetition of academic behaviors that will aid in their improved classroom performance. Annotation is a skill that can be used across subjects and should be modified for personal use as students become more comfortable.
Common symbolsare identified.

The Rhetorical Triangle
The Power Point Presentation and worksheet help teachers and students examine the 3 Parts of the Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, Logos. Today, we also use The Writer, The Audience and The Context to closely read the rhetorical content in a passage and how they relate to Ethos, Pathos and Logos. Having this foundation helps the student develop a familiarity with structure, content and literary terminology.
The Objective: Students will be able to identify the components of the Rhetorical Triangle and how they are used in a text.
The suggested Agenda includes: Three common Parts of Rhetorical Triangle, Their meanings, Three contemporary Parts of Rhetorical Triangle, Their connection to commonly known Parts of Rhetorical Triangle, Use Analyzing Rhetoric Graphic Organizer Worksheet to Identify Ethos, Pathos and Logos within a passage
There are two images of the Rhetorical Triangle with labeling, especially important for visual learners. Students can copy or obtain handouts of these slides to better understand the information.

33 Popular Rhetorical Devices
This Power Point Presentation outlines the 33 most popular and commonly used rhetorical devices that students should know.
The goal is to guide students towards the comprehension of the use and application of specific Rhetorical Devices. The suggested agenda includes: Define Rhetorical Devices, Warm Up Exercise: Adding Style, List of Rhetorical Devices (33), Each Rhetorical Device defined with examples (33), and Next Steps.
This presentation is meant as a starting point to build student knowledge. It can be used as a lesson at the start of a Rhetoric Unit or as an outline. Each slide consists of a Device, the Definition of that device, an Example of that device and, where necessary, further Explanation of how the device is used.
Visuals and other images can be added to the slides to enhance its meaning.
This resources has been adapted from Prestwick House, Inc. (2008) “Rhetorical Devices: A Handbook and Activities for Student Writers”.

Literature Circles: Student Reading Groups
Literature Circle praxis is meant to aid students in reading comprehension. This can take many forms. Student groups should remain 3-4 in size, depending on the regularity of attendance. Student should be able to work in an environment that affords active listening, active reading (including annotation), and writing reflection.
Literature Circles can take one lesson or several days, depending on level and length of reading. The desired outcome can be to engage the reading as a group member with a particular ROLE or to use that ROLE to process a specific aspect of the text.
Roles include:
Discussion Director
Vocabulary Enricher
Literary Luminary
Checker (for task/role objectives)
Summarizer
Artful Artist
Character Captain
Passage Picker
Reporter
Bridge Builder
Any combination of the above roles can be assigned by the teacher. It is up to their discretion which roles should be used and in what groupings. Some roles overlap in responsibilities. Those that overlap are also differentiated for various learners.