496Uploads
162k+Views
70k+Downloads
Chemistry

A level Chemistry: Combined Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.6 Combined Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

A level Chemistry: Further Synthetic Routes
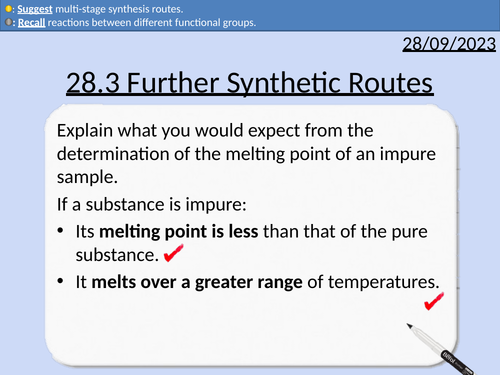
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

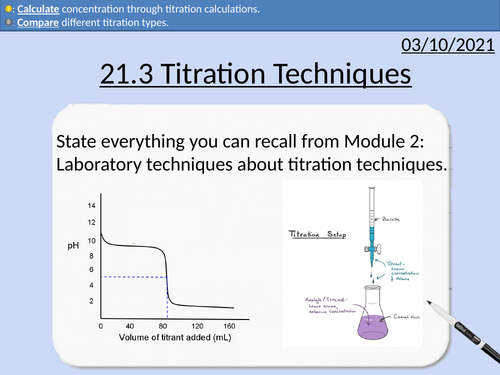
OCR Applied Science: 21.3 Titration Techniques
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
3.1 Titration techniques on consumer products
• Acid-base titration (e.g. limescale removers, eco-disinfectants)
• Precipitation titration (e.g. contact lens saline solution)
• Redox titration, (e.g. bleach, tooth whitener; vitamin C tablets).
• Complexometric titrations (e.g. Milk of Magnesia)
Including explanation and activities on:
Titration calculations
Moles and molar mass
Rearranging Equations
State symbols
Significant Figures
Comparing Data
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Amines, Amino Acids, and Polymers
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
27.1 Amines
27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
27.3 Condensation Polymers
Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons
Amines being derived from ammonia (NH3)
Classifying amines as primary, secondary, and tertiary
Naming amines
Naming ammonium salts
Amines neutralisation reactions with acids
Preparation of aliphatic amines
Preparation of aromatic amines
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers
Recap of addition polymerisation
Identifying monomers and repeat units from condensation polymers
Polyesters and ester links
Polyamides and amide links
Polyesters and polyamides formed from one monomer
Polyesters and polyamide formed from two monomers
Alkali hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Acid hydrolysis of polyamides and polyesters
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.1 The Particle Model
All resources for P1.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
28.1 Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
28.2 Further Practical Techniques
28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Carbonyl and Carboxylic Acids
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
26.1 Carbonyl Compounds
26.2 Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
26.3 Carboxylic Acids
26.4 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
The carbonyl group
Differentiating between aldehydes and ketones
Naming aldehydes and ketones
Oxidation of aldehydes
Electronegativity and polar bonds
Electrophiles, nucleophiles, and nucleophilic addition reactions
Reducing carbonyl compounds with sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (NaH4)
Primary and secondary alcohols from carbonyl compounds
Reacting carbonyl compounds with hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (NaBH4)
Reaction mechanisms for nucleophilic addition using (HCN)
Testing for Carbonyl Groups
Brady’s reagent - 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine - 2,4-DNP
Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones
Tollen’s reagent - silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia
The Carboxyl Group and polarity of bonds.
Naming carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids as weak acids
Reactions of carboxylic acids with:
Metals
Metal oxides
Alkali
Carbonates
Changing solubility of carboxylic acids in water due to carbon chain length.
Naming acyl chlorides
Naming acid anhydrides
Naming esters
Esterification
Acid hydrolysis of esters
Alkali hydrolysis of esters
Producing acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids
Producing carboxylic acids from acyl chlorides
Producing esters from acyl chlorides and phenols
Primary, secondary, and tertiary molecules
Producing primary amides from acyl chlorides
Producing secondary amides with acyl chlorides
Producing esters and carboxylic acids wirh acid anhydride
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds
OCR A level Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds
Defining an electrophile
Substitution reactions
Nitration of Benzene
Reaction mechanisms
Halogenation of Benzene
Common Halogen Carriers
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions
Acyl Chloride
Acylation Reactions of Benzene
Reactivity of Alkenes and Arenes
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene
Naming positions on the aromatic ring
Activating groups and deactivating groups
2-and-4-directing and 3-directing groups
ortho-and-para directing and meta directing groups
Two-step synthesis routes for benzene using directing groups.
Nitration of benzene
Halogenation of benzene
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of benzene
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2.3 Properties of Materials
Resources for C2.3 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Carbon
Changing State
Bulk Properties
Nanoparticles
Bundle

OCR Applied Science: 21.2 Product Testing of Consumer Products
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.
2.3 Effectiveness of test i.e.:
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use (e.g. toxicity, possible mutagenic and
teratogenic effects, microbiological safety)
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
OCR AS level Chemistry: Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkenes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkenes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Comparing pi-bond (π-bond) and sigma bonds (σ-bonds).
Aliphatic alkenes and alicyclic arrangements of molecules
s, p, d orbitals for electrons
Trigonal planar shape of alkanes leading to 120 degree bond angle.
E/Z isomerism
Conditions for trans- and cis- isomerism
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules and priority ordering
Alkene addition reactions:
Hydrogen with a nickel catalyst
Halogens
Hydrogen halide
Steam with an acid catalyst
Test for unsaturated alkenes.
Bond enthalpy for sigma and pi bonds.
Electrophile molecules
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanisms for addition reaction of alkenes and hydrogen halides
Carbocations and stability
Markownikoff’s Rule
Monomers and repeat units
Addition Polymerisation for:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Environmental Concerns from polymers including:
Combustion of polymers
recycling PVC
biogradeable bioplastics
photodegradable polymers
feedstock recycling
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C1 Particles
All resources for P1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
All resources for P4.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Group 7 - The Halogens
Halogen Displacement Reactions
Group 0 - The Noble Gases
The Transition Metals
Reactivity of Elements
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
29.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
29.4 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
29.6 Combined Techniques
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.
Nuclear Spin
Resonance
Tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Chemical Shift ẟ
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift ẟ / ppm
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C3.1 Introducing Chemical Reactions
Resources for C3.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Formulae of elements and molecules
Formulae of ionic compounds
Conservation of mass
Chemical Equations
Half equations and ionic equations
The mole
Mole calculations
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2.1 Purity and Separating Mixtures
All resources for P2.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Relative Formula Mass
Empirical Formula
Pure and Impure Substances
Filtration and Crystallisation
Simple Distillation
Paper Chromatography
Gas and Think Layer Chromatography
Purification and Checking Purity
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Resources for P2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Relative Formula Mass
Empirical Formula
Pure and Impure Substances
Filtration and Crystallisation
Simple Distillation
Paper Chromatography
Purification and Checking Purity
Metals and Non-metals
Electronic Structures
Forming Ions
Ionic Compounds
Simple Molecules
Giant Covalent Structures
Polymer Molecules
Structure of Metals
Carbon
Changing State
Bulk Properties
Nanoparticles
Bundle

OCR AS Chemistry: Module 4 Organic Chemistry
This bundle includes all PowerPoint lessons for Module 4 Organic Chemistry.
All PowerPoints are whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
Basic concepts of organic chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Nomenclature of organic compounds
Representing the formulae of organic compounds
Isomerism
Introduction to reaction mechanisms
Alkanes
Properties of the alkanes
Chemical reactions of the alkanes
Alkenes
Properties of the alkenes
Stereoisomerism
Reactions of alkenes
Electrophilic addition in alkenes
Polymerisation in alkenes
Alcohols
Properties of alcohols
Reactions of alcohols
Haloalkanes
The chemistry of haloalkanes
Organohalogen compounds in the environment
Organic Synthesis
Practical techniques in organic chemistry
Synthetic routes
Spectroscopy
Mass spectrometry
Infrared spectroscopy