496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

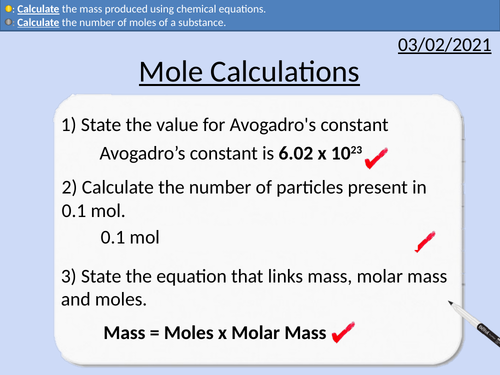
GCSE Chemistry: Mole Calculations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Rearranging Equations
• Stoichiometry as relative abundances
• Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Formula Mass and Molar Mass
• Calculating the number of moles present
• Conservation of mass

OCR AS Physics: Kirchhoff's 1st and 2nd Law
OCR AS level Physics: Kirchhoff’s Laws and circuit diagrams is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Definitions of Kirchhoff’s 1st and 2nd Law
Applying Kirchhoff’s 2nd Law
Drawing circuit diagrams for parallel and series circuits

OCR AS Physics: Total Internal Reflection
OCR AS Physics A: Total Internal Reflection is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE Physics: Atmospheric Pressure
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.3 Atmospheric Pressure
This presentation includes:
Balanced and unbalanced forces
Resultant force
Changing atmospheric pressure
Exam style question with mark scheme

GCSE Physics: Newton's Second Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.4
Newton’s Second Law in Mathematical Form
Proportionalities
Rearranging Equations
Student’s problems with answers
Exam style questions with solutions

GCSE Physics: Work Done and Power
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.7
Work done equation
Rearranging work done equation
Questions and answers for work done
Power equation and definition
Rearranging power equation
Different units for work done: J, N m, kg m^2/s^2

GCSE Physics: Stretching Springs
These two lesson presentations covers the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.1 material.
• Number of forces needed to deform an object
• Elastic and Plastic definitions
• Hooke’s Law
• Rearranging equations
• Determining the gradient
• Determining the spring constant
• Experimental procedure
• Exam style questions with solutions

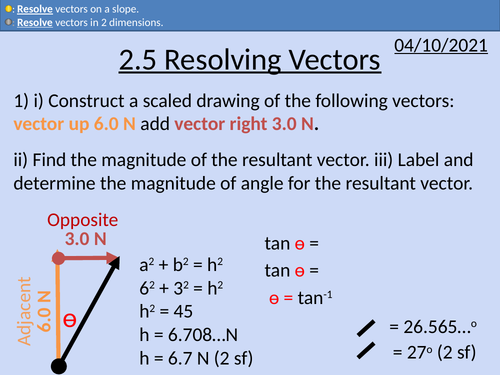
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Using trigonometry to solve vector problems
Vectors in 2 D
Resolving vectors on a slope

OCR AS level Physics: Distance and Speed
OCR AS level Physics: Distance and Speed is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g
OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Definition of free fall and gravitational force.
Dimensional analysis of units for acceleration and g.
Determining g with equations of constant acceleration (suvat equations).
Determining g with finding the gradient of graphs.
Determining g experimentally with stopwatches, trap doors, light gates, and cameras with strobes.

OCR AS level Physics: Force, mass, and weight
OCR AS level Physics: Force, mass, and weight is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Deforming Materials
OCR AS level Physics: Deforming Materials is a part of the Module 3: Materials
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

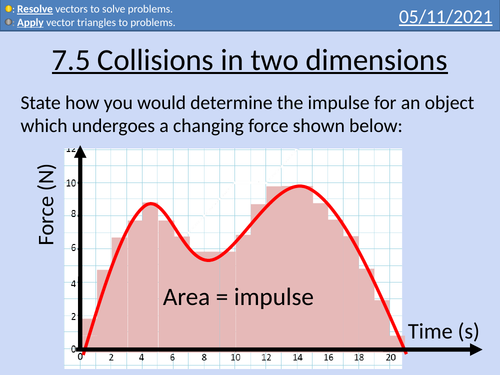
OCR AS level Physics: Collisions in two dimensions
OCR AS level Physics: Collisions in 2D is a part of the Module 3: Laws of Motion and Momentum. Presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

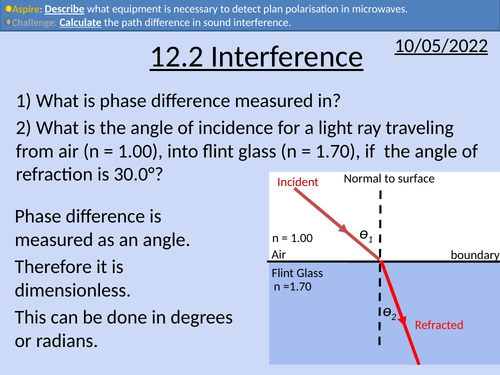
OCR AS level Physics: Interference
OCR AS level Physics: Interference is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

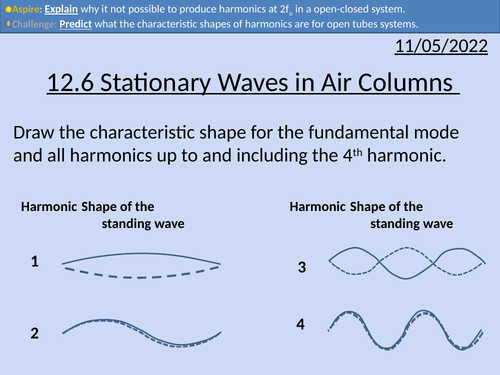
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves in Air Columns
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves in Air Columns is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE Chemistry: Paper Chromatography & Rf Values
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of technique for paper chromatography
• Experimental procedure
• Definitions of stationary and mobile phase
• Application of Rf equation with examples and answers

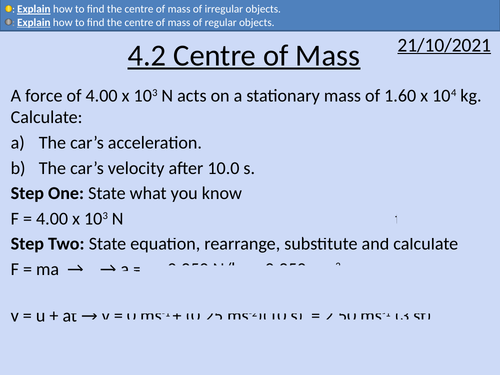
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of Mass
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of mass is a part of the Module 3: Force and Motion
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.

OCR AS Physics: Wave Properties
OCR AS Physics: Wave Properties is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE Physics: Density Practical
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.1
Presentation includes
Conversion from grams (g) to kilograms (kg) and centimetres (cm) to meters (m) with exercise and answers
Finding volume of regular and irregular shapes
Plenary Exam Question and Answer