496Uploads
162k+Views
70k+Downloads
Chemistry

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Tests for Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Chlorine.
Gifs of each gas test
Electron structure for diatomic molecules

GCSE Chemistry: Alkanes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of hydrocarbons
• Carbon and hydrogen saturation
• Mnemonic device for naming alkanes
• Comparing complete and incomplete combustion
• Balancing complete combustion reactions

GCSE Chemistry: Biological Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Proteins as polymers and amino acids as monomers
Carbohydrates and simple sugars
Comparing simple sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose) with complex carbohydrates (starch).
DNA as a polymer and nucleotides as monomers
Structure of nucleotides (phosphate group,
a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base).
Base pairing in DNA and hydrogen bonds

OCR AS Chemistry: Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.2 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Aliphatic, alicyclic, and aromatic compounds.
Naming organic compounds
Drawing organic compounds
Functional Groups
Alkane
Alkene
Alkyne
Alcohols
Haloalkane
Aldehyde
Ketone
Carboxylic Acid
Ester
Amine
Nitrile

OCR AS Chemistry: Representing the formulae of Organic Compounds
OCR AS Chemistry: Formulae for Organic Compounds
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
molecular formula
empirical formula
general formula
displayed formula
structural formula
skeletal formula

OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming Haloalkanes
Classifying Haloalkanes (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanism for hydrolysis
Rates of reactions for hydrolysis
Reaction conditions for hydrolysis

GCSE Chemistry: Producing Electricity Using Chemistry
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Chemical cells uses
Fuel cell uses
Comparing fuel cells and chemical cells
Environmental impact of fuel cells and chemical cells
The structure of fuel cells
The operation of fuel cells
Half-equations for fuel cells

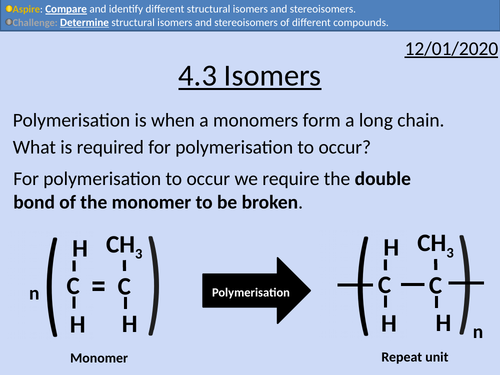
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.1 Types of Testing
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.1 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.2 Testing During Development
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.

OCR Applied Science: 4.2 Polymers and Carbon Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Determining the empirical formula for compounds
Draw monomers and repeat units using structural and skeletal formula of the following polymers:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.3 Effectiveness of Tests
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.3 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.3 Effectiveness of test
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR AS level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Heating under reflux
Distillation
Re-distillation
Purifying Organic Products
Removing impure acids from organic compounds
Drying agents
Functional Groups - Alkane, Alkene, Haloalkane, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acid, Ketone, Aldehyde, Ester, Amine, Nitrile.
One-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Two-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Haloalkanes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Haloalkanes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Naming Haloalkanes
Classifying Haloalkanes (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanism for hydrolysis
Rates of reactions for hydrolysis
Reaction conditions for hydrolysis
Definitions for CFC (Chlorofluorocarbons) and HCFC (Hydachlorofluorocarbons)
Creation of ozone
Depletion of ozone with CFCs
Reaction steps including initiations and propagation
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Naming alcohols
Classifying alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Polar and non-polar molecules
Explaining physical properties of alcohols compared to alkanes
Volatility
Solubility
Melting points
Chain length and London forces
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

OCR Applied Science: 2.2 Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.2 of Module 1: Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions
Addition reactions of alkenes to include full balanced symbol equations
Substitution reactions of alkanes and haloalkanes to include full balanced
equations
Addition polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Condensation polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Definition of a radical
The role played by UV light in producing chlorine radicals from CFCs in the
depletion of the ozone layer
Equations to show how chlorine radicals can destroy many ozone molecules
Displacement reactions to include full balanced equations for metals and halogens.

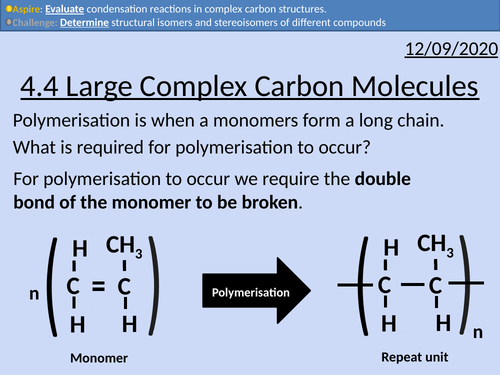
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

OCR Applied Science: 4.1 Principles of Carbon Chemistry
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Alkanes as saturated hydrocarbons containing single C-C and C-H bonds
• Alkenes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C=C double bond
• Alkynes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C ≡ C triple bond
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four members of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
• Aldehydes and ketones as organic compounds containing the C=O group
• Name and draw the structural formulae of the first four aldehydes and the first two ketones
• Alcohols as organic compounds containing the OH group
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four alcohols
• Conversion of alcohols to form aldehydes and ketones is classified as an oxidation reaction
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four carboxylic acids
• Reaction of carboxylic acids with an alkali, to include full equations using structural formulae
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the four C4H8O2 esters
• How an ester can be made from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol