496Uploads
162k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2.2 Newton's Laws
All resources for P2.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and comined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Forces and Interactions
Free Body Diagrams
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s Second Law
Everyday Forces
Momentum
Work Done and Power
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2.1 Motion
All resources for P2.1 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Distance, time and speed
Vectors and Scalars
Acceleration
Distance-time graphs
Velocity-time graphs
Equations of motion
Kinetic Energy

GCSE Physics: Work Done and Power
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.7
Work done equation
Rearranging work done equation
Questions and answers for work done
Power equation and definition
Rearranging power equation
Different units for work done: J, N m, kg m^2/s^2

GCSE Physics: Momentum
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.6
Momentum Equation
Rearranging the momentum equation
Momentum as a vector
Vector addition with momentum
Exam question with worked solutions
Student problems with answers
Proportionalities

GCSE Physics: Every Day Forces
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.5
Presentation comes with worked examples, student questions and answers.
Newton’s first Law
Terminal velocity
Free body diagrams
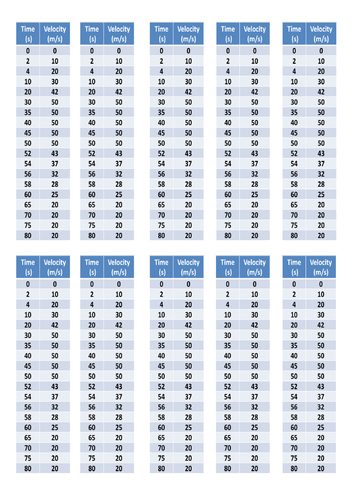
Plotting data
Determining acceleration for a velocity-time graph
Determining distance traveled for a velocity-time graph

GCSE Physics: Newton's Second Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.4
Newton’s Second Law in Mathematical Form
Proportionalities
Rearranging Equations
Student’s problems with answers
Exam style questions with solutions

GCSE Physics: Newton's First Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.3.
PowerPoint with multiple student activities and complete worked answers.
Newton’s First Law definition
Balanced and unbalanced forces producing accelerations
Acceleration being the change in velocity
The principle of inertia
Definition for equilibrium

GCSE Physics: Free Body Diagrams
This presentation covers GCSE Physics OCR Gateway P2.2.2
Vector Addition 1D
Vector Addition 2D - scaled drawings
Vector Addition 2D - finding angles with a protractor
Resultant vectors and acceleration
Student problems with answers.

GCSE Physics: Forces and Interactions
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.1
Newton’s third law
Contact and non-contact forces
Exam style question with solution

GCSE Physics: Equations of Motion
This presentation covers GCSE Physics OCR Gateway P2.1.6
Introduction of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Rearranging of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Derivation of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Three different methods for rearranging equations
Kinetic energy, acceleration and speed problems with answers

GCSE Physics: Kinetic Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.1.6
Kinetic equation
Rearranging equations with three different methods.
Plotting velocity vs kinetic energy
Evaluating square relationships
Worked problems with solutions
Student problems with solutions

GCSE Physics: Velocity-time graphs
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.1.5
Analysing velocity-time graphs
Calculating the gradient
Acceleration from velocity-time graphs
Distance travelled from velocity-time graphs
Worked problems and solutions

GCSE Physics: Distance-time Graphs
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.1.4.
Plotting of distance-time graph
Plotting of displacement-time graph
Worked example for determining gradient of a line
Comparing distance-time and displacement-time graphs

GCSE Physics: Acceleration
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.3.
Content covered:
Definition for acceleration
Worked solutions
Students problems with answers
Exam style question with mark scheme

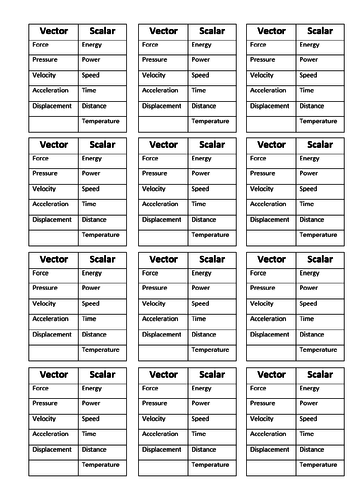
GCSE Physics: Vectors and Scalars
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.2.
Content covered:
Definition for vector and scalar
Vector addition in 1 D
Vector addition in 2 D
Scaled drawings and Pythagoras’ theorem
Worked examples and student problems with answers included

GCSE Physics: Distance, Time and Speed
This presentation covers material for OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 P2.1.1
Covered:
Measuring and calculating
Accuracy of stop watch vs light gate
Conversion of units
Exam style question
Worked examples
Students questions with answers
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P1 Matter Full scheme
All resources for P1 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
End of topic test
Scheme of work
Development of the atomic model
Density
Temperature
Specific Latent Heat
Specific Heat Capacity
Pressure and Temperature
Pressure and Area
Pressure are Volume
Atmospheric Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Sinking and Floating

GCSE Physics: Liquid Pressure
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.4 Liquid Pressure
This presentation includes:
Liquid pressure equation
Worked solutions
Exam style questions with answers
Rearranging equations
Incompressibility of liquids.

GCSE OCR Physics P1 Test
35 mark assessment with mark scheme for P1 from OCR Gateway Physics 9-1.
Includes:
10 multiple choice questions
Density
Specific Latent Heat
Specific Heat Capacity
Pressure
Development of the atomic model
Unit conversion
Included physics equations
PIN cover sheet

GCSE Physics: Floating and Sinking
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.5 Floating and Sinking
Content Covered:
Balanced Forces
Rearranging equations
Mass and weight
Gravitational field strength
Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Difference in pressure causing up thrust
Combining two equations
Worked solutions
Exam Style Questions
Problems with answers
Demonstration