496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.1 Types of Testing
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.1 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.

GCSE Chemistry: Bulk Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Jobs in Material Science
• Bulk properties of metals - malleable and conductors of electricity
• Bulk properties of ionic and covalent structures - brittle
• Explain why substances conducting electricity depends upon the state of matter

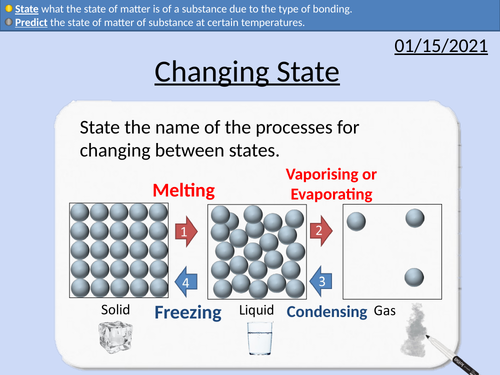
GCSE Chemistry: Changing State
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Define melting and boiling point of a pure substance.
• Predict the state of matter of substance at certain temperatures.
• State what the state of matter is of a substance due to the type of bonding.
• Metals, covalent structures, ionic structures and simple molecules.

GCSE Chemistry: Carbon
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State processes of the carbon cycle.
• Define the word allotrope.
• Explain why allotropes have different properties.
• Graphite, graphene, and fullerenes

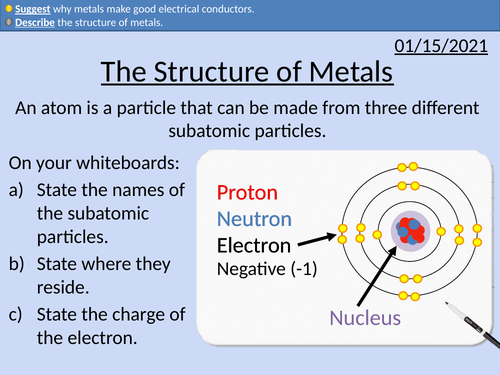
GCSE Chemistry: The Structure of Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State a use for metals
• Describe the structure of metals
• Why metals make good electrical conductors.
• Metals on the periodic table

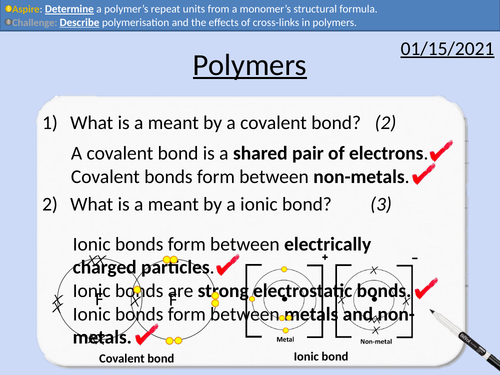
GCSE Chemistry: Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State what is meant by mono- and poly-.
• Describe polymerisation and the effects of cross-links in polymers.
• Determine a polymer’s repeat units from a monomer’s structural formula.

GCSE Chemistry: Covalent Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of giant covalent structures
• An empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms of each compound.
• Melting and boiling point of simple molecules
• Compare physical properties of simple molecules and giant covalent lattices.

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dot and cross diagrams of simple molecules
• Simple molecules form covalent bonds
• The group number on the periodic table informs us how many electrons are in the outer shell.
• Groups on the periodic table

GCSE Chemistry: Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Filled outer shells result in more stable electronic structures.
• The electronic configuration ionic compounds
• Models of giant ionic structures

GCSE Chemistry: Forming Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of ions
• The electronic configuration of ions
• Ions metals and nonmetals form
• Drawing electron configurations

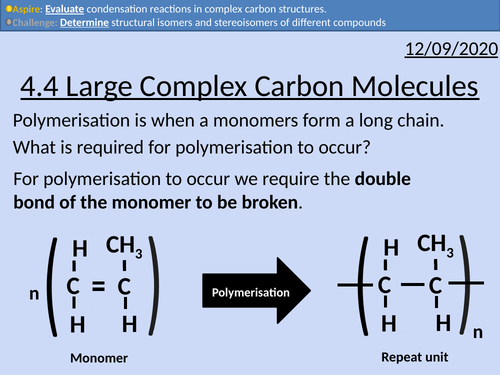
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

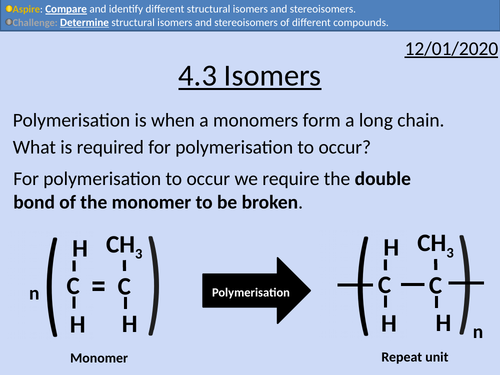
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.

OCR Applied Science: 4.2 Polymers and Carbon Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Determining the empirical formula for compounds
Draw monomers and repeat units using structural and skeletal formula of the following polymers:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)

OCR Applied Science: 4.1 Principles of Carbon Chemistry
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Alkanes as saturated hydrocarbons containing single C-C and C-H bonds
• Alkenes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C=C double bond
• Alkynes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C ≡ C triple bond
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four members of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
• Aldehydes and ketones as organic compounds containing the C=O group
• Name and draw the structural formulae of the first four aldehydes and the first two ketones
• Alcohols as organic compounds containing the OH group
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four alcohols
• Conversion of alcohols to form aldehydes and ketones is classified as an oxidation reaction
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four carboxylic acids
• Reaction of carboxylic acids with an alkali, to include full equations using structural formulae
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the four C4H8O2 esters
• How an ester can be made from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol

GCSE Chemistry: Electronic Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Electrons reside in energy levels (shells) around the nucleus
• The electronic configuration of elements up to 20 is 2,8,8,2
• Groups and periods of the periodic table
• Drawing electron configurations

GCSE Chemistry: Metals and Non-metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using the periodic table to identify metals and non-metals
• Different properties of metal and non-metals (Appearance, melting and boiling point, state of matter at room temperature, ductility, and malleability).
• Exceptions of physical properties (mercury being liquid and carbon conducting electricity).

GCSE Chemistry: Purification and Checking Purity
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Choosing the correct separation technique
• Comparisons of mobile and stationary phases for chromatography
• Rf Values
• Analysing chromatographs in gas chromatography

GCSE Chemistry: Thin Layer and Gas Chromatography
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Experimental Procedure for Thin Layer Chromatography
• Analysing and calculating Rf Values
• Pros and cons of paper and TL chromatography
• Experimental procedure for Gas Chromatography
• Persuasive writing and embedding literacy in science

OCR Applied Science: 6.3 Electrical Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Current as flow of charge in a conductor.
Use the equation: I = ΔQ ÷ Δt
Ohm’s law illustrates the relationship of V ∝ I
Use the equation: potential difference (V) = current (A) × resistance
Use the equations for adding resistors in series and parallel
Compare electromotive force and potential difference
Use the equation: charge © = current (A) × time (s)
Use and recognise the equation for mean drift velocity
Use the equation: energy transferred (work done) (J) = charge © × potential difference (V)
Use the equation: energy transferred (J, kWh) = power (W, kW) × time (s, h)
Use the equation: power (W) = energy (J) ÷ time (s)