496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

OCR Applied Science: 6.2 Physico-chemical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Structure of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Properties of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Forces and bonds of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Phase diagrams – interpreting and calculating changes.
Sublimation and phase diagrams.

OCR Applied Science: 6.1 Mechanical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Interpreting laboratory tests for stress-strain graphs and Young’s modulus
• Awareness that repeated loading cycles may cause failure by fatigue below the yield strength
• Use of diagrams to understand that the way molecules are arranged in polymers determines the properties: chain length, crosslinking, use of plasticizers and crystallinity.
• Use and rearranging of the density equation.

GCSE Chemistry: Paper Chromatography & Rf Values
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of technique for paper chromatography
• Experimental procedure
• Definitions of stationary and mobile phase
• Application of Rf equation with examples and answers

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Distillation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Changes of state
• The technique of simple distillation
• Concentration of solute increasing in distillation
• Jobs related to chemistry
• Key word test Insoluble, Soluble, Solvent, Solute, Solution, Distillation, Filtration, and Crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Filtration and Crystallisation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for solution, solute, solvent, insoluble, soluble.
The technique of filtration
The technique of crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Pure and Impure Substances
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions of pure and impure substances
Definition of an alloy
Identification of purity with melting points
Plotting graphs and data analysis

OCR Applied Science: 2.2 Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.2 of Module 1: Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions
Addition reactions of alkenes to include full balanced symbol equations
Substitution reactions of alkanes and haloalkanes to include full balanced
equations
Addition polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Condensation polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Definition of a radical
The role played by UV light in producing chlorine radicals from CFCs in the
depletion of the ozone layer
Equations to show how chlorine radicals can destroy many ozone molecules
Displacement reactions to include full balanced equations for metals and halogens.

OCR Applied Science: 2.1 Mixtures and Alloys
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Types of mixtures to include solutions, colloids and suspensions
Difference between colloids and suspensions in terms of particle size
Uses of common colloids in nature and medicine
Types of colloids to include aerosols, emulsions, foams, gels and sols
Significance of colloids in nature and medicine
Alloys as mixtures of metals
The character and features of alloys
Uses of common alloys to include amalgam, solder, bronze, titanium alloy

OCR Applied Science: 1.3 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.3 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements react together to form compounds by i.e.
ionic bonding
covalent bonding

OCR Applied Science: 1.2 The Periodic Table
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.2 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements are based on atomic structure and can be classified by the Periodic Table i.e.:
organisation of elements within the table
groups
periods
atomic number
atomic mass atomic radius

OCR Applied Science: 1.1 The Atom
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
nucleus contains protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons
relative masses and charges
nuclear and atomic diameters
nucleon number, proton number and isotopes
proton number defines the type of atom
nuclear notation
attractive and repulsive forces within the nucleus

GCSE Chemistry: Empirical Formula
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Calculate empirical formula and by finding the simplest whole-number ratio
• Calculate relative formula mass from balanced equations.

GCSE Chemistry: Relative Formula Mass
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Relative atomic mass
• Understanding chemical formulas
• Relative formula mass
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C1 Particles
All resources for P1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.1 The Particle Model
All resources for P1.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model

GCSE Chemistry: Development of the Atomic Model
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr’s models
• Comparing different scientific models of the atom

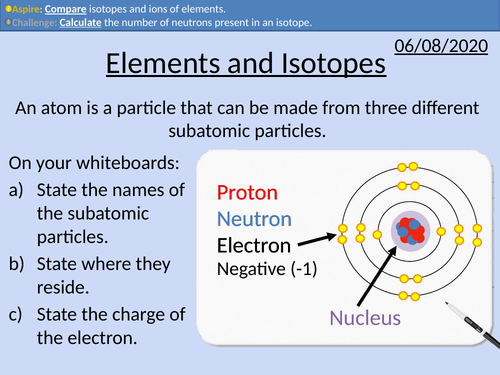
GCSE Chemistry: Isotopes and Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definitions of elements, isotopes, and ions
• State mass number, atomic number, and chemical symbols
• Calculate the number of neutrons

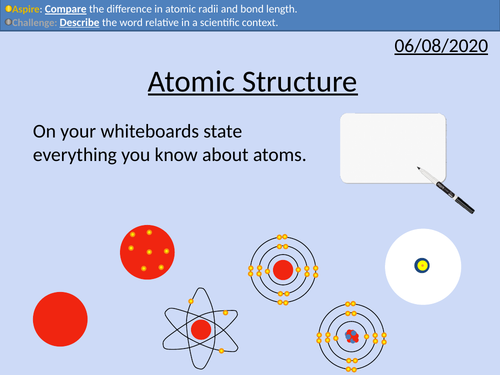
GCSE Chemistry: Atomic Structure
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Scientific models as a concept
• Structure of the atom
• Relative mass and charge of subatomic particles
• Bond length of atoms and molecules

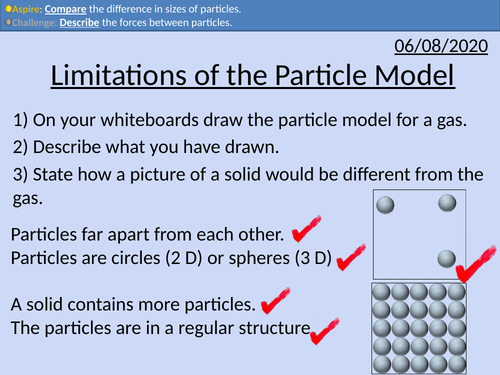
GCSE Chemistry: Limitations of the Particle Model
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Describing the limitations of the model: lack of forces between particles, size of particles, and space between the particles.
• Mathematically comparing sizes and distances of particles