496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Physics

OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force
OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
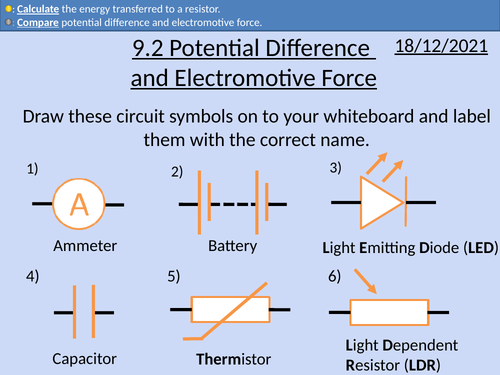
Calculating the base SI units for volts
Comparing potential difference and electromotive force (emf).
Circuit diagrams for measuring potential difference and emf.
Calculating energy dissipated in a circuit.

OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols
OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
All circuit symbols required for OCR A level physics
Polarity of cells and batteries
Electron flow and conventional current
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current
OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
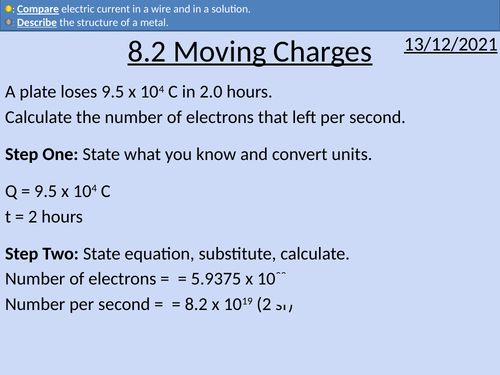
Fundamental charge and relative charge
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics
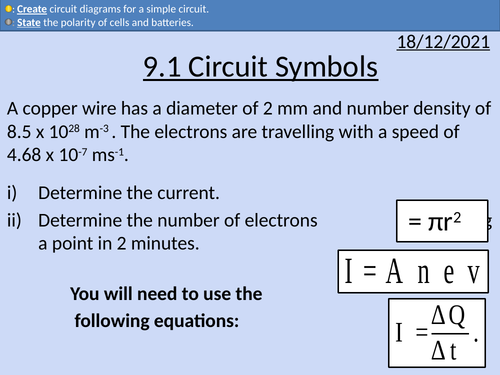
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation

OCR AS level Physics: Mean Drift Velocity
OCR AS level Physics: Mean Drift Velocity is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation

OCR AS level Physics: Kirchhoff's First Law
OCR AS level Physics: Kirchhoff’s First Law is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics

OCR AS level Physics: Moving Charges
OCR AS level Physics: Moving Charges is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors

OCR AS level Physics: Current and Charge
OCR AS level Physics: Current and Charge is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

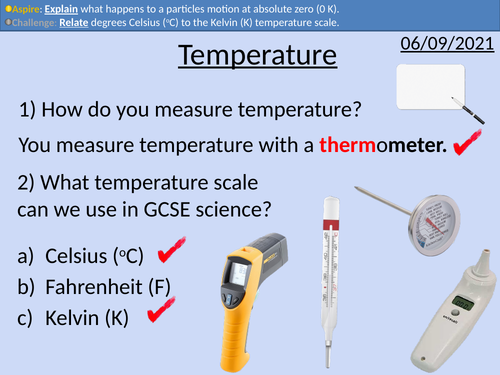
GCSE Physics: Temperature Scales and Changes.
This presentation covers:
Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales
Physical and Chemical Changes
Absolute zero

GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 2
This presentation includes:
Why scientific models change over time
Electric charge
Rutherford’s atomic model
Rutherford’s experiment
Bohr’s atomic model

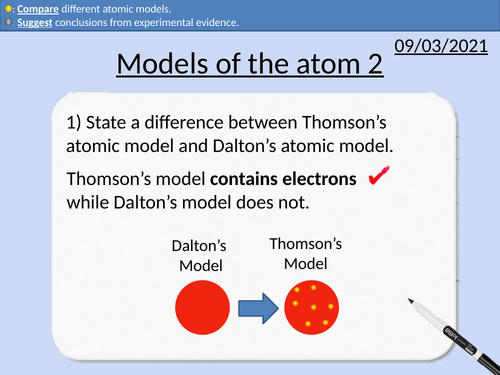
GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 1
This presentation includes:
What is a scientific model
Why scientific models change over time
The Ancient Greek Model
John Dalton’s Model
Thomson’s Plum-Pudding Model

GCSE Physics Equation Tests
Included are 9 lessons with tips on how to learn the equations for GCSE Physics.

GCSE Physics: Efficiency and Sankey Diagrams
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of efficiency
• Analysing and constructing Sankey diagrams
• Using the efficiency equation
• Rearranging the efficiency equation

GCSE Physics: Conservation of Momentum
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definition for conservation of momentum
Rearranging the momentum equation
Adding vectors (momentum)
Applying conservation of momentum
Elastic and inelastic collision
CERN and discovering particles with conservation of momentum

GCSE Physics: Satellites
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.3 Satellites
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships

GCSE Physics: The Big-Bang
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.1 The Big-Bang
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted

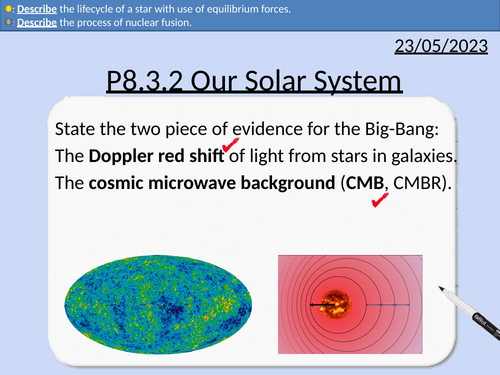
GCSE Physics: The Solar System
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.2 Our Solar System
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Structure of the solar system
Nuclear Fusion
Evolution of large stars
Evolution of Sun like stars
Gravitational force and force from nuclear fusion

GCSE Physics: Fuses and Plugs
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• The function and sizes of fuses
• Wiring a plug
• Identifying faults with plugs

GCSE Physics: Mains Electricity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.4 Mains Electricity
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.

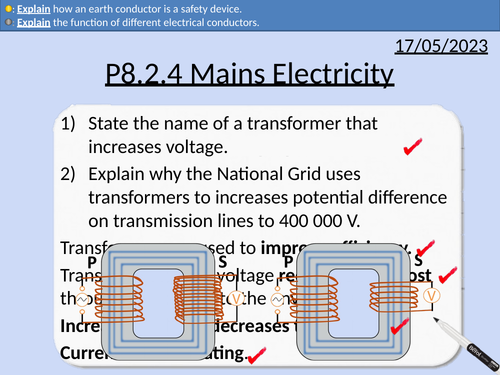
GCSE Physics: The National Grid
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.3 The National Grid
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils

GCSE Physics: Electrical Resistance
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Ohm’s law and units
• Proportionalities
• Resistance in series
• Rearranging equations
• Calculating resistance with ohm’s law